Last Updated on October 24, 2019 by Admin
CCNA 2 v6 RSE Final Exam Answers All in One 2018 2019 100%
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.
-
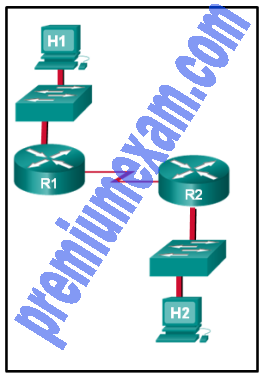
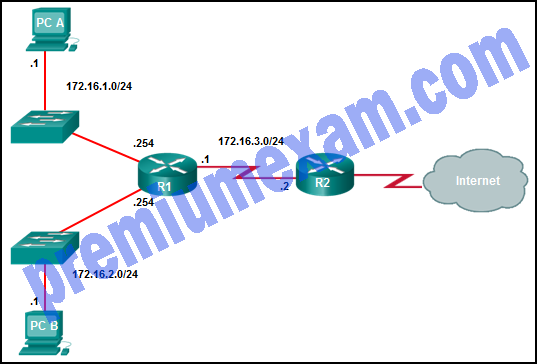
Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that the routing tables are up to date and no ARP messages are needed, after a packet leaves H1, how many times is the L2 header rewritten in the path to H2?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Explanation: H1 creates the first Layer 2 header. The R1 router has to examine the destination IP address to determine how the packet is to be routed. If the packet is to be routed out another interface, as is the case with R1, the router strips the current Layer 2 header and attaches a new Layer 2 header. When R2 determines that the packet is to be sent out the LAN interface, R2 removes the Layer 2 header received from the serial link and attaches a new Ethernet header before transmitting the packet.
-
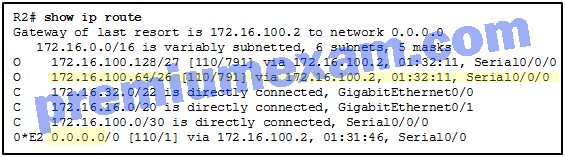
Refer to the exhibit. Which highlighted value represents a specific destination network in the routing table?
- 0.0.0.0
- 172.16.100.64
- 172.16.100.2
- 110
- 791
Explanation: 172.16.100.64 is a destination network. 110 is the administrative distance used by default for the OSPF routing protocol. 791 is the calculated OSPF metric. 172.16.100.2 represents the next-hop IP address used to reach the 172.16.100.64 network. 0.0.0.0 is the default route used to send packets when a destination network is not listed in the routing table.
-
Which type of static route is configured with a greater administrative distance to provide a backup route to a route learned from a dynamic routing protocol?
- standard static route
- floating static route
- default static route
- summary static route
Explanation: There are four basic types of static routes. Floating static routes are backup routes that are placed into the routing table if a primary route is lost. A summary static route aggregates several routes into one, reducing the of the routing table. Standard static routes are manually entered routes into the routing table. Default static routes create a gateway of last resort.
-
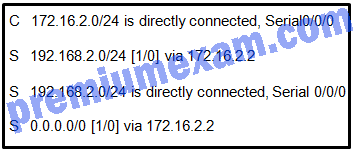
Refer to the exhibit. Which route was configured as a static route to a specific network using the next-hop address?
- C 172.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
- S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2
- S 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 0/0/0
- S 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2
Explanation: The C in a routing table indicates an interface that is up and has an IP address assigned. The S in a routing table signifies that a route was installed using the ip route command. Two of the routing table entries shown are static routes to a specific destination (the 192.168.2.0 network). The entry that has the S denoting a static route and [1/0] was configured using the next-hop address. The other entry (S 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial 0/0/0) is a static route configured using the exit interface. The entry with the 0.0.0.0 route is a default static route which is used to send packets to any destination network that is not specifically listed in the routing table.
-
What network prefix and prefix-length combination is used to create a default static route that will match any IPv6 destination?
- ::/128
- ::/0
- ::1/64
- FFFF::/128
Explanation: A default static route configured for IPv6, is a network prefix of all zeros and a prefix mask of 0 which is expressed as ::/0.
-
A router has used the OSPF protocol to learn a route to the 172.16.32.0/19 network. Which command will implement a backup floating static route to this network?
- ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 S0/0/0 200
- ip route 172.16.32.0 255.255.224.0 S0/0/0 200
- ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.224.0 S0/0/0 100
- ip route 172.16.32.0 255.255.0.0 S0/0/0 100
Explanation: OSPF has an administrative distance of 110, so the floating static route must have an administrative distance higher than 110. Because the target network is 172.16.32.0/19, that static route must use the network 172.16.32.0 and a netmask of 255.255.224.0.
-
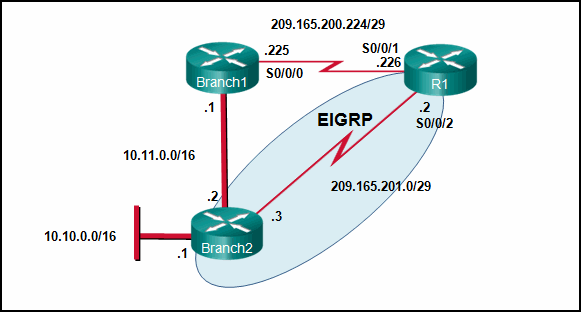
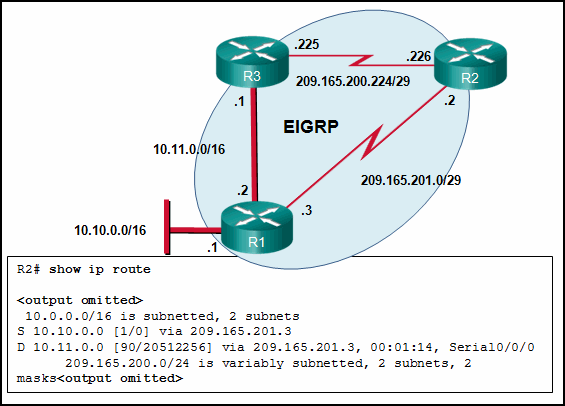
Refer to the exhibit. Currently router R1 uses an EIGRP route learned from Branch2 to reach the 10.10.0.0/16 network. Which floating static route would create a backup route to the 10.10.0.0/16 network in the event that the link between R1 and Branch2 goes down?
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Serial 0/0/0 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.226 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.225 100
- ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 209.165.200.225 50
Explanation: A floating static route needs to have an administrative distance that is greater than the administrative distance of the active route in the routing table. Router R1 is using an EIGRP route which has an administrative distance of 90 to reach the 10.10.0.0/16 network. To be a backup route the floating static route must have an administrative distance greater than 90 and have a next hop address corresponding to the serial interface IP address of Branch1.
-
Which statement describes a route that has been learned dynamically?
- It is automatically updated and maintained by routing protocols.
- It is unaffected by changes in the topology of the network.
- It has an administrative distance of 1.
- It is identified by the prefix C in the routing table.
-
Compared with dynamic routes, what are two advantages of using static routes on a router? (Choose two.)
- They improve network security.
- They use fewer router resources.
- They improve the efficiency of discovering neighboring networks.
- They take less time to converge when the network topology changes.
- They automatically switch the path to the destination network when the topology changes.
Explanation: Static routes are manually configured on a router. Static routes are not automatically updated and must be manually reconfigured if the network topology changes. Thus static routing improves network security because it does not make route updates among neighboring routers. Static routes also improve resource efficiency by using less bandwidth, and no CPU cycles are used to calculate and communicate routes.
-
A network administrator adds the default-information originate command to the configuration of a router that uses RIP as the routing protocol. What will result from adding this command?
- The router will be reset to the default factory information.
- The router will not forward routing information that is learned from other routers.
- The router will propagate a static default route in its RIP updates, if one is present.
- The router will only forward packets that originate on directly connected networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is the administrative distance value that indicates the route for R2 to reach the 10.10.0.0/16 network?
- 1
- 0
- 90
- 20512256
Explanation: In the R2 routing table, the route to reach network 10.10.0.0 is labeled with an administrative distance of 1, which indicates that this is a static route.
-
A network administrator reviews the routing table on the router and sees a route to the destination network 172.16.64.0/18 with a next-hop IP address of 192.168.1.1. What are two descriptions of this route? (Choose two.)
- default route
- supernet route
- ultimate route
- parent route
- level 2 child route
Explanation: A level 2 child route is a subnet of a classful network and an ultimate route is any route that uses an exit interface or next hop address. 172.16.64.0/18 is a subnet of the classful 172.16.0.0/16 network.
-
Which two factors are important when deciding which interior gateway routing protocol to use? (Choose two.)
- scalability
- ISP selection
- speed of convergence
- the autonomous system that is used
- campus backbone architecture
Explanation: There are several factors to consider when selecting a routing protocol to implement. Two of them are scalability and speed of convergence. The other options are irrelevant.
-
Employees of a company connect their wireless laptop computers to the enterprise LAN via wireless access points that are cabled to the Ethernet ports of switches. At which layer of the three-layer hierarchical network design model do these switches operate?
