Last Updated on February 9, 2019 by Admin
8.5.4.3 Lab – Building a Switch and Router Network Answers
Lab – Building a Switch and Router Network (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only.
Topology
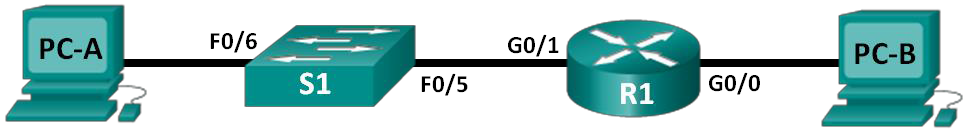
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.0.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.0.1 |
Objectives
Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
- Set up equipment to match the network topology.
- Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
- Assign static IP information to the PC interfaces.
- Configure the router and switch.
- Verify network connectivity.
Part 3: Display Device Information
- Retrieve hardware and software information from the network devices.
- Interpret the output from the routing table.
- Display interface information on the router.
- Display a summary list of the interfaces on the router and switch.
Part 4: Secure Remote Access to the Router
- Set the IP domain name and generate secure keys.
- Create a SSH user and configure VTY lines for SSH-only access.
- Verify SSH Implementation.
Background / Scenario
In this lab, you will cable the equipment as shown in the topology diagram. You will then configure the devices to match the addressing table. After the configurations have been saved, you will verify your configurations by testing for network connectivity.
After the devices have been configured and network connectivity has been verified, you will use IOS commands to retrieve information from the devices to answer questions about your network equipment. You will also access the router remotely via SSH.
Before beginning the lab, verify that there are no previously saved configurations on the devices. Please refer to your Answers for assistance.
Answers Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.4(3) (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used.
Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Answers Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations.
Required Resources
- 1 Router (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.4(3) universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows 10) with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Answers Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on Cisco 1941 routers are autosensing and an Ethernet straight-through cable may be used between the router and PC-B. If using another model Cisco router, it may be necessary to use an Ethernet crossover cable.
Part 1: Set Up Topology and Initialized Devices
- Attach the devices shown in the topology diagram, and then cable, as necessary.
- Power on all the devices in the topology.
- Please refer to your Answers for assistance if the devices have previously saved configurations.
Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
In Part 2, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as the interface IP addresses, device access, and passwords. Refer to the Topology and Addressing Table at the beginning of this lab for device names and address information.
Step 1: Assign static IP information to the PC interfaces.
- Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-A.
- Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-B.
- Ping PC-B from a command prompt window on PC-A. Why were the pings not successful?____________________________________________________________________________________
The router interfaces (default gateways) have not been configured yet so the traffic is not being routed between subnets.
Step 2: Configure the router.
- Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter configuration mode.
- Assign a device name to the router according to the Addressing Table.
- Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
- Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
- Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
- Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
- Configure the IP addresses according to the Addressing Table and activate both Ethernet interfaces on the router.
- Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Note: Use the question mark (?) to help with the correct sequence of parameters needed to execute this command.
Were the pings successful? Explain.
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Yes. The router is routing the ping traffic across the two subnets. The default settings for the 2960 switch will automatically enable the interfaces that are connected to devices.
Step 3: Configure the switch.
- Console into the switch and enable privileged EXEC mode.
- Enter configuration mode.
- Assign a device name to the router.
- Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
- Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
- Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
- Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
- Configure the IP address for the SVI for VLAN 1 according to the Addressing Table and activate the interface.
- Configure the default gateway according to the Addressing Table.
- Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Part 3: Display Device Information
Step 1: Retrieve hardware and software information from the network devices.
- Use the show version command to answer the following questions about the router.
R1# show version
Cisco IOS Software, C1900 Software (C1900-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.4(3)M2, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2015 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 06-Feb-15 17:01 by prod_rel_team
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 15.0(1r)M15, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
R1 uptime is 1 minute
System returned to ROM by reload at 22:53:26 UTC Wed Jun 22 2011
System image file is “flash:c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.154-3.M2.bin”
Last reload type: Normal Reload
Last reload reason: Reload Command
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United
States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and
use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.
Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you
agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable
to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html
If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to
Cisco CISCO1941/K9 (revision 1.0) with 446464K/77824K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FTX1636848Z
2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
2 Serial(sync/async) interfaces
1 terminal line
DRAM configuration is 64 bits wide with parity disabled.
