Last Updated on October 21, 2019 by Admin
RSE CCNA 2 Chapter 8 Quiz Answers 2018 2019
-
Which destination IP address is used when an IPv6 host sends a DHCPv6 SOLICIT message to locate a DHCPv6 server?
- FF02::1:2
- FF02::1
- FE80::1
- FF02::2
Explanation: DHCPv6 hosts will send a DHCP SOLICIT message to the all DHCP routers multicast address of FF02::1:2.
-
An administrator has configured a DHCPv4 relay router and issued these commands:
Router(config)# interface g0/0
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool RELAY
Router(dhcp-config)# endThe clients are not receiving IP parameters from the DHCPv4 server. What is a possible cause?
- The pool cannot be named ‘RELAY’.
- The router is configured as a DHCPv4 client.
- The IP address is incorrect for the subnet mask that is used.
- The ip helper-address command is missing.
Explanation: This router should be configured with the ip helper-address command, followed with the IP address of the DHCPv4 server, because the router is meant to be used as a relay agent. The ip dhcp pool RELAY command just names the DHCPv4 pool, and it does not enable the relay function.
-
What is the destination IP address when an IPv4 host sends a DHCPDISCOVER message?
- 255.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.1
- 0.0.0.0
- 192.168.1.1
Explanation: Because a DHCP client does not have a valid IPv4 address, it must use a broadcast IP address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination address to communicate with the DHCP server. The DHCPDISCOVER message sent by the client is the first message sent in order to make initial contact with a DHCP server.
-
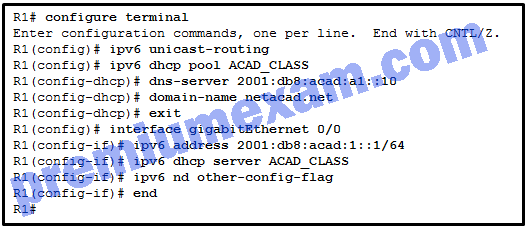
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a router for DHCPv6 operation. Which conclusion can be drawn based on the commands?
- The DHCPv6 server name is ACAD_CLASS.
- The router is configured for stateless DHCPv6 operation.
- Clients would configure the interface IDs above 0010.
- The router is configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation, but the DHCP pool configuration is incomplete.
Explanation: The DHCPv6 is for the stateless DHCPv6 operation that is indicated by changing the O flag to 1 and leaving the M flag as default, which is 0. Therefore, it is not configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation. Although the DNS server has the interface ID 0010, clients in stateless DHCPv6 operation will configure their interface IDs either by EUI-64 or a random number. The ACAD_CLASS is the name of the DHCP pool, not the DHCP server name.
-
What is the most likely scenario in which the WAN interface of a router would be configured as a DHCP client to be assigned a dynamic IP address from an ISP?
- There is a web server for public access on the LAN that is attached to the router.
- The router is also the gateway for a LAN.
- It is a SOHO or home broadband router.
- The router is configured as a DHCP server.
Explanation: SOHO and home broadband routers are typically set to acquire an IPv4 address automatically from the ISP. The IP address that is assigned is typically a dynamic address to reduce the cost, but a static IP address is possible with more cost. However, if the router is assigned a dynamic IP address, DNS issues will result in the web server behind the router not being easily accessible to the public. Routers are typically also gateways for LANs, but this has no bearing on whether the router is configured as a DHCP client on its WAN link or not. Likewise, a router can be configured to be a DHCP client in order to obtain an IP address from the ISP, but at the same time, it can be configured as a DHCP server to serve the IP addressing for the devices on its LAN.
-
After booting, a client receives an ICMPv6 RA message with the M flag set to 0 and the O flag set to 1. What does this indicate?
- The client should request an IPv6 address directly from a DHCPv6 server.
- The client should automatically configure an IPv6 address without contacting a DHCPv6 server.
- The client should automatically configure an IPv6 address and then contact a DHCPv6 server for more information.
- The client should be statically configured with an IPv6 address because the local router does not support autoconfiguration.
Explanation: The Managed Address Configuration (M) flag and the Other Configuration (O) flag in ICMPv6 RA messages are used to indicate to an IPv6 client how it should configure its IPv6 addresses. If the M flag is set to 0 it means that the host should automatically configure its own IPv6 interface address rather than asking for one from a DHCPv6 server. If the O flag is set to 1, it means that the client can find additional addressing information, such as a DNS server address, by contacting a DHCPv6 server after it has automatically configured its own address.
-
In which alternative to DHCPv6 does a router dynamically provide IPv6 configuration information to hosts?
- ARP
- EUI-64
- ICMPv6
- SLAAC
Explanation: Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) can be used as an alternative to DHCPv6. In this approach, a router provides global routing prefix, prefix length, default gateway, and DNS server information to a host. The host is not provided with a global unicast address by SLAAC. Instead, SLAAC suggests that the host create its own global unicast address based on the supplied global routing prefix. ARP is not used in IPv6. ICMPv6 messages are used by SLAAC to provide addressing and other configuration information. EUI-64 is a process in which a host will create an Interface ID from its 48-bit MAC address.
