Last Updated on February 9, 2019 by Admin
3.5.2.5 Lab – Connect to a Wireless Router Answers
Lab – Connect to a Wireless Router (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only.
Objectives
- Connect a PC to a wireless router using Ethernet cable
- Configure the PC with an appropriate IPv4 address
- Verify the PC configuration using a Command Prompt
Background / Scenario
For a PC to communicate in the local network and the Internet, it must be connected to a network device.
Required Resources
- 2 PCs (Windows 10) with wired Ethernet NIC on each PC
- 1 Wireless router
- 2 Straight-through Ethernet cables
Step 1: Identify Ethernet ports.
- On the wireless router, locate the Ethernet (Local Area Network) LAN ports. The Ethernet LAN ports connect your network hosts and devices. The four LAN ports are grouped together in the center of the router as shown in the following figure.

- On the PC, locate the Ethernet port. The port could be integrated into the motherboard or it could be an adapter. In either case, the port will be an RJ-45 port.
Step 2: Connect the cable between the PC and the router.
- Connect one end of the straight-through Ethernet cable to an Ethernet LAN port on the router.
- Connect the other end of the cable to the PC Ethernet port.
- Repeat this procedure for the second PC.
Step 3: Assign the PCs an IPv4 address and default gateway.
- Right-click Start button > select Network Connections.
- In this example, right-click the Local Area Connection for the wired connection. Select Properties.

- Double-click the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) option to open the TCP/IP properties window.
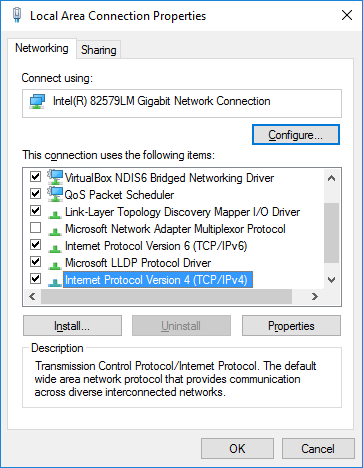
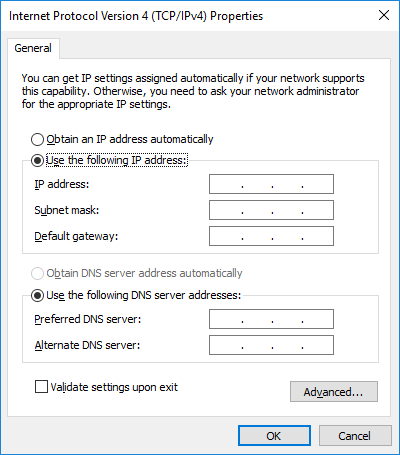
- You will enter an IPv4 address configuration consisting of an IPv4 address, a subnet mask, and default gateway address. To enter the address information, click the Use the following IPv4 address button.
- In the IPv4 address field, enter 192.168.10.2. In the subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0. In the default gateway field, enter 192.168.10.1 as shown in the figure. The DNS server information is not necessary at this time.
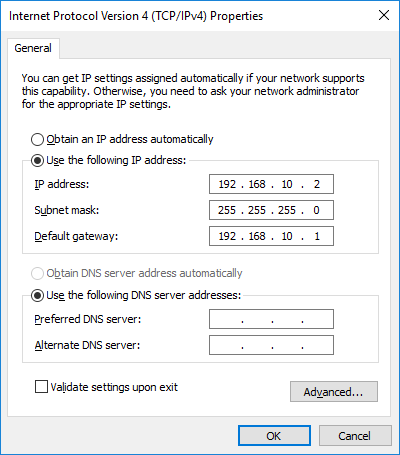
- When finished, click OK to return to the Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4) Properties window. Click OK to apply the changes.
After the changes are applied, you will be returned to the Network Connections window. - Because the two computers are on the same network, their IPv4 addresses will be similar, their subnet masks will be identical, and their default gateways will be identical. Perform the same procedures on the second PC to assign an IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway using the following information:
IPv4 address: ………… 192.168.10.3
Subnet mask:………… 255.255.255.0
Default gateway: …… 192.168.10.1
Why do you think the IPv4 addresses are different, but the subnet masks and default gateways are the same?____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Student’s own opinion on this. Each device on the network must have a unique identifier. The IPv4 address is one way of uniquely identifying each network host or device. The default gateway represents the way of communicating with devices that are NOT on your own network.
Step 4: Verify the IPv4 address configuration
- Right-click Start and select Command Prompt.
- At the prompt, type ipconfig /all to verify the configured IPv4 address and the default gateway from the previous step for both PCs.
Step 5: Test connectivity between the two PCs.
- From the command prompt on the first PC, test connectivity with the second PC by typing ping 192.168.10.3.
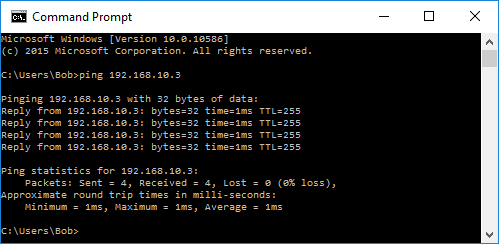
- The pings should be successful. If the pings are not successful, perform the appropriate troubleshooting steps, such as checking the cabling and checking your IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway assignments.