Last Updated on January 28, 2021 by Admin
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam Answers 2019
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.03 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Chapter 4 Exam | Chapter 4 Exam | Chapter 4 Exam | Online Test |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 5 Exam | Chapter 5 Exam | Chapter 5 Exam | Online Test |
| Lab Activities | |||
| No Lab Activities | |||
-
A network designer must provide a rationale to a customer for a design which will move an enterprise from a flat network topology to a hierarchical network topology. Which two features of the hierarchical design make it the better choice? (Choose two.)
- lower bandwidth requirements
- reduced cost for equipment and user training
- easier to provide redundant links to ensure higher availability
- less required equipment to provide the same performance levels
- simpler deployment for additional switch equipment
Explanation: A hierarchical design for switches helps network administrators when planning and deploying a network expansion, performing fault isolation when a problem occurs, and providing resiliency when traffic levels are high. A good hierarchical design has redundancy when it can be afforded so that one switch does not cause all networks to be down.
-
What is a collapsed core in a network design?
- a combination of the functionality of the access and distribution layers
- a combination of the functionality of the distribution and core layers
- a combination of the functionality of the access and core layers
- a combination of the functionality of the access, distribution, and core layers
Explanation: A collapsed core design is appropriate for a small, single building business. This type of design uses two layers (the collapsed core and distribution layers consolidated into one layer and the access layer). Larger businesses use the traditional three-tier switch design model.
-
What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
- access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
- access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
- distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
- access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
Explanation: Maintaining three separate network tiers is not always required or cost-efficient. All network designs require an access layer, but a two-tier design can collapse the distribution and core layers into one layer to serve the needs of a small location with few users.
-
What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture distribution layer?
- acting as a backbone
- aggregating all the campus blocks
- aggregating Layer 3 routing boundaries
- providing access to end user devices
Explanation: One of the basic functions of the distribution layer of the Cisco Borderless Architecture is to perform routing between different VLANs. Acting as a backbone and aggregating campus blocks are functions of the core layer. Providing access to end user devices is a function of the access layer.
-
Which two previously independent technologies should a network administrator attempt to combine after choosing to upgrade to a converged network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
- user data traffic
- VoIP phone traffic
- scanners and printers
- mobile cell phone traffic
- electrical system
Explanation: A converged network provides a single infrastructure that combines voice, video, and data. Analog phones, user data, and point-to-point video traffic are all contained within the single network infrastructure of a converged network.
-
What type of network uses one common infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals?
- switched
- borderless
- converged
- managed
Explanation: A converged network has only one physical network to install and manage. This results in substantial savings over the installation and management of separate voice, video, and data networks.
-
A local law firm is redesigning the company network so that all 20 employees can be connected to a LAN and to the Internet. The law firm would prefer a low cost and easy solution for the project. What type of switch should be selected?
- fixed configuration
- modular configuration
- stackable configuration
- StackPower
- StackWise
Explanation: By looking at the graphic in 1.1.2.2 #2 and #3 and comparing those photos to the graphics used in the Cisco switch design model shown in 1.1.1.5 #2, you can see that the smaller rack unit fixed configuration switch is used as an access layer switch. The modular configuration switch would be used at the distribution and core layers.
-
What are two advantages of modular switches over fixed-configuration switches? (Choose two.)
- lower cost per switch
- increased scalability
- lower forwarding rates
- need for fewer power outlets
- availability of multiple ports for bandwidth aggregation
Explanation: Fixed-configuration switches, although lower in price, have a designated number of ports and no ability to add ports. They also typically provide fewer high-speed ports. In order to scale switching on a network that consists of fixed-configuration switches, more switches need to be purchased. This increases the number of power outlets that need to be used. Modular switches can be scaled simply by purchasing additional line cards. Bandwidth aggregation is also easier, because the backplane of the chassis can provide the bandwidth that is needed for the switch port line cards.
-
Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
- destination IP address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- source MAC address
Explanation: When a switch receives a frame with a source MAC address that is not in the MAC address table, the switch will add that MAC address to the table and map that address to a specific port. Switches do not use IP addressing in the MAC address table.