-
Which command will allow a network administrator to check the IP address that is assigned to a particular MAC address?
- Router# show ip dhcp binding
- Router# show ip dhcp pool
- Router# show ip dhcp server statistics
- Router# show running-config I section_dhcp
Explanation: The show ip dhcp binding command will show the leases, including IP addresses, MAC addresses, lease expiration, type of lease, client ID, and user name.
-
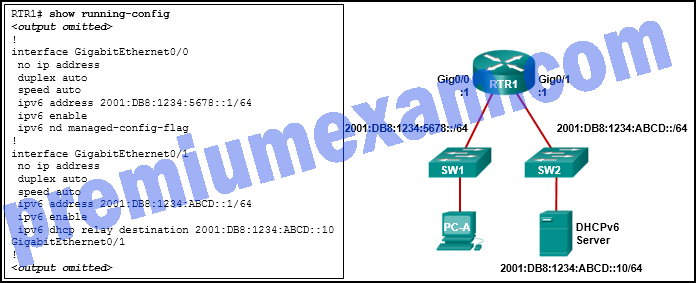
Refer to the exhibit. PC-A is unable to receive an IPv6 address from the stateful DHCPv6 server. What is the problem?
- The ipv6 dhcp relay command should be applied to interface Gig0/0.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag should be applied to interface Gig0/1.
- The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command should be ipv6 nd other-config-flag.
- The ipv6 dhcp relay command should use the link-local address of the DHCP server.
Explanation: The ipv6 dhcp relay command must be applied to the interface where the clients are located. The ipv6 dhcp relay command can use either the link-local or global unicast address of the DHCPv6 server, or even a multicast address. The ipv6 nd managed-config-flag indicates to the clients that they should use stateful DHCPv6 and is also applied to the interface where the clients are located.
-
Which message does an IPv4 host use to reply when it receives a DHCPOFFER message from a DHCP server?
- DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
Explanation: When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message.
-
When a client is requesting an initial address lease from a DHCP server, why is the DHCPREQUEST message sent as a broadcast?
- The client does not yet know the IP address of the DHCP server that sent the offer.
- The DHCP server may be on a different subnet, so the request must be sent as a broadcast.
- The client does not have a MAC address assigned yet, so it cannot send a unicast message at Layer 2.
- The client may have received offers from multiple servers, and the broadcast serves to implicitly decline those other offers.
Explanation: During the initial DHCP exchange between a client and server, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message looking for DHCP servers. Multiple servers may be configured to respond to this request with DHCPOFFER messages. The client will choose the lease from one of the servers by sending a DHCPREQUEST message. It sends this message as a broadcast so that the other DHCP servers that sent offers will know that their offers were declined and the corresponding address can go back into the pool.
-
What process is used in ICMPv6 for a host to verify that an IPv6 address is unique before configuring it on an interface?
- DAD
- SLAAC
- EUI-64
- ARP
Explanation: Before an IPv6 host can enable and use an assigned IPv6 address, the host must verify that the address is unique on the network. To verify that no other hosts are using the IPv6 address, the host performs the duplicate address detection (DAD) process by sending a Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message to the IPv6 address.
-
Fill in the blank. Do not abbreviate.
An administrator is troubleshooting a DHCPv4 issue on a router. By issuing the debug ip dhcp server events command, the administrator can watch, in real time, the IP address assignments that are performed by the router.- Noted: In netacad system, you can fill in one of the following: “server events” or “server event“, but in our system you can fill in only “server events“.
Explanation: The debug ip dhcp server events command reports IP address assignments and database updates as they happen.
- Noted: In netacad system, you can fill in one of the following: “server events” or “server event“, but in our system you can fill in only “server events“.
-
Match the DHCP message types to the order of the DHCPv4 process. (Not all options are used.)
- Step 1 –> DHCPDISCOVER
- Step 2 –> DHCPOFFER
- Step 3 –> DHCPREQUEST
- Step 4 –> DHCPACK
Explanation: The broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message finds DHCPv4 servers on the network. When the DHCPv4 server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message, it reserves an available IPv4 address to lease to the client and sends the unicast DHCPOFFER message to the requesting client. When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message. DHCPREPLY and DHCPINFORMATION-REQUEST are DHCPv6 messages.
-
Which command should be configured on a router interface to set the router as a stateful DHCPv6 client?
- ipv6 enable
- ipv6 address dhcp
- ipv6 address autoconfigure
- ipv6 dhcp server stateful
Explanation: When the ipv6 address dhcp command is configured on a router interface, it enables the router as a DHCPv6 client on this interface. The ipv6 enable command enables IPv6 on an interface and allows the router to configure its link-local address. The ipv6 address autoconfigure command tells the router to use either SLAAC or stateless DHCPv6 to configure its global unicast address. The ipv6 dhcp server command is used on a router that is running a DHCPv6 server to indicate what address information should be served to clients.