Last Updated on October 30, 2018 by Admin
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers
Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista (Answers Version)
Introduction
In this lab, you will explore Task Manager and manage processes from within Task Manager.
Recommended Equipment
The following equipment is required for this exercise:
- A computer running Windows 7 or Vista
Step 1: Work in the Applications Tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Log on to Windows as an administrator.
- Open a browser and a folder.
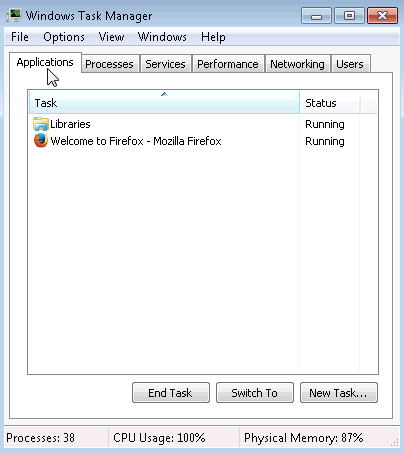
- Click the desktop and press Ctrl-Alt-Delete > Start Task Manager > Applications tab.
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 01
- Select the open browser and then click Switch To.
What happened to the browser?
____________________________________________________________________________________
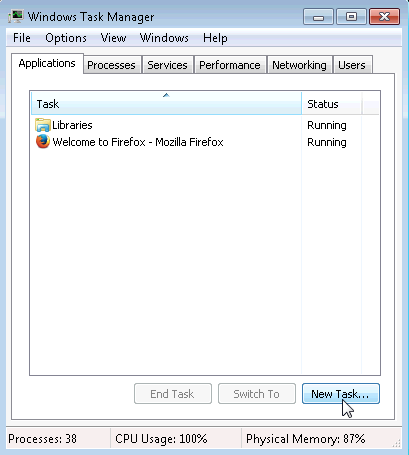
The browser became the active window. - Bring Windows Task Manager to the front of the desktop. Click New Task to open the Create New Task window.
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 02
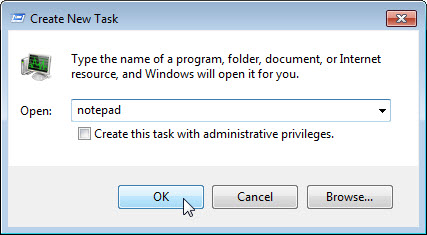
- In the Open field, type Notepad and click OK.
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 03
What happens?
____________________________________________________________________________________Notepad opens.
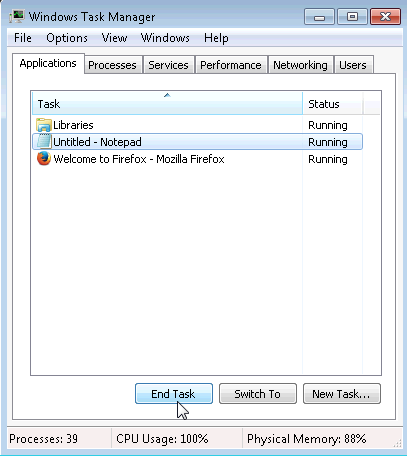
- Navigate back to the Windows Task Manager, select Notepad, and click End Task.
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 04
What happens?
____________________________________________________________________________________Notepad closes.
Step 2: Work in the Services tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Click the Services tab. Use the scroll bar on the right of the Services window to view all the services listed
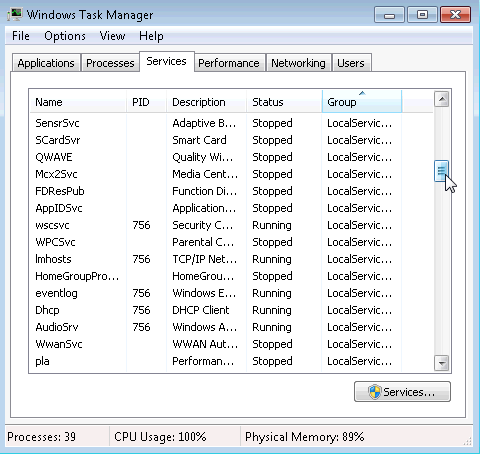
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 05
What are the statuses listed?
____________________________________________________________________________________
Stopped and Running.
Step 3: Work in the Performance tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Click the Performance tab.
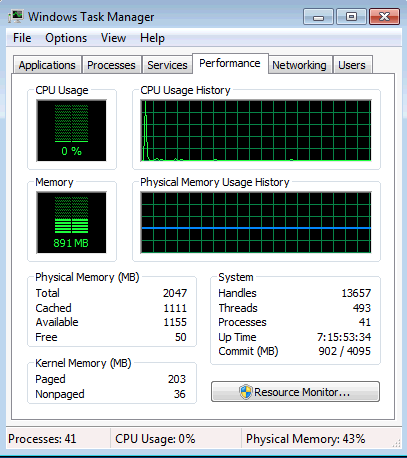
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 06
How many threads are running?
