Last Updated on October 21, 2019 by Admin
RSE CCNA 2 Chapter 2 Quiz Answers 2018 2019
-
Why would a summarized static route be configured on a router?
- to reduce the number of public IP addresses required by an organization
- to provide a better route than a particular routing protocol
- to provide a default gateway for a router that connects to an ISP
- to reduce the size of the routing table
- to reduce the size of the routing protocol update to a neighboring router
Explanation: A summary route represents multiple networks. A summarized static route does not necessarily provide a better route than a routing protocol does. A default static route would provide a default gateway for a router that is connected to an ISP. Routing protocol updates may not necessarily be reduced in if static route routes are also used.
-
Which static route statement shows a recursive IPv6 static route?
- ipv6 route 0::/0 S0/0/0
- ipv6 route 0::/0 S0/0/0 254
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 S0/0/0
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 2001:db8:1000:10::1
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 S0/0/0 2001:db8:1000:10::1
Explanation: In a recursive static route, only the next-hop IPv6 address is specified. As a consequence, the router must perform a recursive route table lookup to find an exit interface associated with the network of the IPv6 address.
-
A network administrator notices that a correctly entered static route is not in the routing table. What two router commands would an administrator use to determine if the exit interface was up and the next hop address is available? (Choose two.)
- ping
- show ip protocols
- show ip interface brief
- show ip route
- tracert
Explanation: The network administrator could use the show ip interface brief command to verify that the exit interface or the interface connected to the next hop address is up and up. The ping command can be used to see if the next hop address is reachable. The show ip route command displays the routing table. The show ip protocols command is used when a routing protocol is enabled. The tracert command is used from a Windows PC.
-
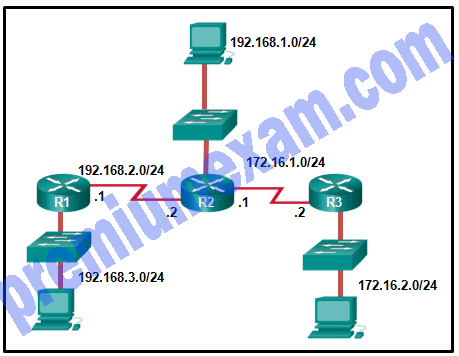
Fill in the blank. Refer to the exhibit.
On R1, the command to configure a static route to network 172.16.2.0 by specifying the next-hop IP address is ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2 .
Explanation: When a static route is to be configured via the next-hop IP address, the IP address of the interface of the next router in the path to the destination is used.
-
Fill in the blank.
A floating static route can be used to provide a backup route to a dynamically learned route.Explanation: An example of a floating static route used in conjunction with the EIGRP routing protocol would be as follows.
(config)# ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 95
Notice the extra number at the end of the static route. This route only appears in the routing table if the EIGRP-learned route with an administrative distance of 90 went down. That floating static route cannot appear in the routing table when a route with a better administrative distance exists. -
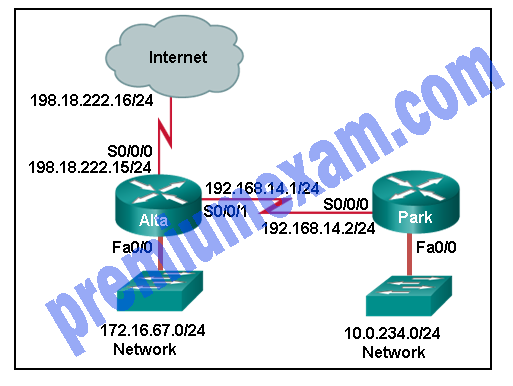
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of commands will configure static routes that will allow the Park and the Alta routers to a) forward packets to each LAN and b) direct all other traffic to the Internet?
- Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0 - Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 198.18.222.0 255.255.255.255 s0/0/0 - Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2 - Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1
- Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
-
What network address and subnet mask combination would be used to create a default static route that matches any IPv4 destination?
- 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
- 255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255
- 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
Explanation: For a route to be considered a default static route it must use a network ID and subnetmask combination that will match any destination IP address. The address and mask of 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 in a static route will create a route table entry that matches any destination.
-
A network administrator enters the following command into Router1: ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 S0/1/0. Router1 then receives a packet that is destined for 192.168.0.22/24. After finding the recently configured static route in the routing table, what does Router1 do next to process the packet?
