Last Updated on October 21, 2019 by Admin
Implementing Network Security ( Version 2.0) – CCNAS Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2019 Full 100%
-
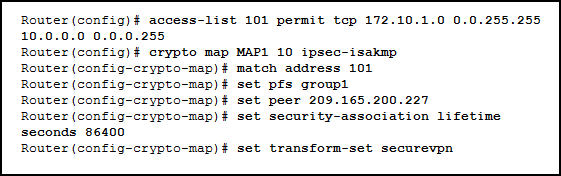
Refer to the exhibit. How will traffic that does not match that defined by access list 101 be treated by the router?
- It will be sent encrypted.
- It will be discarded.
- It will be sent unencrypted.
- It will be blocked.
Explanation: The access list 101 is part of the crypto map configuration on the router. The purpose of the access list is to identify interesting traffic that should be sent encrypted over a VPN. Traffic that does not match the access-list is not interesting and is not sent encrypted but rather sent unencrypted in plain text.
-
What three protocols must be permitted through the company firewall for establishment of IPsec site-to-site VPNs? (Choose three.)
- ESP
- NTP
- HTTPS
- AH
- ISAKMP
- SSH
Explanation: ESP, AH, and ISAKMP must all be permitted through the perimeter routers and firewalls in order for IPsec site-to-site VPNs to be established. NTP and HTTPS are application protocols and are not required for IPsec.
-
Which statement describes the effect of key length in deterring an attacker from hacking through an encryption key?
- The length of a key will not vary between encryption algorithms.
- The length of a key does not affect the degree of security.
- The shorter the key, the harder it is to break.
- The longer the key, the more key possibilities exist.
Explanation: While preventing brute-force attacks and other forced decryption concerns, the longer the key length, the harder it is to break. A 64-bit key can take one year to break with a sophisticated computer, while a 128-bit key may take 1019 years to decrypt. Different encryption algorithms will provide varying key lengths for implementation.
-
What is the purpose of configuring multiple crypto ACLs when building a VPN connection between remote sites?
- By applying the ACL on a public interface, multiple crypto ACLs can be built to prevent public users from connecting to the VPN-enabled router.
- Multiple crypto ACLs can be configured to deny specific network traffic from crossing a VPN.
- When multiple combinations of IPsec protection are being chosen, multiple crypto ACLs can define different traffic types.
- Multiple crypto ACLs can define multiple remote peers for connecting with a VPN-enabled router across the Internet or network.
Explanation: A crypto ACL can define “interesting traffic” that is used to build a VPN, and forward that “interesting traffic” across the VPN to another VPN-enabled router. Multiple crypto ACLs are used to define multiple different types of traffic and utilize different IPsec protection corresponding to the different types of traffic.
-
Consider the following configuration on a Cisco ASA:
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-DES-SHA esp-des esp-sha-hmac
What is the purpose of this command?
- to define only the allowed encryption algorithms
- to define the ISAKMP parameters that are used to establish the tunnel
- to define what traffic is allowed through and protected by the tunnel
- to define the encryption and integrity algorithms that are used to build the IPsec tunnel
Explanation: The transform set is negotiated during Phase 2 of the IPsec VPN connection process. The purpose of the transform set is to define what encryption and authentication schemes can be used. The device doing the VPN initiation offers the acceptable transform sets in order of preference, in this case, ESP authentication using DES for encryption or ESP authentication using SHA-HMAC authentication and integrity for the data payload. Remember that ESP provides confidentiality with encryption and integrity with authentication. The ESP-DES-SHA is the name of the transform set. The parameters that follow (esp-des and esp-sha-hmac) are the specific types of encryption or authentication that is supported by the ASA for the VPN tunnel that uses this transform set.
-
Which transform set provides the best protection?
- crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-DES-SHA esp-des esp-sha-hmac
- crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
- crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-DES-SHA esp-aes-256 esp-sha-hmac
- crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-DES-SHA esp-aes esp-des esp-sha-hmac
Explanation: DES uses 56-bit keys. 3DES uses 56-bit keys, but encrypts three times. AES uses 128-bit keys. AES-256 uses 256-bit keys and is the strongest.
-
Which two protocols must be allowed for an IPsec VPN tunnel is operate properly? (Choose two.)