____________________________________________________________________________________Answer may vary. The example displays 493.
How many processes are running?____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. The example displays 41.What is the total physical memory (MB)?____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. The example displays 2047.What is the available physical memory (MB)?____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. The example displays 1155.How much physical memory (MB) is being used by the system?____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. This can be calculated by subtracting Free Physical Memory from Total Physical Memory. In the example the calculation would be 2047 – 50 = 1,997MB.
Step 4: Work in the Networking tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Click the Networking tab.
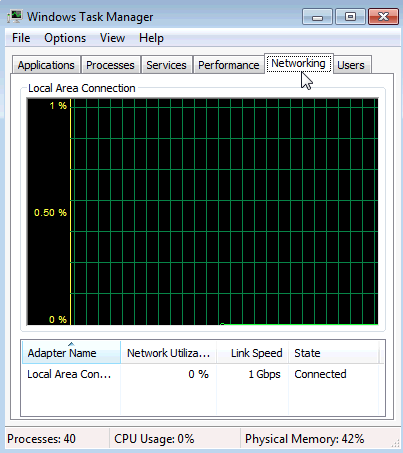
6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista Answers 07
What is the link speed?
____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. The examples displays 1 Gbps.
Step 5: Work in the Users tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Click the Users tab.
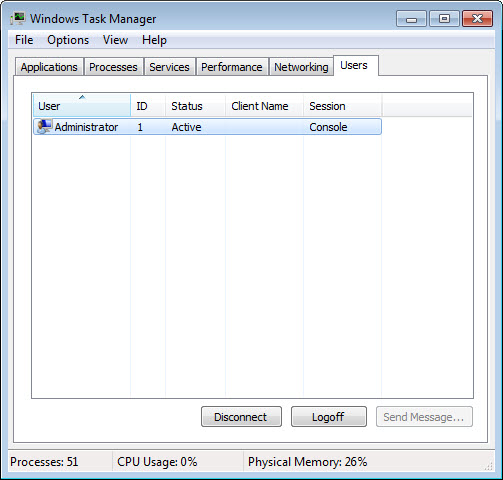 List all users and their status.
List all users and their status.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer may vary. The example displays one user, Administrator, with a status of active.
What actions can you perform on the user from this window?____________________________________________________________________________________
Three actions are displayed: Disconnect, Logoff, and Send Message. But only Disconnect and Logoff can be performed on the user.
Step 6: Work in the Processes tab of Windows Task Manager.
- Click the Processes tab.
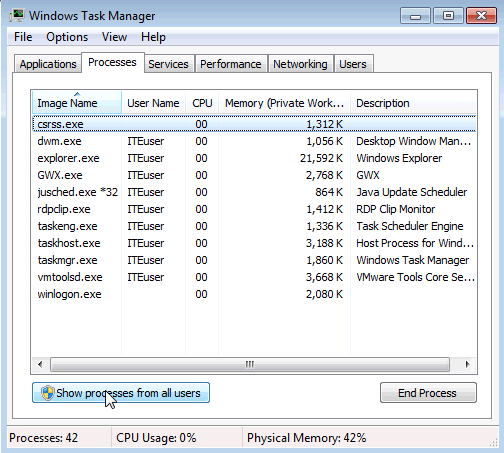
- Check the checkbox Show processes from all users.
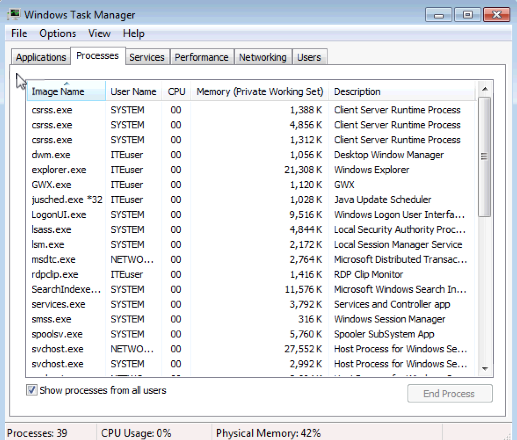
- Double-click the white border around the Processes tab. This changes the view of Windows Task Manager to compact mode.
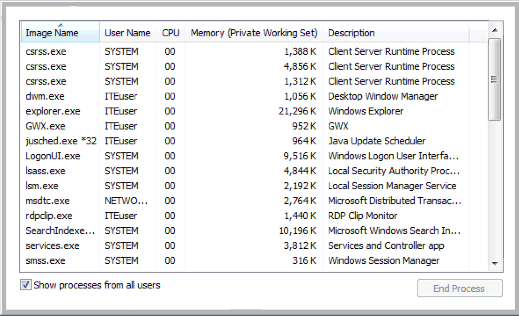 Note: The User Account Control window may open in Vista asking for permission to continue. Click Continue.
