Last Updated on October 29, 2020 by Admin
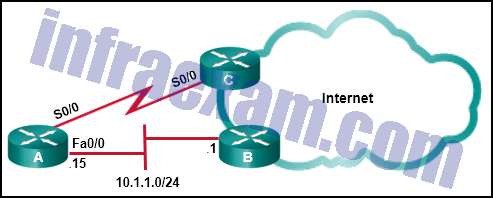
Refer to the exhibit. This network has two connections to the ISP, one via router C and one via router B. The serial link between router A and router C supports EIGRP and is the primary link to the Internet. If the primary link fails, the administrator needs a floating static route that avoids recursive route lookups and any potential next-hop issues caused by the multiaccess nature of the Ethernet segment with router B. What should the administrator configure?
- Create a static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 1.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 95.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 95.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A floating static route is a static route with an administrative distance higher than that of another route already in the routing table. If the route in the table disappears, the floating static route will be put into the routing table in its place. Internal EIGRP has an AD of 90, so a floating static route in this scenario would need to have an AD higher than 90. Also, when creating a static route to a multiaccess interface like a FastEthernet segment a fully specified route should be used, with both a next-hop IP address and an exit interface. This prevents the router from doing a recursive lookup, but still ensures the correct next-hop device on the multiaccess segment forwards the packet.