- drops the packet because the destination host is not listed in the routing table
- looks up the MAC address of the S0/1/0 interface to determine the destination MAC address of the new frame
- performs a recursive lookup for the IP address of the S0/1/0 interface before forwarding the packet
- encapsulates the packet into a frame for the WAN link and forwards the packet out the S0/1/0 interface
-
Consider the following command:
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
Which route would have to go down in order for this static route to appear in the routing table?
- a default route
- a static route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
- an OSPF-learned route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
- an EIGRP-learned route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
Explanation: The administrative distance of 5 added to the end of the static route creates a floating static situation for a static route that goes down. Static routes have a default administrative distance of 1. This route that has an administrative distance of 5 will not be placed into the routing table unless the previously entered static route to the 192.168.10.0/24 goes down or was never entered. The administrative distance of 5 added to the end of the static route configuration creates a floating static route that will be placed in the routing table when the primary route to the same destination network goes down. By default, a static route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network has an administrative distance of 1. Therefore, the floating route with an administrative distance of 5 will not be placed into the routing table unless the previously entered static route to the 192.168.10.0/24 goes down or was never entered. Because the floating route has an administrative distance of 5, the route is preferred to an OSPF-learned route (with the administrative distance of 110) or an EIGRP-learned route (with the administrative distance of 110) to the same destination network.
-
What type of static route is created when the next-hop IP address and exit interface are specified?
- recursive static route
- directly connected static route
- fully specified static route
- floating static route
Explanation: A fully specified static route has the next-hop IP address and exit interface specified. A recursive static route has only the next-hop IP address specified. A directly attached static route has only the router exit interface specified. A floating static route has a higher metric than the dynamic routes and serves as a backup route.
-
Which IPv6 static route would serve as a backup route to a dynamic route learned through OSPF?
- Router1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 2001:db8:acad:6::2 100
- Router1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 2001:db8:acad:6::100
- Router1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 2001:db8:acad:6::2 200
- Router1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 gigabitethernet0/0 2001:db8:acad:6::100 100
Explanation: The command ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 2001:db8:acad:6::2 200, specifies a floating static route to the 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 network with an administrative distance of 200. Since OSPF has an administrative distance of 110, the static route would only be placed in the routing table if the OSPF learned route was removed.
-
What are two reasons why an administrator might choose to use static routing rather than dynamic routing? (Choose two.)
- Static routing is easier to maintain in large networks.
- Static routing is more secure.
- Static routing is more scalable.
- Static routing uses less router processing and bandwidth.
- Static routing does not require complete knowledge of the whole network.
Explanation: Because static routes must be created and changed manually, they require a larger investment of administrative time and do not scale easily. Static routes do not require additional CPU cycles to calculate and advertise routes, and they provide more security because they are not advertised over the network. Proper implementation of static routes requires the administrator to have a complete understanding of the network topology.
-
Fill in the blank.
A stub network is a network that is accessed by a single route.
- Noted: In netacad system you can use one of the following: “stub“, “Stub” or “STUB” but in our online system, you can use only “stub“.
-
What is a characteristic of a default static route?
- It backs up a route already discovered by a dynamic routing protocol.
- It uses a single network address to send multiple static routes to one destination address.
- It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.
- It is configured with a higher administrative distance than is the original dynamic routing protocol.
Explanation: A default static route is a route that matches all packets. It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which the router does not have a learned or static route. A default static route is simply a static route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination IPv4 address. Configuring a default static route creates a gateway of last resort.
-
What command, or set of commands, would be used to determine if the following configuration on router HQ works as designed?
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0/0 10
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/1/0- HQ(config)# interface serial 0/1/0
HQ(config-if)# shutdown
HQ(config-if)# end
HQ# show ip route - HQ# traceroute 128.107.0.99
- HQ# show ip interface brief
- HQ# ping 128.107.0.99
HQ# ping 64.100.0.5 - HQ# show ip route
Explanation: To test a floating static route, take down the main route/link in order to see whether the backup link appears in the routing table. The show ip route command simply shows the routing table. Only one of the static routes would be shown at any one time.
- HQ(config)# interface serial 0/1/0
-
Which command would create a valid IPv6 default route?
- ipv6 route ::/0 fe80::1
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/64 ::1
- ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:2::a
- ipv6 route ::/128 2001:db8:acad:1::1
Explanation: The correct prefix and prefix length for a default route is ::/0, which matches any address. ::/128 matches only the specific address of all zeros. When creating a static route that uses a link-local address as the next hop, an exit interface must also be specified for the route to be valid.