Note: The User Account Control window may open in Vista asking for permission to continue. Click Continue. - Click the heading Image Name. Click Image Name again.
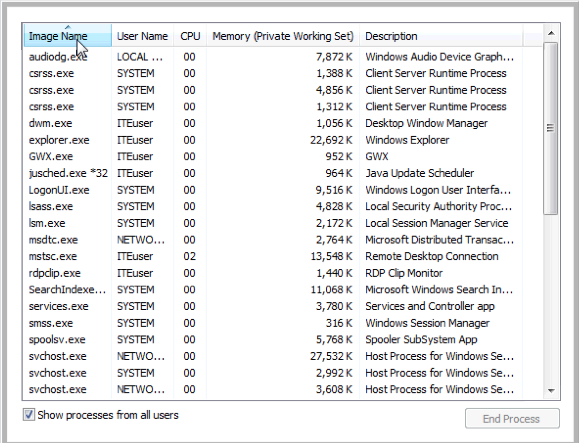 What effect does this have on the columns?____________________________________________________________________________________
What effect does this have on the columns?____________________________________________________________________________________
Places the names in alphabetical order. Each time you click the Image Name heading, it reverses the order (A to Z, then Z to A). - Click Memory (Private Working Set).
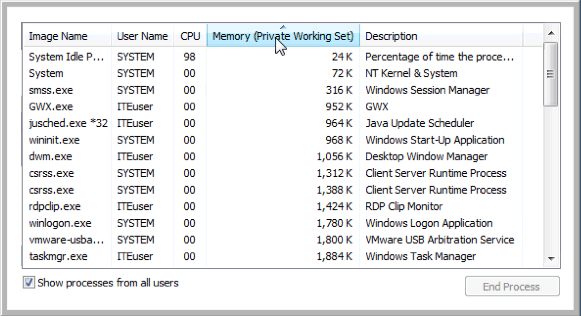 What affect does this have on the columns?____________________________________________________________________________________
What affect does this have on the columns?____________________________________________________________________________________
Places the numbers in ascending or descending order. - Double-click the outside border again to return to tabs mode.
- Open a browser.
Note: Firefox is used in this lab. However, any browser will work. Just substitute your browser name whenever you see the word Firefox. - Return to the Windows Task Manager. Click Image Name so the list is in alphabetical order, then locate and select firefox.exe.
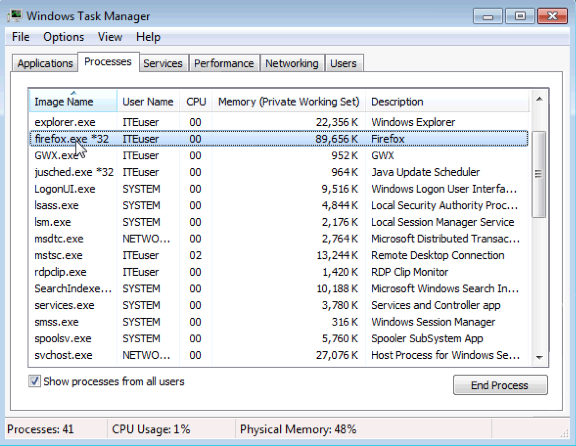
- Right-click firefox.exe > Set Priority.
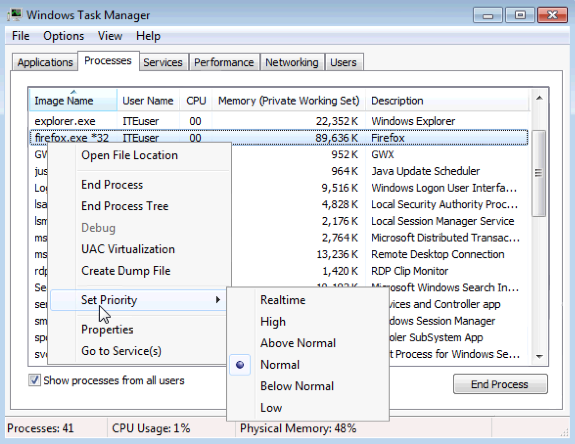 What is the default priority for the browser?____________________________________________________________________________________
What is the default priority for the browser?____________________________________________________________________________________
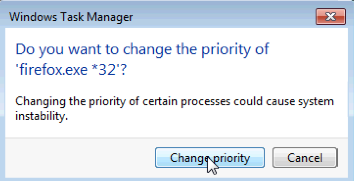
Normal. - Set the priority to Above Normal. Then click Change priority in the Windows Task Manager warning message.