- distribution
- data link
- physical
- access
- core
-
What is a characteristic of the distribution layer in the three layer hierarchical model?
- acts as the backbone for the network, aggregating and distributing network traffic throughout the campus
- provides access to the rest of the network through switching, routing, and network access policies
- distributes access to end users
- represents the network edge
Explanation: One of the functions of the distribution layer is aggregating large-scale wiring closet networks. Providing access to end users is a function of the access layer, which is the network edge. Acting as a backbone is a function of the core layer.
-
Which information does a switch use to populate the MAC address table?
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port
Explanation: To maintain the MAC address table, the switch uses the source MAC address of the incoming packets and the port that the packets enter. The destination address is used to select the outgoing port.
-
Which statement is correct about Ethernet switch frame forwarding decisions?
- Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the CAM table.
- Cut-through frame forwarding ensures that invalid frames are always dropped.
- Only frames with a broadcast destination address are forwarded out all active switch ports.
- Unicast frames are always forwarded regardless of the destination MAC address.
Explanation: Cut-through frame forwarding reads up to only the first 22 bytes of a frame, which excludes the frame check sequence and thus invalid frames may be forwarded. In addition to broadcast frames, frames with a destination MAC address that is not in the CAM are also flooded out all active ports. Unicast frames are not always forwarded. Received frames with a destination MAC address that is associated with the switch port on which it is received are not forwarded because the destination exists on the network segment connected to that port.
-
Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- borderless switching
- cut-through switching
- ingress port buffering
- store-and-forward switching
Explanation: The FCS check is used with store-and-forward switching to drop any frame with a FCS that does not match the FCS calculation that is made by a switch. Cut-through switching does not perform any error checking. Borderless switching is a network architecture, not a switching method. Ingress port buffering is used with store-and-forward switching to support different Ethernet speeds, but it is not a switching method.
-
In what situation would a Layer 2 switch have an IP address configured?
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to forward user traffic to another device
- when the Layer 2 switch is the default gateway of user traffic
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to be remotely managed
- when the Layer 2 switch is using a routed port
Explanation: Layer 2 switches can be configured with an IP address so that they can be remotely managed by an administrator. Layer 3 switches can use an IP address on routed ports. Layer 2 switches do not need a configured IP address to forward user traffic or act as a default gateway.
-
A network administrator is configuring a new Cisco switch for remote management access. Which three items must be configured on the switch for the task? (Choose three.)
- IP address
- VTP domain
- vty lines
- default VLAN
- default gateway
- loopback address
Explanation: To enable the remote management access, the Cisco switch must be configured with an IP address and a default gateway. In addition, vty lines must configured to enable either Telnet or SSH connections. A loopback address, default VLAN, and VTP domain configurations are not necessary for the purpose of remote switch management.
-
A network technician has been asked to secure all switches in the campus network. The security requirements are for each switch to automatically learn and add MAC addresses to both the address table and the running configuration. Which port security configuration will meet these requirements?
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
Explanation: With sticky secure MAC addressing, the MAC addresses can be either dynamically learned or manually configured and then stored in the address table and added to the running configuration file. In contrast, dynamic secure MAC addressing provides for dynamically learned MAC addressing that is stored only in the address table.
-
A network administrator is configuring port security on a Cisco switch. When a violation occurs, which violation mode that is configured on an interface will cause packets with an unknown source address to be dropped with no notification sent?
- off
- restrict
- protect
- shutdown
Explanation: On a Cisco switch, an interface can be configured for one of three violation modes, specifying the action to be taken if a violation occurs:Protect – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. There is no notification that a security violation has occurred.
Restrict – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. In this mode, there is a notification that a security violation has occurred.
Shutdown – The interface immediately becomes error-disabled and the port LED is turned off.
-
Two employees in the Sales department work different shifts with their laptop computers and share the same Ethernet port in the office. Which set of commands would allow only these two laptops to use the Ethernet port and create violation log entry without shutting down the port if a violation occurs?
- switchport mode access
switchport port-security - switchport mode access
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum 2
switchport port-security mac-address sticky
switchport port-security violation restrict - switchport mode access
switchport port-security maximum 2
switchport port-security mac-address sticky - switchport mode access
switchport port-security maximum 2
switchport port-security mac-address sticky
switchport port-security violation protectExplanation: The switchport port-security command with no parameters must be entered before any other port security options. The parameter maximum 2 ensures that only the first two MAC addresses detected by the switch are allowed. The mac-address sticky option allows the switch to learn the first two MAC addresses that come into the specific port. The violation restrict option keeps track of the number of violations.
- switchport mode access
-
Refer to the exhibit. What protocol should be configured on SW-A Port 0/1 if it is to send traffic from multiple VLANs to switch SW-B?
- Spanning Tree
- RIP v2
- IEEE 802.1Q
- ARP
- Rapid Spanning Tree
-
A Cisco Catalyst switch has been added to support the use of multiple VLANs as part of an enterprise network. The network technician finds it necessary to clear all VLAN information from the switch in order to incorporate a new network design. What should the technician do to accomplish this task?
- Erase the startup configuration and reboot the switch.
- Erase the running configuration and reboot the switch.
- Delete the startup configuration and the vlan.dat file in the flash memory of the switch and reboot the switch.
- Delete the IP address that is assigned to the management VLAN and reboot the switch.
-
What VLANs are allowed across a trunk when the range of allowed VLANs is set to the default value?
- All VLANs will be allowed across the trunk.
- Only VLAN 1 will be allowed across the trunk.
- Only the native VLAN will be allowed across the trunk.
- The switches will negotiate via VTP which VLANs to allow across the trunk.
-
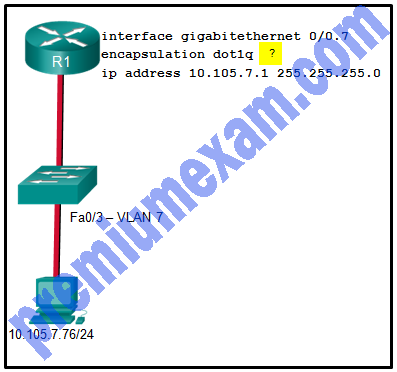
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring inter-VLAN routing on a network. For now, only one VLAN is being used, but more will be added soon. What is the missing parameter that is shown as the highlighted question mark in the graphic?
- It identifies the subinterface.
- It identifies the VLAN number.
- It identifies the native VLAN number.
- It identifies the type of encapsulation that is used.
- It identifies the number of hosts that are allowed on the interface.
Explanation: The completed command would be encapsulation dot1q 7. The encapsulation dot1q part of the command enables trunking and identifies the type of trunking to use. The 7 identifies the VLAN number.
-
A network administrator is designing an ACL. The networks 192.168.1.0/25, 192.168.0.0/25, 192.168.0.128/25, 192.168.1.128/26, and 192.168.1.192/26 are affected by the ACL. Which wildcard mask, if any, is the most efficient to use when specifying all of these networks in a single ACL permit entry?
- 0.0.0.127
- 0.0.0.255
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.255.255
- A single ACL command and wildcard mask should not be used to specify these particular networks or other traffic will be permitted or denied and present a security risk.
Explanation: Write all of the network numbers in binary and determine the binary digits that are identical in consecutive bit positions from left to right. In this example, 23 bits match perfectly. The wildcard mask of 0.0.1.255 designates that 25 bits must match.
-
The computers used by the network administrators for a school are on the 10.7.0.0/27 network. Which two commands are needed at a minimum to apply an ACL that will ensure that only devices that are used by the network administrators will be allowed Telnet access to the routers? (Choose two.)
- access-class 5 in
- access-list 5 deny any
- access-list standard VTY
permit 10.7.0.0 0.0.0.127 - access-list 5 permit 10.7.0.0 0.0.0.31
- ip access-group 5 out
- ip access-group 5 in
Explanation: Numbered and named access lists can be used on vty lines to control remote access. The first ACL command, access-list 5 permit 10.7.0.0 0.0.0.31, allows traffic that originates from any device on the 10.7.0.0/27 network. The second ACL command, access-class 5 in, applies the access list to a vty line.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is examining a configuration implemented by a new intern who attached an IP phone to a switch port and configured the switch. Identify the issue, if any, with the configuration.
- The voice VLAN has not been specified on the interface.
- The configuration is correct.
- There must be a data VLAN added.
- The spanning-tree BPDU guard feature is missing.
- The switch port is not configured as a trunk.
-
What is the reason why the DHCPREQUEST message is sent as a broadcast during the DHCPv4 process?
- to notify other DHCP servers on the subnet that the IP address was leased
- to notify other hosts not to request the same IP address
- for hosts on other subnets to receive the information
- for routers to fill their routing tables with this new information
Explanation: The DHCPREQUEST message is broadcast to inform other DHCP servers that an IP address has been leased.
-
Which set of commands will configure a router as a DHCP server that will assign IPv4 addresses to the 192.168.100.0/23 LAN while reserving the first 10 and the last addresses for static assignment?
- ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.100.1 - dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.254
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
default-router 192.168.101.1 - ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.9
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.101.254
ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-100
ip network 192.168.100.0 255.255.254.0
ip default-gateway 192.168.100.1Explanation: The /23 prefix is equivalent to a network mask of 255.255.254.0. The network usable IPv4 address range is 192.168.100.1 to 192.168.101.254 inclusive. The commands dhcp pool, ip default-gateway, and ip network are not valid DHCP configuration commands.
- ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.10
-
Which command, when issued in the interface configuration mode of a router, enables the interface to acquire an IPv4 address automatically from an ISP, when that link to the ISP is enabled?
- ip dhcp pool
- ip address dhcp
- service dhcp
- ip helper-address
Explanation: The ip address dhcp interface configuration command configures an Ethernet interface as a DHCP client. The service dhcp global configuration command enables the DHCPv4 server process on the router. The ip helper-address command is issued to enable DHCP relay on the router. The ip dhcp pool command creates the name of a pool of addresses that the server can assign to hosts.
-
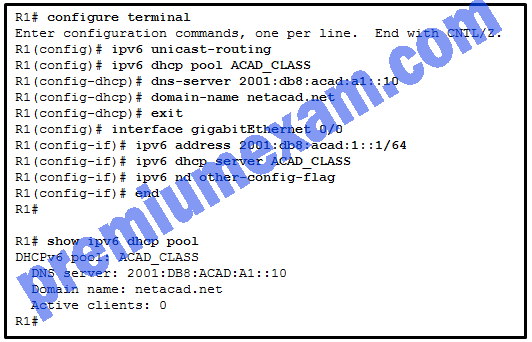
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a router as a DHCPv6 server. The administrator issues a show ipv6 dhcp pool command to verify the configuration. Which statement explains the reason that the number of active clients is 0?
- The default gateway address is not provided in the pool.
- No clients have communicated with the DHCPv6 server yet.
- The IPv6 DHCP pool configuration has no IPv6 address range specified.
- The state is not maintained by the DHCPv6 server under stateless DHCPv6 operation.
Explanation: Under the stateless DHCPv6 configuration, indicated by the command ipv6 nd other-config-flag, the DHCPv6 server does not maintain the state information, because client IPv6 addresses are not managed by the DHCP server. Because the clients will configure their IPv6 addresses by combining the prefix/prefix-length and a self-generated interface ID, the ipv6 dhcp pool configuration does not need to specify the valid IPv6 address range. And because clients will use the link-local address of the router interface as the default gateway address, the default gateway address is not necessary .
-
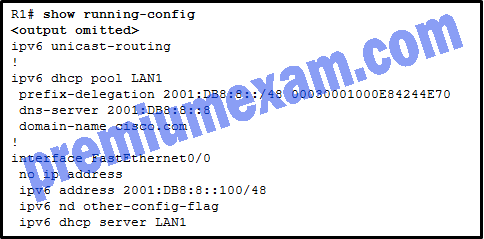
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement shown in the output allows router R1 to respond to stateless DHCPv6 requests?
- ipv6 unicast-routing
- dns-server 2001:DB8:8::8
- ipv6 dhcp server LAN1
- ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- prefix-delegation 2001:DB8:8::/48 00030001000E84244E70
Explanation: The interface command ipv6 nd other-config-flag allows RA messages to be sent on this interface, indicating that additional information is available from a stateless DHCPv6 server.
-
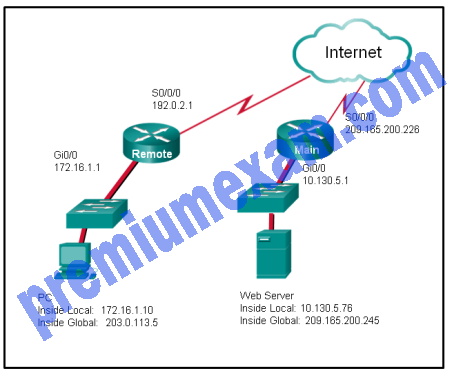
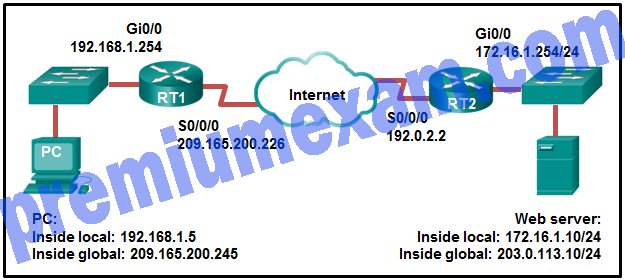
Refer to the exhibit. NAT is configured on Remote and Main. The PC is sending a request to the web server. What IPv4 address is the source IP address in the packet between Main and the web server?
- 10.130.5.76
- 209.165.200.245
- 203.0.113.5
- 172.16.1.10
- 192.0.2.1
- 209.165.200.226
Explanation: Because the packet is between Main and the web server, the source IP address is the inside global address of PC, 203.0.113.5.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct based on the output as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
- The output is the result of the show ip nat translations command.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 192.168.10.10.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 209.165.200.235.
- Traffic with the destination address of a public web server will be sourced from the IP of 192.168.1.10.
- The output is the result of the show ip nat statistics command.
Explanation: The output displayed in the exhibit is the result of the show ip nat translations command. Static NAT entries are always present in the NAT table, while dynamic entries will eventually time out.
-
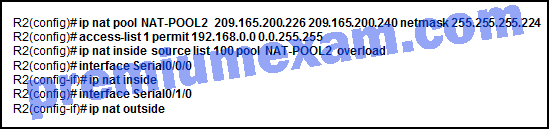
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured R2 for PAT. Why is the configuration incorrect?
- The static NAT entry is missing.
- NAT-POOL2 is bound to the wrong ACL.
- The ACL does not define the list of addresses to be translated.
- The overload keyword should not have been applied.
Explanation: In the exhibit, NAT-POOL 2 is bound to ACL 100, but it should be bound to the configured ACL 1. This will cause PAT to fail. 100, but it should be bound to the configured ACL 1. This will cause PAT to fail.
-
A college marketing department has a networked storage device that uses the IP address 10.18.7.5, TCP port 443 for encryption, and UDP port 4365 for video streaming. The college already uses PAT on the router that connects to the Internet. The router interface has the public IP address of 209.165.200.225/30. The IP NAT pool currently uses the IP addresses ranging from 209.165.200.228-236. Which configuration would the network administrator add to allow this device to be accessed by the marketing personnel from home?
- ip nat pool mktv 10.18.7.5 10.18.7.5
- ip nat outside source static 10.18.7.5 209.165.200.225
- ip nat inside source static tcp 10.18.7.5 443 209.165.200.225 443
ip nat inside source static udp 10.18.7.5 4365 209.165.200.225 4365 - ip nat inside source static tcp 209.165.200.225 443 10.18.7.5 443
ip nat inside source static udp 209.165.200.225 4365 10.18.7.5 4365 - No additional configuration is necessary.
Explanation: This scenario requires port forwarding because the storage device has a private address and needs to be accessible from the external network. To configure port forwarding, the ip nat inside source static command is used.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what type of NAT has been implemented?
- dynamic NAT with a pool of two public IP addresses
- PAT using an external interface
- static NAT with one entry
- static NAT with a NAT pool
Explanation: The output shows that there are two inside global addresses that are the same but that have different port numbers. The only time port numbers are displayed is when PAT is being used. The same output would be indicative of PAT that uses an address pool. PAT with an address pool is appropriate when more than 4,000 simultaneous translations are needed by the company.
-
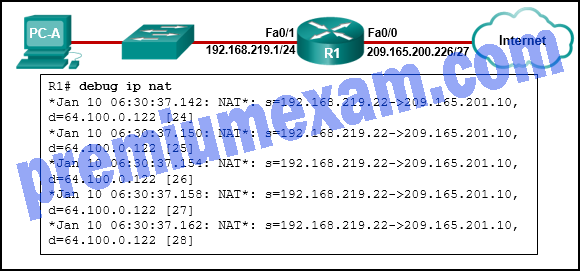
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure PAT on R1, but PC-A is unable to access the Internet. The administrator tries to ping a server on the Internet from PC-A and collects the debugs that are shown in the exhibit. Based on this output, what is most likely the cause of the problem?
- The address on Fa0/0 should be 64.100.0.1.
- The NAT source access list matches the wrong address range.
- The inside global address is not on the same subnet as the ISP.
- The inside and outside NAT interfaces have been configured backwards.
Explanation: The output of debug ip nat shows each packet that is translated by the router. The “s” is the source IP address of the packet and the “d” is the destination. The address after the arrow (“->”) shows the translated address. In this case, the translated address is on the 209.165.201.0 subnet but the ISP facing interface is in the 209.165.200.224/27 subnet. The ISP may drop the incoming packets, or might be unable to route the return packets back to the host because the address is in an unknown subnet.