-
Which network device can be used to eliminate collisions on an Ethernet network?
- firewall
- hub
- router
- switch
Explanation: A switch provides microsegmentation so that no other device competes for the same Ethernet network bandwidth.
-
What two criteria are used by a Cisco LAN switch to decide how to forward Ethernet frames? (Choose two.)
- path cost
- egress port
- ingress port
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
Explanation: Cisco LAN switches use the MAC address table to make decisions of traffic forwarding. The decisions are based on the ingress port and the destination MAC address of the frame. The ingress port information is important because it carries the VLAN to which the port belongs.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?
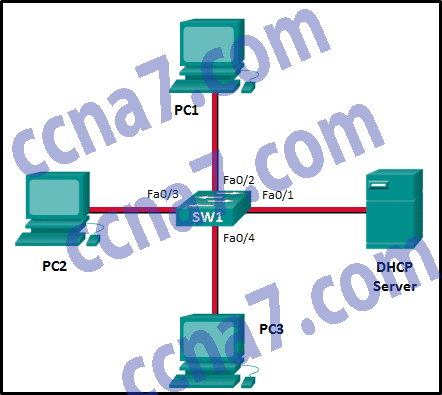
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam 003
- to Fa0/1 only
- to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
Explanation: Because this is a broadcast frame, SW1 will send it to all ports except to the ingress one (the port in which the request was received).
-
What is one function of a Layer 2 switch?
- forwards data based on logical addressing
- duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port
- learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address
- determines which interface is used to forward a frame based on the destination MAC address
Explanation: A switch builds a MAC address table of MAC addresses and associated port numbers by examining the source MAC address found in inbound frames. To forward a frame onward, the switch examines the destination MAC address, looks in the MAC address for a port number associated with that destination MAC address, and sends it to the specific port. If the destination MAC address is not in the table, the switch forwards the frame out all ports except the inbound port that originated the frame.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
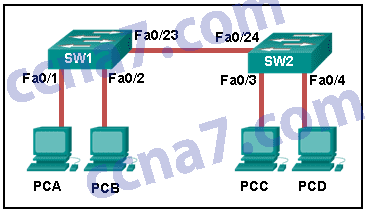
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam 002
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
Explanation: When a switch powers on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. The switch forwards based on the destination MAC address found in the frame header. If a switch has no entries in the MAC address table or if the destination MAC address is not in the switch table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the port that brought the frame into the switch.
-
A small publishing company has a network design such that when a broadcast is sent on the LAN, 200 devices receive the transmitted broadcast. How can the network administrator reduce the number of devices that receive broadcast traffic?
- Add more switches so that fewer devices are on a particular switch.
- Replace the switches with switches that have more ports per switch. This will allow more devices on a particular switch.
- Segment the LAN into smaller LANs and route between them.
- Replace at least half of the switches with hubs to reduce the size of the broadcast domain.
Explanation: By dividing the one big network into two smaller network, the network administrator has created two smaller broadcast domains. When a broadcast is sent on the network now, the broadcast will only be sent to the devices on the same Ethernet LAN. The other LAN will not receive the broadcast.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are displayed?
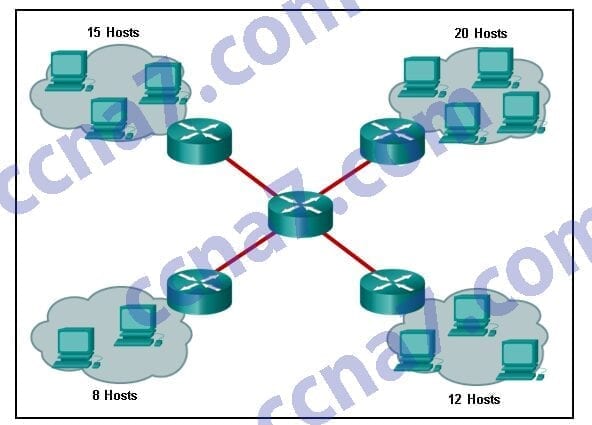
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam 001
- 1
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 55
Explanation: A router defines a broadcast boundary, so every link between two routers is a broadcast domain. In the exhibit, 4 links between routers make 4 broadcast domains. Also, each LAN that is connected to a router is a broadcast domain. The 4 LANs in the exhibit result in 4 more broadcast domains, so there are 8 broadcast domains in all.