- 50
- 51
- 168
- 169
- 500
- 501
Explanation: ESP uses protocol 50. AH uses protocol 51. ISAKMP uses UDP port 500.
-
When is a security association (SA) created if an IPsec VPN tunnel is used to connect between two sites?
- only during Phase 1
- only during Phase 2
- during both Phase 1 and 2
- after the tunnel is created, but before traffic is sent
Explanation: As seen in the 8.4.1.1 Figure, an IPsec VPN connection creates two SAs: (1) at the completion of the IKE Phase 1 once the peers negotiate the IKE SA policy, and (2) at the end of IKE Phase 2 after the transform sets are negotiated.
-
Which two statements accurately describe characteristics of IPsec? (Choose two.)
- IPsec works at the application layer and protects all application data.
- IPsec works at the transport layer and protects data at the network layer.
- IPsec works at the network layer and operates over all Layer 2 protocols.
- IPsec is a framework of proprietary standards that depend on Cisco specific algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of standards developed by Cisco that relies on OSI algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of open standards that relies on existing algorithms.
Explanation: IPsec can secure a path between two network devices. IPsec can provide the following security functions:
- Confidentiality – IPsec ensures confidentiality by using encryption.
- Integrity – IPsec ensures that data arrives unchanged at the destination using a hash algorithm, such as MD5 or SHA.
- Authentication – IPsec uses Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to authenticate users and devices that can carry out communication independently. IKE uses several types of authentication, including username and password, one-time password, biometrics, pre-shared keys (PSKs), and digital certificates.
- Secure key exchange – IPsec uses the Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithm to provide a public key exchange method for two peers to establish a shared secret key.
-
Which action do IPsec peers take during the IKE Phase 2 exchange?
- exchange of DH keys
- negotiation of IPsec policy
- verification of peer identity
- negotiation of IKE policy sets
Explanation: The IKE protocol executes in two phases. During Phase 1 the two sides negotiate IKE policy sets, authenticate each other, and set up a secure channel. During the second phase IKE negotiates security associations between the peers.
-
Which three statements describe the IPsec protocol framework? (Choose three.)
- AH uses IP protocol 51.
- AH provides encryption and integrity.
- AH provides integrity and authentication.
- ESP uses UDP protocol 50.
- ESP requires both authentication and encryption.
- ESP provides encryption, authentication, and integrity.
Explanation: The two primary protocols used with IPsec are AH and ESP. AH is protocol number 51 and provides data authentication and integrity for IP packets that are exchanged between the peers. ESP, which is protocol number 50, performs packet encryption.
-
Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of IPsec?
- IPsec works at the application layer and protects all application data.
- IPsec works at the transport layer and protects data at the network layer.
- IPsec is a framework of open standards that relies on existing algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of proprietary standards that depend on Cisco specific algorithms.
- IPsec is a framework of standards developed by Cisco that relies on OSI algorithms.
Explanation: IPsec can secure a path between two network devices. IPsec can provide the following security functions:
- Confidentiality – IPsec ensures confidentiality by using encryption.
- Integrity – IPsec ensures that data arrives unchanged at the destination using a hash algorithm, such as MD5 or SHA.
- Authentication – IPsec uses Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to authenticate users and devices that can carry out communication independently. IKE uses several types of authentication, including username and password, one-time password, biometrics, pre-shared keys (PSKs), and digital certificates.
- Secure key exchange– IPsec uses the Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithm to provide a public key exchange method for two peers to establish a shared secret key.
-
Which two IPsec protocols are used to provide data integrity?
- MD5
- SHA
- AES
- DH
- RSA
Explanation: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two popular algorithms used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. AES is an encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm used for key exchange. RSA is an algorithm used for authentication.
-
What is the function of the Diffie-Hellman algorithm within the IPsec framework?
- allows peers to exchange shared keys
- provides strong data encryption
- guarantees message integrity
- provides authentication
Explanation: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm used for key exchange. DH is a public key exchange method that allows two IPsec peers to establish a shared secret key over an insecure channel.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What HMAC algorithm is being used to provide data integrity?
- SHA
- MD5
- DH
- AES
Explanation: Two popular algorithms that are used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. The command Router1(config-isakmp)# hash sha indicates that SHA is being used. AES is an encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm that is used for key exchange. RSA is an algorithm used for authentication.
-
What is needed to define interesting traffic in the creation of an IPsec tunnel?