-
A network engineer is interested in obtaining specific information relevant to the operation of both distribution and access layer Cisco devices. Which command provides common information relevant to both types of devices?
- show ip protocols
- show ip interface
- show cdp neighbors
- show port-security
- show mac-address-table
Explanation: In this case the show cdp neigbors command is the only command that will provide information relevant to both distribution and access layer devices. The show mac-address-table and show port-security commands will display information that is more related to access layer operations. The show ip protocols and show ip interface commands will display information more related to routing and network layer functions performed by devices in the distribution layer.
-
Which two statements are correct if a configured NTP master on a network cannot reach any clock with a lower stratum number? (Choose two.)
- The NTP master will claim to be synchronized at the configured stratum number.
- The NTP master will be the clock with 1 as its stratum number.
- An NTP server with a higher stratum number will become the master.
- Other systems will be willing to synchronize to that master using NTP.
- The NTP master will lower its stratum number.
Explanation: If the network NTP master cannot reach any clock with a lower stratum number, the system will claim to be synchronized at the configured stratum number, and other systems will be willing to synchronize to it using NTP.
-
What are three functions provided by the syslog service? (Choose three.)
- to gather logging information for monitoring and troubleshooting
- to select the type of logging information that is captured
- to specify the destinations of captured messages
- to periodically poll agents for data
- to provide statistics on packets that are flowing through a Cisco device
- to provide traffic analysis
Explanation: There are three primary functions provided by the syslog service:
- gathering logging information
- selection of the type of information to be logged
- selection of the destination of the logged information
-
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is examining the message in a syslog server. What can be determined from the message?
- This is a notification message for a normal but significant condition.
- This is an alert message for which immediate action is needed.
- This is an error message for which warning conditions exist.
- This is an error message that indicates the system is unusable.
Explanation: The number 5 in the message output %SYS-5-CONFIG_I, indicated this is a notification level message that is for normal but significant conditions.
-
When a customer purchases a Cisco IOS 15.0 software package, what serves as the receipt for that customer and is used to obtain the license as well?
- Software Claim Certificate
- End User License Agreement
- Unique Device Identifier
- Product Activation Key
Explanation: A customer who purchases a software package will receive a Product Activation Key (PAK) that serves as a receipt and is used to obtain the license for the software package.
-
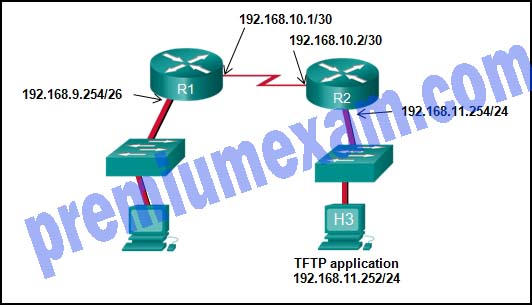
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
- 192.168.9.254
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.168.11.252
- 192.168.11.254
Explanation: The requested address is the address of the TFTP server. A TFTP server is an application that can run on a multitude of network devices including a router, server, or even a networked PC.
-
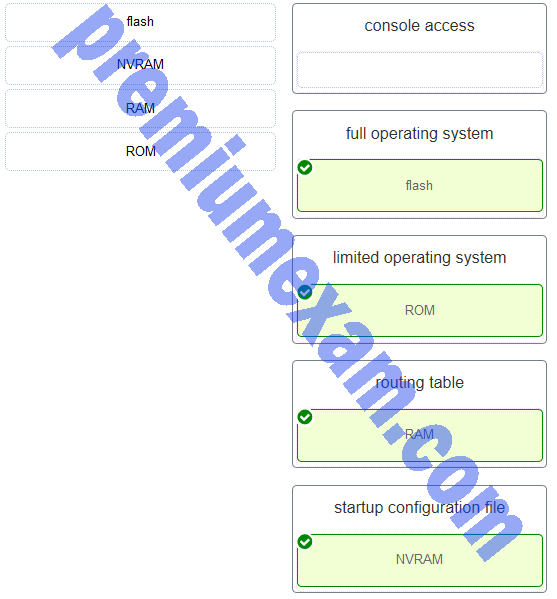
Match the router memory type that provides the primary storage for the router feature. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Console access – Even though the commands a technician types while connected to the console port will be held in RAM, console access itself does not match a memory type.
Flash – holds the full operating system.
NVRAM – holds the startup configuration file.
RAM – holds the running configuration (commands as they are being typed, ARP cache, and the routing table).
ROM – holds a small, limited functionality operating system. -
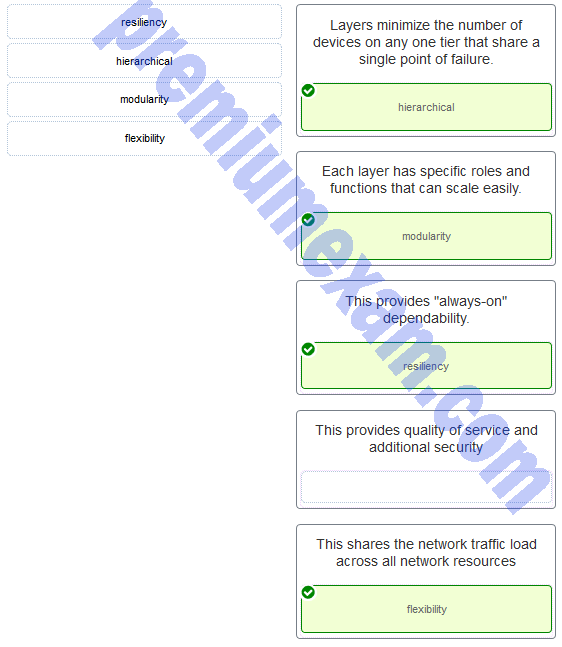
Match each borderless switched network principle to its description. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Borderless switched networks deploy devices hierarchically in specific layers or tiers, each with specific roles. Each layer can be viewed as a module whose services can be replicated or expanded as needed. This modularity allows the network to change and grow with user needs, provides a resilient structure to keep services “always on,” and has the flexibility to share the traffic load across all network resources.
-
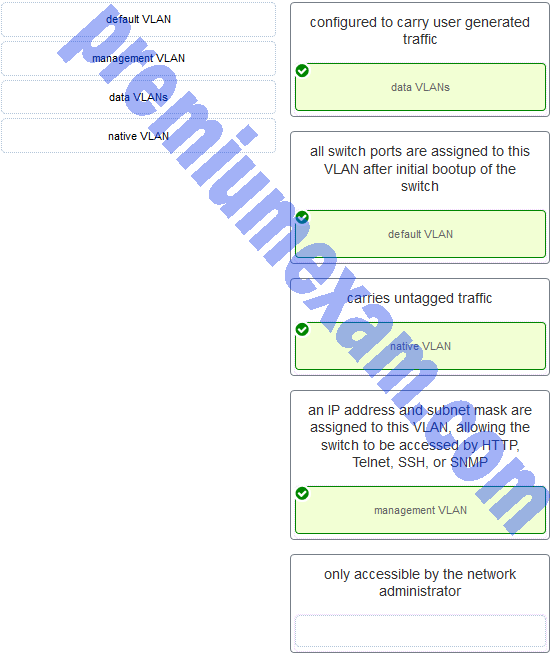
Match the description to the correct VLAN type. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: A data VLAN is configured to carry user-generated traffic. A default VLAN is the VLAN where all switch ports belong after the initial boot up of a switch loading the default configuration. A native VLAN is assigned to an 802.1Q trunk port, and untagged traffic is placed on it. A management VLAN is any VLAN that is configured to access the management capabilities of a switch. An IP address and subnet mask are assigned to it, allowing the switch to be managed via HTTP, Telnet, SSH, or SNMP.
-
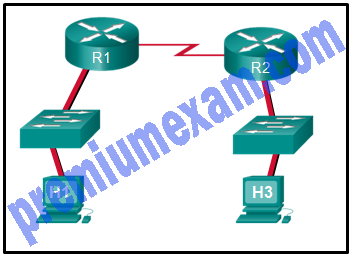
Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that the routing tables are up to date and no ARP messages are needed, after a packet leaves H1, how many times is the L2 header rewritten in the path to H3?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Explanation: H1 creates the first Layer 2 header. The R1 router has to examine the destination IP address to determine how the packet is to be routed. If the packet is to be routed out another interface, as is the case with R1, the router strips the current Layer 2 header and attaches a new Layer 2 header. When R2 determines that the packet is to be sent out the LAN interface, R2 removes the Layer 2 header received from the serial link and attaches a new Ethernet header before transmitting the packet.
-
On which two routers would a default static route be configured? (Choose two.)
- stub router connection to the rest of the corporate or campus network
- any router where a backup route to dynamic routing is needed for reliability
- edge router connection to the ISP
- any router running an IOS prior to 12.0
- the router that serves as the gateway of last resort
Explanation: A stub router or an edge router connected to an ISP has only one other router as a connection. A default static route works in those situations because all traffic will be sent to one destination. The destination router is the gateway of last resort. The default route is not configured on the gateway, but on the router sending traffic to the gateway. The router IOS does not matter.