-
Which solution would help a college alleviate network congestion due to collisions?
- a firewall that connects to two Internet providers
- a high port density switch
- a router with two Ethernet ports
- a router with three Ethernet ports
Explanation: Switches provide microsegmentation so that one device does not compete for the same Ethernet network bandwidth with another network device, thus practically eliminating collisions. A high port density switch provides very fast connectivity for many devices.
-
Which network device can serve as a boundary to divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain?
- router
- Ethernet bridge
- Ethernet hub
- access point
Explanation: Layer 1 and 2 devices (LAN switch and Ethernet hub) and access point devices do not filter MAC broadcast frames. Only a Layer 3 device, such as a router, can divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain.
-
What is the destination address in the header of a broadcast frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- 11-11-11-11-11-11
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Explanation: In a Layer 2 broadcast frame, the destination MAC address (contained in the frame header) is set to all binary ones, therefore, the format of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF. The binary format of 11 in hexadecimal is 00010001. 255.255.255.255 and 0.0.0.0 are IP addresses.
-
Which statement describes a result after multiple Cisco LAN switches are interconnected?
- The broadcast domain expands to all switches.
- One collision domain exists per switch.
- Frame collisions increase on the segments connecting the switches.
- There is one broadcast domain and one collision domain per switch.
Explanation: In Cisco LAN switches, the microsegmentation makes it possible for each port to represent a separate segment and thus each switch port represents a separate collision domain. This fact will not change when multiple switches are interconnected. However, LAN switches do not filter broadcast frames. A broadcast frame is flooded to all ports. Interconnected switches form one big broadcast domain.
-
What does the term “port density” represent for an Ethernet switch?
- the memory space that is allocated to each switch port
- the number of available ports
- the numbers of hosts that are connected to each switch port
- the speed of each port
Explanation: The term port density represents the number of ports available in a switch. A one rack unit access switch can have up to 48 ports. Larger switches may support hundreds of ports.
-
What are two reasons a network administrator would segment a network with a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
- to create fewer collision domains
- to enhance user bandwidth
- to create more broadcast domains
- to eliminate virtual circuits
- to isolate traffic between segments
- to isolate ARP request messages from the rest of the network
Explanation: A switch has the ability of creating temporary point-to-point connections between the directly-attached transmitting and receiving network devices. The two devices have full-bandwidth full-duplex connectivity during the transmission.
-
Fill in the blank.
A converged network is one that uses the same infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals.