Step 7: Change the fields that are displayed in the Windows Task Manager.
- Click View > Select Columns.
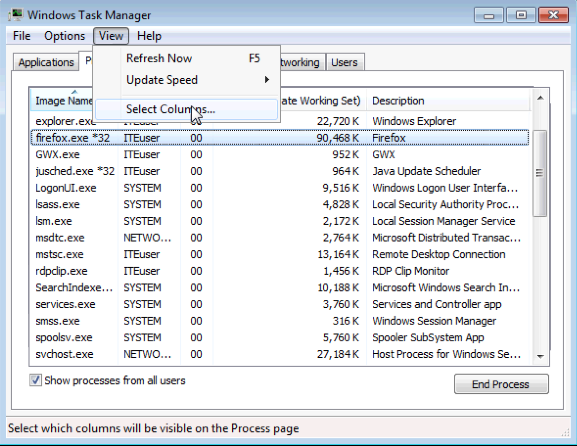
- The Select Process Page Columns window opens. Check Base Priority and click OK.
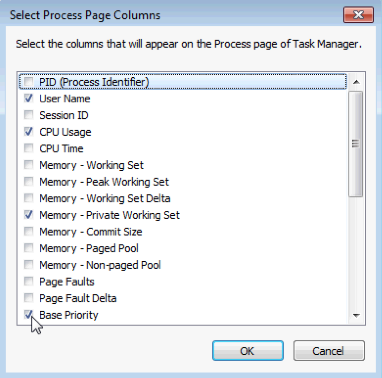
- Expand the width of the Windows Task Manager so the Base Priority column is visible.
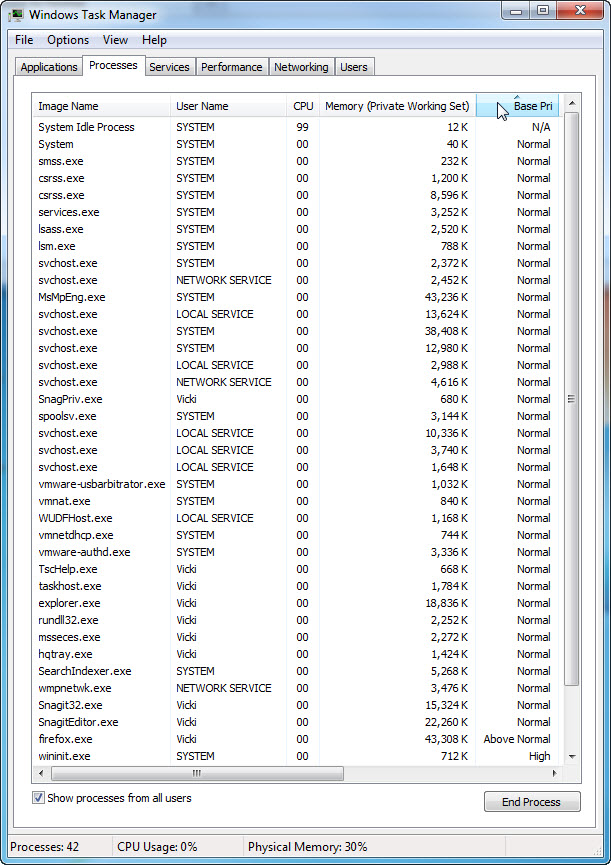 List the name of the image that has a base priority of Above Normal?____________________________________________________________________________________
List the name of the image that has a base priority of Above Normal?____________________________________________________________________________________
Firefox.exe.
Which image name has a base priority of N/A?____________________________________________________________________________________
System Idle Process. - Reset Firefox.exe base priority to normal. To do this, right-click firefox.exe > Set Priority > Normal > Change priority.
- Click View > Select Columns. Uncheck Base Priority and click OK.
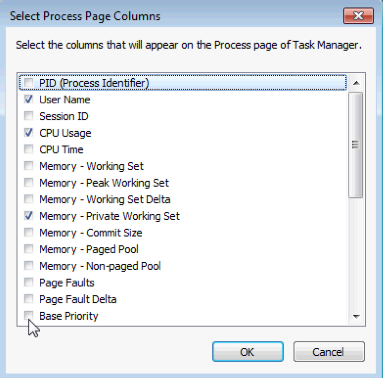
- Close Firefox.
Is Firefox listed as a process?
____________________________________________________________________________________
No, it is removed from the list of processes when it closes. - Close all open windows.
Reflection
Why is it important for an administrator to understand how to work within the Windows Task Manager?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Answers may vary. The Windows Task Manager can be a valuable tool for an administrator when troubleshooting problems with a Windows PC. It provides information about memory, CPU usage, and processes. It also allows the administrator to control process priority levels, and provides a way to end tasks or cancel processes.