-
Which command will create a static route on R2 in order to reach PC B?
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
Explanation: The correct syntax is:
router(config)# ip route destination-network destination-mask {next-hop-ip-address | exit-interface}
If the local exit interface instead of the next-hop IP address is used then the route will be displayed as a directly connected route instead of a static route in the routing table. Because the network to be reached is 172.16.2.0 and the next-hop IP address is 172.16.3.1, the command is R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
-
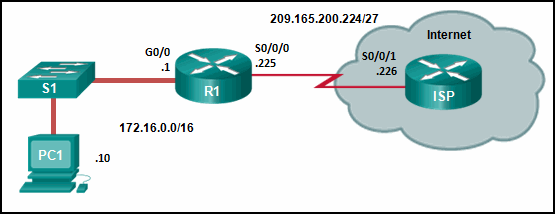
Refer to the exhibit. R1 was configured with the static route command ip route 209.165.200.224 255.255.255.224 S0/0/0 and consequently users on network 172.16.0.0/16 are unable to reach resources on the Internet. How should this static route be changed to allow user traffic from the LAN to reach the Internet?
- Add the next-hop neighbor address of 209.165.200.226.
- Change the exit interface to S0/0/1.
- Change the destination network and mask to 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0.
- Add an administrative distance of 254.
Explanation: The static route on R1 has been incorrectly configured with the wrong destination network and mask. The correct destination network and mask is 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0.
-
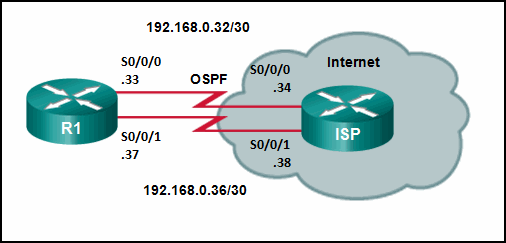
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has an OSPF neighbor relationship with the ISP router over the 192.168.0.32 network. The 192.168.0.36 network link should serve as a backup when the OSPF link goes down. The floating static route command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/1 100 was issued on R1 and now traffic is using the backup link even when the OSPF link is up and functioning. Which change should be made to the static route command so that traffic will only use the OSPF link when it is up?
- Add the next hop neighbor address of 192.168.0.36.
- Change the administrative distance to 1.
- Change the destination network to 192.168.0.34.
- Change the administrative distance to 120.
Explanation: The problem with the current floating static route is that the administrative distance is set too low. The administrative distance will need to be higher than that of OSPF, which is 110, so that the router will only use the OSPF link when it is up.
-
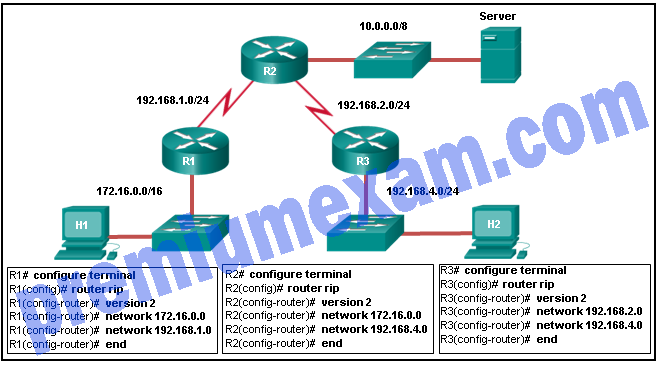
Refer to the exhibit. All hosts and router interfaces are configured correctly. Pings to the server from both H1 and H2 and pings between H1 and H2 are not successful. What is causing this problem?
- RIPv2 does not support VLSM.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R1.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R2.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R3.
- RIPv2 does not support discontiguous networks.
Explanation: RIP configuration on a router should contain network statements for connected networks only. Remote networks are learned from routing updates from other routers.
-
What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer?
- aggregates Layer 2 broadcast domains
- aggregates Layer 3 routing boundaries
- provides access to the user
- provides fault isolation
Explanation: A function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer is providing network access to the users. Layer 2 broadcast domain aggregation, Layer 3 routing boundaries aggregation, and high availability are distribution layer functions. The core layer provides fault isolation and high-speed backbone connectivity.
-
What is the name of the layer in the Cisco borderless switched network design that would have more switches deployed than other layers in the network design of a large organization?
- access
- core
- data link
- network
- network access
Explanation: Access layer switches provide user access to the network. End user devices, such as PCs, access points, printers, and copiers, would require a port on a switch in order to connect to the network. Thus, more switches are needed in the access layer than are needed in the core and distribution layers.
-
What will a Cisco LAN switch do if it receives an incoming frame and the destination MAC address is not listed in the MAC address table?
- Drop the frame.
- Send the frame to the default gateway address.
- Use ARP to resolve the port that is related to the frame.
- Forward the frame out all ports except the port where the frame is received.
Explanation: A LAN switch populates the MAC address table based on source MAC addresses. When a switch receives an incoming frame with a destination MAC address that is not listed in the MAC address table, the switch forwards the frame out all ports except for the ingress port of the frame. When the destination device responds, the switch adds the source MAC address and the port on which it was received to the MAC address table.
-
Which advantage does the store-and-forward switching method have compared with the cut-through switching method?
- collision detecting
- frame error checking
- faster frame forwarding
- frame forwarding using IPv4 Layer 3 and 4 information
Explanation: A switch using the store-and-forward switching method performs an error check on an incoming frame by comparing the FCS value against its own FCS calculations after the entire frame is received. In comparison, a switch using the cut-through switching method makes quick forwarding decisions and starts the forwarding process without waiting for the entire frame to be received. Thus a switch using cut-through switching may send invalid frames to the network. The performance of store-and-forward switching is slower compared to cut-through switching performance. Collision detection is monitored by the sending device. Store-and-forward switching does not use IPv4 Layer 3 and 4 information for its forwarding decisions.
-
As part of the new security policy, all switches on the network are configured to automatically learn MAC addresses for each port. All running configurations are saved at the start and close of every business day. A severe thunderstorm causes an extended power outage several hours after the close of business. When the switches are brought back online, the dynamically learned MAC addresses are retained. Which port security configuration enabled this?
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
Explanation: With sticky secure MAC addressing, the MAC addresses can be either dynamically learned or manually configured and then stored in the address table and added to the running configuration file. In contrast, dynamic secure MAC addressing provides for dynamically learned MAC addressing that is stored only in the address table.
-
A network administrator is configuring port security on a Cisco switch. The company security policy specifies that when a violation occurs, packets with unknown source addresses should be dropped and no notification should be sent. Which violation mode should be configured on the interfaces?
- off
- restrict
- protect
- shutdown
Explanation: On a Cisco switch, an interface can be configured for one of three violation modes, specifying the action to be taken if a violation occurs:
Protect – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. There is no notification that a security violation has occurred.
Restrict – Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses are removed, or the number of maximum allowable addresses is increased. In this mode, there is a notification that a security violation has occurred.
Shutdown – The interface immediately becomes error-disabled and the port LED is turned off.
-
What caused the following error message to appear?
01:11:12: %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: psecure-violation error detected on Fa0/8, putting Fa0/8 in err-disable state
01:11:12: %PORT_SECURITY-2-PSECURE_VIOLATION: Security violation occurred, caused by MAC address 0011.a0d4.12a0 on port FastEthernet0/8.
01:11:13: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/8, changed state to down
01:11:14: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/8, changed state to down- Another switch was connected to this switch port with the wrong cable.
- An unauthorized user tried to telnet to the switch through switch port Fa0/8.
- NAT was enabled on a router, and a private IP address arrived on switch port Fa0/8.
- A host with an invalid IP address was connected to a switch port that was previously unused.
- Port security was enabled on the switch port, and an unauthorized connection was made on switch port Fa0/8.
-
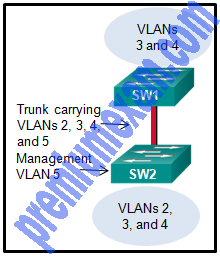
Refer to the exhibit. A small business uses VLANs 2, 3, 4, and 5 between two switches that have a trunk link between them. What native VLAN should be used on the trunk if Cisco best practices are being implemented?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Explanation: Cisco recommends using a VLAN that is not used for anything else for the native VLAN. The native VLAN should also not be left to the default of VLAN 1. VLAN 6 is the only VLAN that is not used and not VLAN 1.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of the extended range VLANs that are created on a Cisco 2960 switch?
- They are numbered VLANs 1002 to 1005.
- They cannot be used across multiple switches.
- They are reserved to support Token Ring VLANs.
- They are not stored in the vlan.dat file.
Explanation: The extended range VLANs are identified by VLAN ID 1006 to 4096. By default, they are saved in the running-config file, not in the vlan.dat file. VLANs 1002 to 1005 are reserved to support Token Ring and FDDI VLANs. The extended range VLANs can be manually configured on multiple switches.