-
Math the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
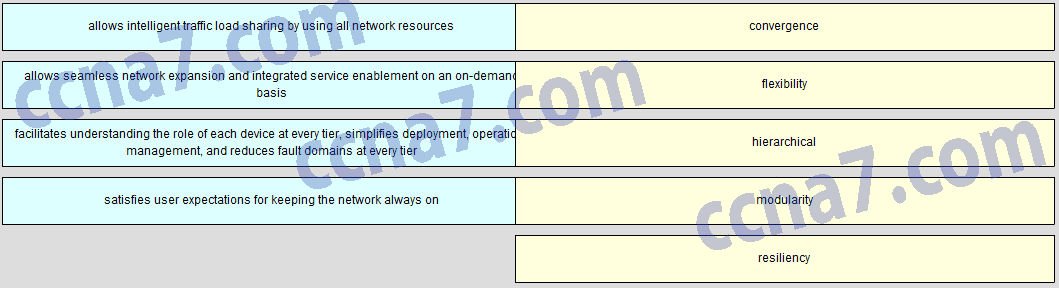
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam Q001
- Answer

CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam A001
- Question
-
Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
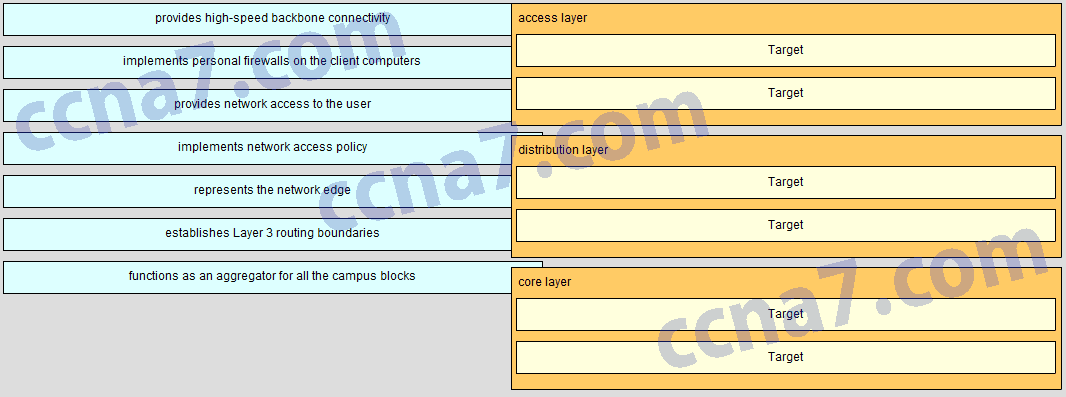
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam Q002
- Answer
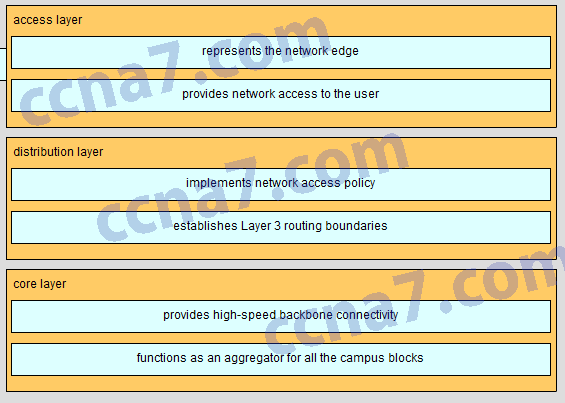
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam A002
- Question
-
Match the forwarding characteristic to its type. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
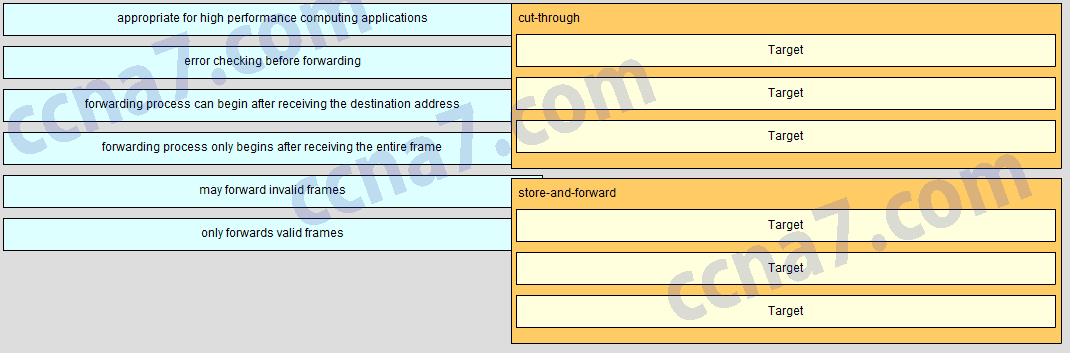
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam Q003
- Answer

CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 4 Exam A003
- Question
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.03 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Chapter 4 Exam | Chapter 4 Exam | Chapter 4 Exam | Online Test |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 5 Exam | Chapter 5 Exam | Chapter 5 Exam | Online Test |
| Lab Activities | |||
| No Lab Activities | |||