255K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
124400K bytes of USB Flash usbflash0 (Read/Write)
250880K bytes of ATA System CompactFlash 0 (Read/Write)
License Info:
License UDI:
————————————————-
Device# PID SN
————————————————-
*1 CISCO1941/K9 FTX1636848Z
Technology Package License Information for Module:’c1900′
————————————————————————
Technology Technology-package Technology-package
Current Type Next reboot
————————————————————————
ipbase ipbasek9 Permanent ipbasek9
security disable None disable
data disable None disable
Configuration register is 0x2102
- What is the name of the IOS image that the router is running?____________________________________________________________________________________
Image version may vary, but answers should be something like c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.152-4.M3.bin. - Use the show version command to answer the following questions about the switch.
S1# show version
Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.0(2)SE7, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2012 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Sat 28-Jul-12 00:29 by prod_rel_team
ROM: Bootstrap program is C2960 boot loader
BOOTLDR: C2960 Boot Loader (C2960-HBOOT-M) Version 12.2(53r)SEY3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
S1 uptime is 1 hour, 2 minutes
System returned to ROM by power-on
System image file is ” flash:c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE7.bin”
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United
States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and
use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.
Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you
agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable
to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html
If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to
cisco WS-C2960-24TT-L (PowerPC405) processor (revision R0) with 65536K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FCQ1628Y5LE
Last reset from power-on
1 Virtual Ethernet interface
24 FastEthernet interfaces
2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
The password-recovery mechanism is enabled.
64K bytes of flash-simulated non-volatile configuration memory.
Base ethernet MAC Address : 0C:D9:96:E2:3D:00
Motherboard assembly number : 73-12600-06
Power supply part number : 341-0097-03
Motherboard serial number : FCQ16270N5G
Power supply serial number : DCA1616884D
Model revision number : R0
Motherboard revision number : A0
Model number : WS-C2960-24TT-L
System serial number : FCQ1628Y5LE
Top Assembly Part Number : 800-32797-02
Top Assembly Revision Number : A0
Version ID : V11
CLEI Code Number : COM3L00BRF
Hardware Board Revision Number : 0x0A
Switch Ports Model SW Version SW Image
—— —– —– ———- ———-
* 1 26 WS-C2960-24TT-L 15.0(2)SE7 C2960-LANBASEK9-M
Configuration register is 0xF
S1#
What is the name of the IOS image that the switch is running?____________________________________________________________________________________
Image version may vary, but answers should be something like c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE.bin.
What is the model number of the switch?____________________________________________________________________________________
Answers may vary, but the answer should appear in this form: WS-C2960-24TT-L.
Step 2: Display the routing table on the router.
Use the show ip route command on the router to answer the following questions.
R1# show ip route
Codes: L – local, C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route, H – NHRP, l – LISP
+ – replicated route, % – next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
What code is used in the routing table to indicate a directly connected network? _____
The C designates a directly connected network. An L designates a local interface. Both answers are correct.
How many route entries are coded with a C code in the routing table? _________ 2
What interface types are associated to the C coded routes?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Answers may vary depending on router type, but on the 1941 the correct answer is G0/0 and G0/1.
Step 3: Display interface information on the router.
Use the show interface g0/1 to answer the following questions.
R1# show interfaces g0/1
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is fc99.4775.c3e1 (bia fc99.4775.c3e1)
Internet address is 192.168.1.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full Duplex, 100Mbps, media type is RJ45
output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:06, output 00:00:04, output hang never
Last clearing of “show interface” counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
17 packets input, 5409 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 17 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog, 13 multicast, 0 pause input
14 packets output, 1743 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets
3 unknown protocol drops
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
What is the operational status of the G0/1 interface?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
What is the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the G0/1 interface?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Answers will vary but will appear in the form of: xxxx.xxxx.xxxx, where each x will be replaced with a hexadecimal number.
How is the Internet address displayed in this command?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Internet address is 192.168.1.1/24.
Step 4: Display a summary list of the interfaces on the router and switch.
There are several commands that can be used to verify an interface configuration. One of the most useful of these is the show ip interface brief command. The command output displays a summary list of the interfaces on the device and provides immediate feedback to the status of each interface.
- Enter the show ip interface brief command on the router.
R1# show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.0.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
R1#
- Enter the show ip interface brief command on the switch.