-
A network administrator is using the router-on-a-stick method to configure inter-VLAN routing. Switch port Gi1/1 is used to connect to the router. Which command should be entered to prepare this port for the task?
- Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 1 - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk - Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 1Explanation: With the router-on-a-stick method, the switch port that connects to the router must be configured as trunk mode. This can be done with the command Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk. The other options do not put the switch port into trunk mode.
- Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/1
-
A network administrator is configuring an ACL with the command access-list 10 permit 172.16.32.0 0.0.15.255. Which IPv4 address matches the ACE?
- 172.16.20.2
- 172.16.26.254
- 172.16.47.254
- 172.16.48.5
Explanation: With the wildcard mask of 0.0.15.255, the IPv4 addresses that match the ACE are in the range of 172.16.32.0 to 172.16.47.255.
-
What will be the result of adding the command ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.4.1 172.16.4.5 to the configuration of a local router that has been configured as a DHCP server?
- Traffic that is destined for 172.16.4.1 and 172.16.4.5 will be dropped by the router.
- Traffic will not be routed from clients with addresses between 172.16.4.1 and 172.16.4.5.
- The DHCP server function of the router will not issue the addresses from 172.16.4.1 through 172.16.4.5 inclusive.
- The router will ignore all traffic that comes from the DHCP servers with addresses 172.16.4.1 and 172.16.4.5.
-
A host on the 10.10.100.0/24 LAN is not being assigned an IPv4 address by an enterprise DHCP server with the address 10.10.200.10/24. What is the best way for the network engineer to resolve this problem?
- Issue the command ip helper-address 10.10.200.10 on the router interface that is the 10.10.100.0/24 gateway.
- Issue the command default-router 10.10.200.10 at the DHCP configuration prompt on the 10.10.100.0/24 LAN gateway router.
- Issue the command ip helper-address 10.10.100.0 on the router interface that is the 10.10.200.0/24 gateway.
- Issue the command network 10.10.200.0 255.255.255.0 at the DHCP configuration prompt on the 10.10.100.0/24 LAN gateway
Explanation: The DHCP server is not on the same network as the hosts, so DHCP relay agent is required. This is achieved by issuing the ip helper-address command on the interface of the router that contains the DHCPv4 clients, in order to direct DHCP messages to the DHCPv4 server IP address.
-
What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
Explanation: The EUI-64 process uses the MAC address of an interface to construct an interface ID (IID). Because the MAC address is only 48 bits in length, 16 additional bits (FF:FE) must be added to the MAC address to create the full 64-bit interface ID.
-
Refer to the exhibit. NAT is configured on RT1 and RT2. The PC is sending a request to the web server. What IPv4 address is the source IP address in the packet between RT2 and the web server?
- 192.0.2.2
- 172.16.1.10
- 203.0.113.10
- 172.16.1.254
- 192.168.1.5
- 209.165.200.245
Explanation: Because the packet is between RT2 and the web server, the source IP address is the inside global address of PC, 209.165.200.245.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct based on the output as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.) The output is the result of the show ip nat translations command.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 192.168.10.10.
- The host with the address 209.165.200.235 will respond to requests by using a source address of 209.165.200.235.
- Traffic with the destination address of a public web server will be sourced from the IP of 192.168.1.10.
- The output is the result of the show ip nat statistics command.
Explanation:
The output displayed in the exhibit is the result of the show ip nat translations command. Static NAT entries are always present in the NAT table, while dynamic entries will eventually time out.
-
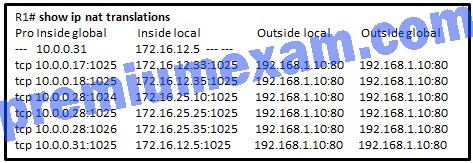
Refer to the exhibit. A company has an internal network of 172.16.25.0/24 for their employee workstations and a DMZ network of 172.16.12.0/24 to host servers. The company uses NAT when inside hosts connect to outside network. A network administrator issues the show ip nat translations command to check the NAT configurations. Which one of source IPv4 addresses is translated by R1 with PAT?
- 10.0.0.31
- 172.16.12.5
- 172.16.12.33
- 172.16.25.35
- 192.168.1.10
Explanation: From the output, three IPv4 addresses (172.16.25.10, 172.16.25.25, and 172.16.25.35) are translated into the same IPv4 address (10.0.0.28) with three different ports, thus these three IPv4 addresses are translated with PAT. The IPv4 addresses 172.16.12.33 and 172.16.12.35 are translated with dynamic NAT. The IPv4 address 172.16.12.5 is translated with static NAT.
-
What benefit does NAT64 provide?
- It allows sites to use private IPv6 addresses and translates them to global IPv6 addresses.
- It allows sites to connect multiple IPv4 hosts to the Internet via the use of a single public IPv4 address.
- It allows sites to connect IPv6 hosts to an IPv4 network by translating the IPv6 addresses to IPv4 addresses.
- It allows sites to use private IPv4 addresses, and thus hides the internal addressing structure from hosts on public IPv4 networks.
Explanation: NAT64 is a temporary IPv6 transition strategy that allows sites to use IPv6 addresses and still be able to connect to IPv4 networks. This is accomplished by translating the IPv6 addresses into IPv4 addresses before sending the packets onto the IPv4 network.
-
A network administrator is verifying a configuration that involves network monitoring. What is the purpose of the global configuration command logging trap 4?
- System messages will be forwarded to the number following the logging trap argument.
- System messages that exist in levels 4-7 must be forwarded to a specific logging server.
- System messages that match logging levels 0-4 will be forwarded to a specified logging device.
- System messages will be forwarded using a SNMP version that matches the argument that follows the logging trap command.
Explanation: System messages that match logging levels 0-4 will be forwarded to a specified logging device via the command logging trap 4 and logging ip-address.
-
What is the purpose of the Cisco PAK?
- It is a key for enabling an IOS feature set.
- It is a proprietary encryption algorithm.
- It is a compression file type used when installing IOS 15 or an IOS upgrade.
- It is a way to compress an existing IOS so that a newer IOS version can be co-installed on a router.
Explanation: PAK is a product activation key from Cisco. To activate a particular technology package for IOS 15, you must provide Cisco with the router product ID with associated serial number and a PAK that has been purchased.
-
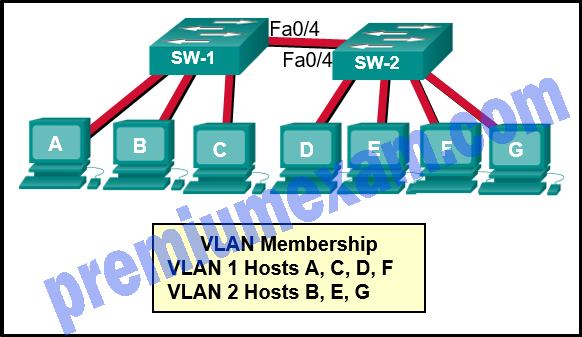
Refer to the exhibit. Which three hosts will receive ARP requests from host A, assuming that port Fa0/4 on both switches is configured to carry traffic for multiple VLANs? (Choose three.)
- host B
- host C
- host D
- host E
- host F
- host G
Explanation: ARP requests are sent out as broadcasts. That means the ARP request is sent only throughout a specific VLAN. VLAN 1 hosts will only hear ARP requests from hosts on VLAN 1. VLAN 2 hosts will only hear ARP requests from hosts on VLAN 2.
-
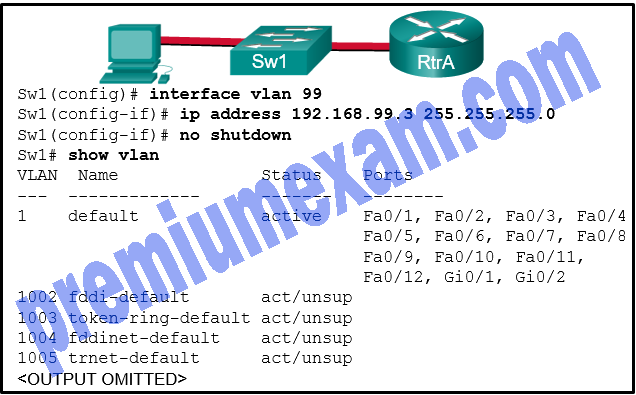
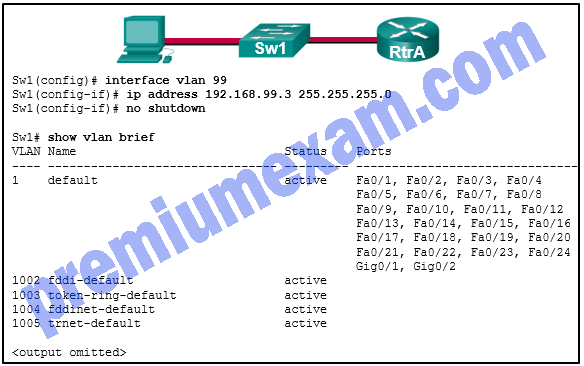
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited configuration and output, why is VLAN 99 missing?