- access list
- security associations
- transform set
- hashing algorithm
Explanation: In order to bring up an IPsec tunnel, an access list must be configured with a permit statement that will identify interesting traffic. Once interesting traffic is detected by matching the access list, the tunnel security associations can be negotiated.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What algorithm will be used for providing confidentiality?
- AES
- Diffie-Hellman
- RSA
- DES
Explanation: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two popular algorithms that are used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity) are MD5 and SHA. AES is an encryption protocol and provides data confidentiality. DH (Diffie-Hellman) is an algorithm that is used for key exchange. RSA is an algorithm used for authentication.
-
Which technique is necessary to ensure a private transfer of data using a VPN?
- authorization
- encryption
- scalability
- virtualization
Explanation: Confidential and secure transfers of data with VPNs require data encryption.
-
Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Explanation: A VPN is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections routed through a public network between two network devices.
-
Which protocol provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality services and is a type of VPN?
- AES
- ESP
- IPsec
- MD5
Explanation: IPsec services allow for authentication, integrity, access control, and confidentiality. With IPsec, the information exchanged between remote sites can be encrypted and verified. Both remote-access and site-to-site VPNs can be deployed using IPsec.
-
What is the purpose of NAT-T?
- upgrades NAT for IPv4
- allows NAT to be used for IPv6 addresses
- enables NAT for PC-based VPN clients
- permits VPN to work when NAT is being used on one or both ends of the VPN
Explanation: Establishing a VPN between two sites has been a challenge when NAT is involved at either end of the tunnel. The enhanced version of original IKE, IKE version 2, now supports NAT-T. NAT-T has the ability to encapsulate ESP packets inside UDP so that the VPN tunnel can be established through a device that has NAT enabled.
-
Which term describes a situation where VPN traffic that is is received by an interface is routed back out that same interface?
- split tunneling
- hairpinning
- MPLS
- GRE
Explanation: Hairpinning allows VPN traffic that is received on a single interface to be routed back out that same interface. Split tunneling allows traffic that originates from a remote-access client to be split according to traffic that must cross a VPN and traffic destined for the public Internet. MPLS and GRE are two types of Layer 3 VPNs.
-
What is an important characteristic of remote-access VPNs?
- Internal hosts have no knowledge of the VPN.
- The VPN configuration is identical between the remote devices.
- Information required to establish the VPN must remain static.
- The VPN connection is initiated by the remote user.
Explanation: With remote-access VPNs, the remote user does not necessarily have the VPN connection set up at all times. The remote user PC is responsible for initiating the VPN. Information required to establish the VPN connection changes dynamically depending on the location of the user when attempting to connect.
-
Which type of site-to-site VPN uses trusted group members to eliminate point-to-point IPsec tunnels between the members of a group?
- DMVPN
- GETVPN
- GRE
- MPLS
Explanation: Group Encrypted Transport VPN (GETVPN) uses a trusted group to eliminate point-to-point tunnels and their associated overlay routing. GETVPN is often described as “tunnel-less.” Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) enables auto-provisioning of site-to-site IPsec VPNs using a combination of three Cisco IOS features: NHRP, GRE, and IPsec VPNs. Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco that encapsulates multiprotocol traffic between remote Cisco routers, but does not encrypt data. An MPLS VPN consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network.
-
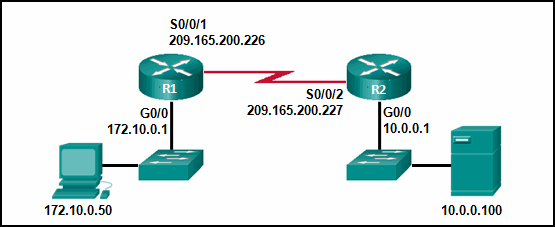
Refer to the exhibit. Which pair of crypto isakmp key commands would correctly configure PSK on the two routers?
- R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 hostname R1
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 hostname R2 - R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.227
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.226 - R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.226
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.227 - R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.226
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key secure address 209.165.200.227Explanation: The correct syntax of the crypto isakmp key command is as follows:
crypto isakmp key keystring address peer-address
or
crypto isakmp key keystring hostname peer-hostnameSo, the correct answer would be the following:
R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.227
R2(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 209.165.200.226
- R1(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 hostname R1