-
S1# show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/4 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/5 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/6 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/7 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/8 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/9 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/10 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/11 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/12 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/13 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/14 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/15 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/16 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/17 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/18 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/19 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/20 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/21 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/22 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/23 unassigned YES unset down down
FastEthernet0/24 unassigned YES unset down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
S1#
Part 4: Secure Remote Access to the Router
Step 1: Set the IP domain name and generate secure keys.
- On R1, configure the domain name as academy.net.
R1(config)# ip domain-name academy.net - Generate RSA keys with a 1024 key length.
R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024
The name for the keys will be: R1.academy.net% The key modulus size is 1024 bits
% Generating 1024 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable…
[OK] (elapsed time was 2 seconds)
*Jun 26 04:58:35.679: %SSH-5-ENABLED: SSH 1.99 has been enabled
Step 2: Create a SSH user and configure VTY lines for SSH-only access.
- Create a user with SSHuser as the username and cisco as the secret password.
R1(config)# username SSHuser secret cisco - Configure the VTY lines to use the local username database for login credentials.
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# login local - The VTY lines should only allow SSH for remote access.
R1(config-line)# transport input ssh
Step 3: Verify SSH Implementation.
- On PCA, click Start and type Tera Term. Select Tera Term in the results list.
- Enter 192.168.1.1 in the Host field. Click OK to continue.
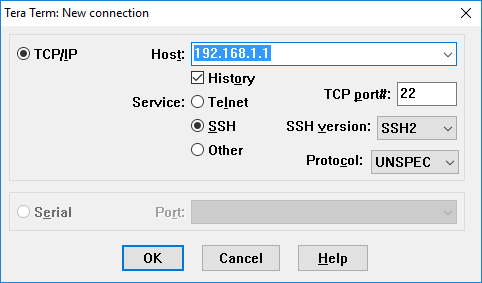
- Click Continue in the Security Warning dialog box. Enter the username SSHuser and password cisco. Click OK to continue.
What is the displayed message?____________________________________________________________________________________
The configured banner MOTD is displayed.
You should be at the prompt of R1. If you are not successful, verify the configurations are correct and the credentials were entered correctly. Please refer to your Answers for further assistance.
Reflection
- If the G0/1 interface showed administratively down, what interface configuration command would you use to turn the interface up?
- _______________________________________________________________________________________
- R1(config-if)# no shutdown
- What would happen if you had incorrectly configured interface G0/1 on the router with an IP address of 192.168.1.2?
- _______________________________________________________________________________________
- _______________________________________________________________________________________
- PC-A would not be able to ping PC-B. This is because PC-B is on a different network than PC-A which requires the default-gateway router to route these packets. PC-A is configured to use the IP address of 192.168.1.1 for the default-gateway router, but this address is not assigned to any device on the LAN. Any packets that need to be sent to the default-gateway for routing will never reach their destination.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Interface Summary | ||||
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the router type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Device Configs
Router R1
R1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1360 bytes
!
version 15.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
enable secret 5 $1$4HPV$aFAZ.qMnNivBjow5d6sBG/
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 15
!
ip domain name academy.net
ip cef
no ipv6 cef
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
username SSHuser secret 5 $1$nfMP$zgvD4FctdSDOWHQG6wvdO.
!
interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0/0
no ip address
shutdown
clock rate 2000000
!
interface Serial0/0/1
no ip address
shutdown
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^CUnauthorized access prohibited!
^C
!
line con 0
password 7 110A1016141D
login
line aux 0
line 2
no activation-character
no exec
transport preferred none
transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
login local
transport input ssh
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
!
end
Switch S1
S1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1531 bytes
!
version 15.0
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname S1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$8h3n$ku6UXwpo13O6cs6iybo5s1
!
no aaa new-model
system mtu routing 1500
!
spanning-tree mode pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
!
interface FastEthernet0/6
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
!
interface FastEthernet0/11
!
interface FastEthernet0/12
!
interface FastEthernet0/13
!
interface FastEthernet0/14
!
interface FastEthernet0/15
!
interface FastEthernet0/16
!
interface FastEthernet0/17
!
interface FastEthernet0/18
!
interface FastEthernet0/19
!
interface FastEthernet0/20
!
interface FastEthernet0/21
!
interface FastEthernet0/22
!
interface FastEthernet0/23
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
!
interface Vlan1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited.^C
!
line con 0
password 7 094F471A1A0A
login
line vty 0 4
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
end