- because there is a cabling problem on VLAN 99
- because VLAN 99 is not a valid management VLAN
- because VLAN 1 is up and there can only be one management VLAN on the switch
- because VLAN 99 has not yet been created
Explanation: VLAN 99 is the management VLAN and must be added to the VLAN database before it will appear in the show vlan output. To do so, enter the following commands:
Sw1(config)# vlan 99
Sw1(config-vlan)# name Management
SW1(config-vlan)# exit
-
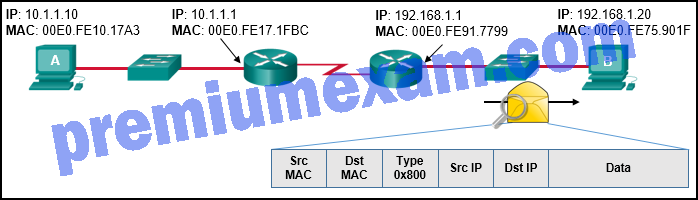
Refer to the exhibit. Host A has sent a packet to host B. What will be the source MAC and IP addresses on the packet when it arrives at host B?
- Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 192.168.1.1 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE10.17A3
Source IP: 10.1.1.10 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 10.1.1.10 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE10.17A3
Source IP: 192.168.1.1 - Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
Source IP: 10.1.1.1Explanation: As a packet traverses the network, the Layer 2 addresses will change at every hop as the packet is de-encapsulated and re-encapsulated, but the Layer 3 addresses will remain the same.
- Source MAC: 00E0.FE91.7799
-
What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
Explanation: When the ipv6 unicast-routing command is implemented on a router, it enables the router as an IPv6 router. Use of this command also assigns the router to the all-routers multicast group.
-
What is a characteristic of a static route that creates a gateway of last resort?
- It backs up a route already discovered by a dynamic routing protocol.
- It uses a single network address to send multiple static routes to one destination address.
- It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.
- It is configured with a higher administrative distance than the original dynamic routing protocol has.
Explanation: A default static route is a route that matches all packets. It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route. A default static route is simply a static route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination IPv4 address. Configuring a default static route creates a gateway of last resort.
-
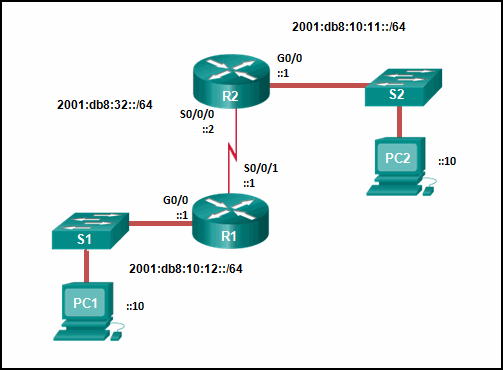
Refer to the exhibit. Which command will properly configure an IPv6 static route on R2 that will allow traffic from PC2 to reach PC1 without any recursive lookups by router R2?
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/0
- R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/1
Explanation: A nonrecursive route must have an exit interface specified from which the destination network can be reached. In this example 2001:db8:10:12::/64 is the destination network and R2 will use exit interface S0/0/0 to reach that network. Therefore, the static route would be ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/0.
-
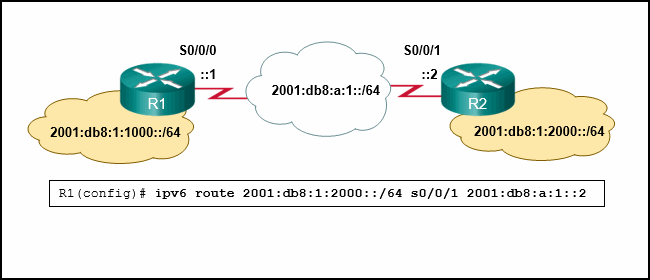
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is attempting to install an IPv6 static route on router R1 to reach the network attached to router R2. After the static route command is entered, connectivity to the network is still failing. What error has been made in the static route configuration?
- The network prefix is incorrect.
- The destination network is incorrect.
- The interface is incorrect.
- The next hop address is incorrect.
Explanation: In this example the interface in the static route is incorrect. The interface should be the exit interface on R1, which is s0/0/0.
-
To enable RIPv1 routing for a specific subnet, the configuration command network 172.16.64.32 was entered by the network administrator. What address, if any, appears in the running configuration file to identify this network?
- 172.16.64.32
- 172.16.64.0
- 172.16.0.0
- No address is displayed.
Explanation:
RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol, meaning it will automatically convert the subnet ID that was entered into the classful address of 172.16.0.0 when it is displayed in the running configuration.
-
Which route will a router use to forward an IPv4 packet after examining its routing table for the best match with the destination address?
- a level 1 child route
- a level 1 parent route
- a level 1 ultimate route
- a level 2 supernet route
Explanation: If the best match is a level 1 ultimate route then the router will forward the packet to that network. Level 1 parent route is a route that contains subnets and is not used to forward packets. Level 1 child routes and level 2 supernet routes are not valid routing table entries.
-
Which two factors are important when deciding which interior gateway routing protocol to use? (Choose two.) scalability
- ISP selection
- speed of convergence
- the autonomous system that is used
- campus backbone architecture
Explanation: There are several factors to consider when selecting a routing protocol to implement. Two of them are scalability and speed of convergence. The other options are irrelevant.
-
Which network design may be recommended for a small campus site that consists of a single building with a few users?
- a network design where the access and core layers are collapsed into a single layer
- a collapsed core network design
- a three-tier campus network design where the access, distribution, and core are all separate layers, each one with very specific functions
- a network design where the access and distribution layers are collapsed into a single layer
Explanation: In some cases, maintaining a separate distribution and core layer is not required. In smaller campus locations where there are fewer users who are accessing the network or in campus sites that consist of a single building, separate core and distribution layers may not be needed. In this scenario, the recommendation is the alternate two-tier campus network design, also known as the collapsed core network design.
-
Which information does a switch use to keep the MAC address table information current? the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port
Explanation: To maintain the MAC address table, the switch uses the source MAC address of the incoming packets and the port that the packets enter. The destination address is used to select the outgoing port.
-
Which characteristic describes cut-through switching?
- Error-free fragments are forwarded, so switching occurs with lower latency.
- Frames are forwarded without any error checking.
- Only outgoing frames are checked for errors.
- Buffering is used to support different Ethernet speeds.
Explanation: Cut-through switching reduces latency by forwarding frames as soon as the destination MAC address and the corresponding switch port are read from the MAC address table. This switching method does not perform any error checking and does not use buffers to support different Ethernet speeds. Error checking and buffers are characteristics of store-and-forward switching.
-
What is a result of connecting two or more switches together?
- The number of broadcast domains is increased.
- The size of the broadcast domain is increased.
- The number of collision domains is reduced.
- The size of the collision domain is increased.
Explanation: When two or more switches are connected together, the size of the broadcast domain is increased and so is the number of collision domains. The number of broadcast domains is increased only when routers are added.
-
Which commands are used to re-enable a port that has been disabled as a result of a port security violation?
- shutdown
no shutdown - shutdown
no switchport port-security - shutdown
no switchport port-security violation shutdown - shutdown
no switchport port-security maximumExplanation: When a switch security violation occurs, by default the port enters in the error-disable state and the port does not become active again automatically if the condition that triggered the violation disappears.
- shutdown
-
Which two characteristics describe the native VLAN? (Choose two.)
- Designed to carry traffic that is generated by users, this type of VLAN is also known as the default VLAN.
- The native VLAN traffic will be untagged across the trunk link.
- This VLAN is necessary for remote management of a switch.
- High priority traffic, such as voice traffic, uses the native VLAN.
- The native VLAN provides a common identifier to both ends of a trunk.
Explanation: The native VLAN is assigned to 802.1Q trunks to provide a common identifier to both ends of the trunk link. Whatever VLAN native number is assigned to a port, or if the port is the default VLAN of 1, the port does not tag any frame in that VLAN as the traffic travels across the trunk. At the other end of the link, the receiving device that sees no tag knows the specific VLAN number because the receiving device must have the exact native VLAN number. The native VLAN should be an unused VLAN that is distinct from VLAN1, the default VLAN, as well as other VLANs. Data VLANs, also known as user VLANs, are configured to carry user-generated traffic, with the exception of high priority traffic, such as VoIP. Voice VLANs are configured for VoIP traffic. The management VLAN is configured to provide access to the management capabilities of a switch.
-
Which type of traffic is designed for a native VLAN?
- user-generated
- tagged
- untagged
- management
Explanation: A native VLAN carries untagged traffic, which is traffic that does not come from a VLAN. A data VLAN carries user-generated traffic. A management VLAN carries management traffic.
-
An administrator is trying to remove configurations from a switch. After using the command erase startup-config and reloading the switch, the administrator finds that VLANs 10 and 100 still exist on the switch. Why were these VLANs not removed?
- These VLANs are default VLANs that cannot be removed.
- These VLANs cannot be deleted unless the switch is in VTP client mode.
