Last Updated on January 28, 2021 by Admin
ITN Chapter 6 Quiz Answers Cisco 2019 100%
This quiz covers the content in CCNA R&S Introduction to Networks Chapter 6. It is designed to provide an additional opportunity to practice the skills and knowledge presented in the chapter and to prepare for the Chapter Exam.
-
What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
- placing data on the network medium
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
Explanation: The network layer is primarily concerned with passing data from a source to a destination on another network. IP addresses supply unique identifiers for the source and destination. The network layer provides connectionless, best-effort delivery. Devices rely on higher layers to supply services to processes.
-
How does the network layer use the MTU value?
- The network layer depends on the higher level layers to determine the MTU.
- The network layer depends on the data link layer to set the MTU, and adjusts the speed of transmission to accommodate it.
- The MTU is passed to the network layer by the data link layer.
- To increase speed of delivery, the network layer ignores the MTU.
Explanation: The data link layer indicates to the network layer the MTU for the medium that is being used. The network layer uses that information to determine how large the packet can be when it is forwarded. When packets are received on one medium and forwarded on a medium with a smaller MTU, the network layer device can fragment the packet to accommodate the smaller size.
-
If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the metric is used to determine which route is used in the routing table.
- Noted: There are 2 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: metric or Metric. But in our system, you can fill in only metric.
Explanation: If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the metric is used to decide which route appears in the routing table.
- Noted: There are 2 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: metric or Metric. But in our system, you can fill in only metric.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
A packet leaving PC-1 has to traverse 3 hops to reach PC-4.
- Noted: There are 4 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: 3, three, Three, or THREE. But in our system, you can fill in only 3.
Explanation: A hop is an intermediary Layer 3 device that a packet has to traverse to reach its destination. In this case, the number of hops a packet has to traverse from PC-1 to PC-4 is three, as there are three routers from source to destination.
- Noted: There are 4 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: 3, three, Three, or THREE. But in our system, you can fill in only 3.
-
Here is a link to the PT Activity.
Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which interfaces in each router are active and operational?- R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/1 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/0 and S0/0/1 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/0 - R1: G0/0 and S0/0/1
R2: G0/1 and S0/0/1Explanation: The command to use for this activity is show ip interface brief in each router. The active and operational interfaces are represented by the value “up” in the “Status” and “Protocol” columns. The interfaces in R1 with these characteristics are G0/0 and S0/0/0. In R2 they are G0/1 and S0/0/0.
- R1: G0/0 and S0/0/0
-
Within a production network, what is the purpose of configuring a switch with a default gateway address?
- Hosts that are connected to the switch can use the switch default gateway address to forward packets to a remote destination.
- A switch must have a default gateway to be accessible by Telnet and SSH.
- The default gateway address is used to forward packets originating from the switch to remote networks.
- It provides a next-hop address for all traffic that flows through the switch.
Explanation: A default gateway address allows a switch to forward packets that originate on the switch to remote networks. A default gateway address on a switch does not provide Layer 3 routing for PCs that are connected on that switch. A switch can still be accessible from Telnet as long as the source of the Telnet connection is on the local network.
-
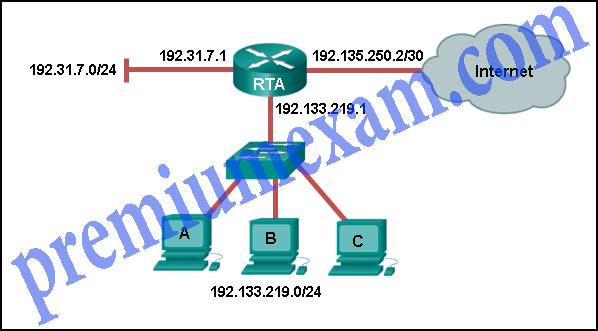
Refer to the exhibit. Using the network in the exhibit, what would be the default gateway address for host A in the 192.133.219.0 network?
- 192.135.250.1
- 192.31.7.1
- 192.133.219.0
- 192.133.219.1
-
Fill in the blank.
The acronym PAT is used to define the process that allows multiple devices to share a single routable IP address.
- Noted: There are 6 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: PAT, Pat, pat, NAT, Nat, or nat. But in our system, you can fill in only PAT.
Explanation: NAT or Network Address Translation is the process of modifying the IP packet header information on packets going outside the corporate network. Corporate networks typically use private addresses on the inside LAN and need a public address to be able to communicate through the WAN.
- Noted: There are 6 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: PAT, Pat, pat, NAT, Nat, or nat. But in our system, you can fill in only PAT.
-
Which IPv4 address can a host use to ping the loopback interface?
- 126.0.0.1
- 127.0.0.0
- 126.0.0.0
- 127.0.0.1
Explanation: A host can ping the loopback interface by sending a packet to a special IPv4 address within the network 127.0.0.0/8.
-
Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Differentiated Services
- Fragment Offset
- Header Length
- Time-to-Live
Explanation: When a router receives a packet, the router will decrement the Time-to-Live (TTL) field by one. When the field reaches zero, the receiving router will discard the packet and will send an ICMP Time Exceeded message to the sender.
-
Which portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host portion
- broadcast address
- network portion
- gateway address
-
During the boot process, where will the router bootstrap program look for the IOS image by default?
- flash
- NVRAM
- RAM
- ROM
Explanation: The IOS image is typically stored in flash memory. If the image is not in flash memory when the router boots, the router bootstrap program can look for it on a TFTP server.
-
When transporting data from real-time applications, such as streaming audio and video, which field in the IPv6 header can be used to inform the routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packets in the same conversation?
- Next Header
- Flow Label
- Traffic Class
- Differentiated Services
Explanation: The Flow Label in IPv6 header is a 20-bit field that provides a special service for real-time applications. This field can be used to inform routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packet flow so that packets will not be reordered.
-
A router may have to fragment a packet when forwarding it from one medium to another medium that has a smaller maximum transmission unit .
- Noted: There are 4 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: maximum transmission unit, Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU, or mtu. But in our system, you can fill in only PAT.
-
Which key combination allows a user to abort setup mode?
- Ctrl-C
- Ctrl-R
- Ctrl-Z
- Ctrl-Shift-6
Explanation: The setup mode can be interrupted at any time using the Ctrl-C key combination.