- These VLANs can only be removed from the switch by using the no vlan 10 and no vlan 100 commands.
- Because these VLANs are stored in a file that is called vlan.dat that is located in flash memory, this file must be manually deleted.
Explanation: Standard range VLANs (1-1005) are stored in a file that is called vlan.dat that is located in flash memory. Erasing the startup configuration and reloading a switch does not automatically remove these VLANs. The vlan.dat file must be manually deleted from flash memory and then the switch must be reloaded.
-
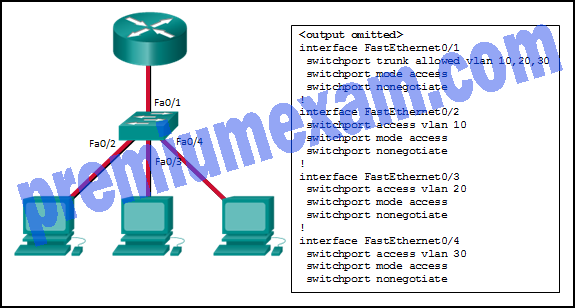
Refer to the exhibit. Inter-VLAN communication between VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 is not successful. What is the problem?
- The access interfaces do not have IP addresses and each should be configured with an IP address.
- The switch interface FastEthernet0/1 is configured as an access interface and should be configured as a trunk interface.
- The switch interface FastEthernet0/1 is configured to not negotiate and should be configured to negotiate.
- The switch interfaces FastEthernet0/2, FastEthernet0/3, and FastEthernet0/4 are configured to not negotiate and should be configured to negotiate.
Explanation: To forward all VLANs to the router, the switch interface Fa0/1 must be configured as a trunk interface with the switchport mode trunk command.
-
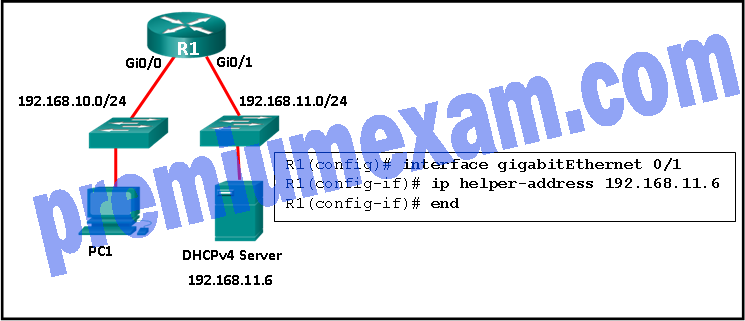
Refer to the exhibit. R1 has been configured as shown. However, PC1 is not able to receive an IPv4 address. What is the problem?
- A DHCP server must be installed on the same LAN as the host that is receiving the IP address.
- R1 is not configured as a DHCPv4 server.
- The ip address dhcp command was not issued on the interface Gi0/1.
- The ip helper-address command was applied on the wrong interface.
Explanation: The ip helper-address command has to be applied on interface Gi0/0. This command must be present on the interface of the LAN that contains the DHCPv4 client PC1 and must be directed to the correct DHCPv4 server.
-
Which type of traffic would most likely have problems when passing through a NAT device?
- Telnet
- IPsec
- HTTP
- ICMP
- DNS
Explanation: IPsec protocols often perform integrity checks on packets when they are received to ensure that they have not been changed in transit from the source to the destination. Because NAT changes values in the headers as packets pass from inside to outside, these integrity checks can fail, thus causing the packets to be dropped at the destination.
-
A small company has a web server in the office that is accessible from the Internet. The IP address 192.168.10.15 is assigned to the web server. The network administrator is configuring the router so that external clients can access the web server over the Internet. Which item is required in the NAT configuration?
- an IPv4 address pool
- an ACL to identify the local IPv4 address of the web server
- the keyword overload for the ip nat inside source command
- the ip nat inside source command to link the inside local and inside global addresses
Explanation: A static NAT configuration is necessary for a web server that is accessible from the Internet. The configuration is achieved via an ip nat inside source static <inside local> <inside global> command under the global configuration mode. An IP address pool and an ACL are necessary when configuring dynamic NAT and PAT. The keyword overload is used to configure PAT.
-
Which configuration would be appropriate for a small business that has the public IP address of 209.165.200.225/30 assigned to the external interface on the router that connects to the Internet?
- access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ip nat inside source list 1 interface serial 0/0/0 overload - access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ip nat pool comp 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.8 netmask 255.255.255.240
ip nat inside source list 1 pool comp - access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ip nat pool comp 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.8 netmask 255.255.255.240
ip nat inside source list 1 pool comp overload - access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
ip nat pool comp 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.8 netmask 255.255.255.240
ip nat inside source list 1 pool comp overload
ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.5 209.165.200.225Explanation: With the command, ip nat inside source list 1 interface serial 0/0/0 overload, the router is configured to translate internal private IP addresses in the range of 10.0.0.0/8 to a single public IP address, 209.165.200.225/30. The other options will not work, because the IP addresses defined in the pool, 192.168.2.0/28, are not routable on the Internet.
- access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
-
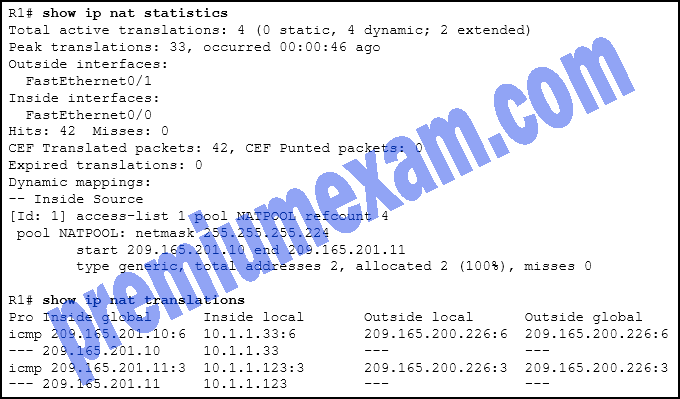
Refer to the exhibit. A PC at address 10.1.1.45 is unable to access the Internet. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- The NAT pool has been exhausted.
- The wrong netmask was used on the NAT pool.
- Access-list 1 has not been configured properly.
- The inside and outside interfaces have been configured backwards.
Explanation: The output of show ip nat statistics shows that there are 2 total addresses and that 2 addresses have been allocated (100%). This indicates that the NAT pool is out of global addresses to give new clients. Based on the show ip nat translations, PCs at 10.1.1.33 and 10.1.1.123 have used the two available addresses to send ICMP messages to a host on the outside network.
-
What is indicated by the M in the Cisco IOS image name c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.153-3.M.bin?
- a maintenance deployment release
- a minor release
- a mainline release
- an extended maintenance release
Explanation: The file name c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.153-3.M.bin indicates a version of Cisco IOS that includes the major release, minor release, maintenance release, and maintenance rebuild numbers. The M indicates this is an extended maintenance release.
-
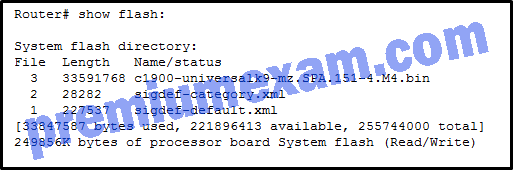
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is preparing to upgrade the IOS system image on a Cisco 2901 router. Based on the output shown, how much space is available for the new image?
- 25574400 bytes
- 249856000 bytes
- 221896413 bytes
- 33591768 bytes
Explanation: There are 221896413 bytes of space available in flash for the new image according to the line “[33847587 bytes used, 221896413 available, 255744000 total]” from the output.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited configuration and output, what are two reasons VLAN 99 missing? (Choose two.)
- because there is a cabling problem on VLAN 99
- because VLAN 99 is not a valid management VLAN
- because VLAN 1 is up and there can only be one management VLAN on the switch
- because VLAN 99 needs to be entered as a VLAN under an interface before it can become an active interface
- because the VLAN 99 has not been manually entered into the VLAN database with the vlan 99 command
NavigationExplanation: VLAN 99 was not manually created on switch Sw1. When a VLAN interface is created, the VLAN is not automatically populated into the VLAN database.
-
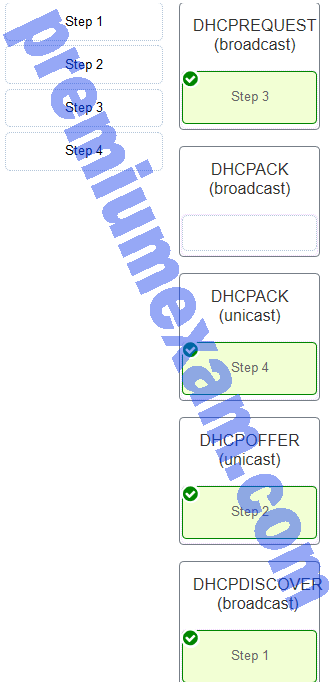
Order the DHCP process steps. (Not all options are used.)
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.