Last Updated on October 18, 2019 by Admin
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security specialist is checking if files in the directory contain ADS data. Which switch should be used to show that a file has ADS attached?

CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 05
- /a
- /d
- /r
- /s
Explanation: By using NTFS, Alternate Data Streams (ADSs) can be connected to a file as an attribute called $DATA. The command dir /r can be used to see if a file contains ADS data.
-
When attempting to improve system performance for Linux computers with a limited amount of memory, why is increasing the size of the swap file system not considered the best solution?
- A swap file system only supports the ex2 file system.
- A swap file system does not have a specific file system.
- A swap file system cannot be mounted on an MBR partition.
- A swap file system uses hard disk space to store inactive RAM content.
Explanation: The swap file system is used by Linux when it runs out of physical memory. When needed, the kernel moves inactive RAM content to the swap partition on the hard disk. Storing and retrieving content in the swap partition is much slower than RAM is, and therefore using the swap partition should not be considered the best solution to improving system performance.
-
How much overhead does the TCP header add to data from the application layer?
- 8 bytes
- 16 bytes
- 20 bytes
- 40 bytes
Explanation: The Layer 4 header in a TCP segment is the TCP header, which is 20 bytes in length. This adds 20 bytes of overhead to the data from the application layer in the composition of a TCP segment.
-
Which three fields are found in both the TCP and UDP headers? (Choose three.)
- options
- source port
- destination port
- checksum
- sequence number
- window
Explanation: The UPD header has four fields. Three of these fields are in common with the TCP header. These three fields are the source port, destination port, and checksum.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security specialist is using Wireshark to review a PCAP file generated by tcpdump. When the client initiated a file download request, which source socket pair was used?
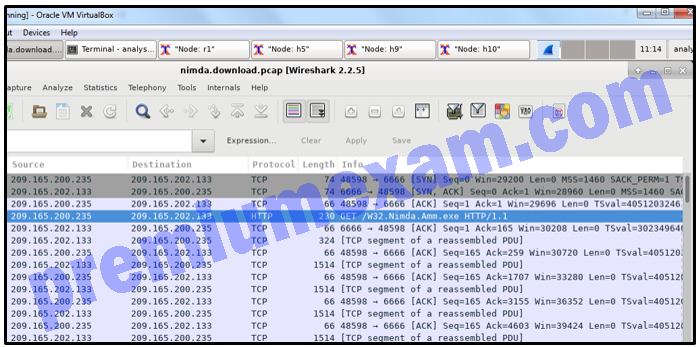
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 02
- 209.165.202.133:6666
- 209.165.200.235:6666
- 209.165.202.133:48598
- 209.165.200.235:48598
Explanation: The combination of the source IP address and source port number, or the destination IP address and destination port number, is known as a socket. A socket is shown as the IP address and associated port number with a colon in between the two (IP_address:port_number).
-
Which field in the IPv6 header points to optional network layer information that is carried in the IPv6 packet?
- flow label
- version
- traffic class
- next header
Explanation: Optional Layer 3 information about fragmentation, security, and mobility is carried inside of extension headers in an IPv6 packet. The next header field of the IPv6 header acts as a pointer to these optional extension headers if they are present.
-
Which three IPv4 header fields have no equivalent in an IPv6 header? (Choose three.)
- fragment offset
- flag
- identification
- version
- protocol
- TTL
Explanation: Unlike IPv4, IPv6 routers do not perform fragmentation. Therefore, all three fields supporting fragmentation in the IPv4 header are removed and have no equivalent in the IPv6 header. These three fields are fragment offset, flag, and identification. IPv6 does support host packet fragmentation through the use of extension headers, which are not part of the IPv6 header.
-
Which technology is used by Cisco Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) in defending and protecting against known and emerging threats?
- network admission control
- website filtering and blacklisting
- network profiling
- threat intelligence
Explanation: Cisco AMP uses threat intelligence along with known file signatures to identify and block policy-violating file types and exploitations.
-
When establishing a network profile for an organization, which element describes the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination?
- total throughput
- session duration
- routing protocol convergence
- bandwidth of the Internet connection
Explanation: A network profile should include some important elements, such as the following:
- Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
- Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
- Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
A network administrator is creating a network profile to generate a network baseline. What is included in the critical asset address space element?
- the list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
- the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
- the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
Explanation: A network profile should include some important elements, such as the following:
- Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
- Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
- Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
When a server profile for an organization is being established, which element describes the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server?
- listening ports
- service accounts
- software environment
- critical asset address space
Explanation: A server profile will often contain the following:
- Listening ports – the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
- User accounts – the parameters defining user access and behavior
- Service accounts – the definitions of the type of service that an application is allowed to run on a server
- Software environment – the tasks, processes, and applications that are permitted to run on the server
-
When establishing a server profile for an organization, which element describes the type of service that an application is allowed to run on the server?
- user account
- listening port
- service account
- software environment
Explanation: A server profile should contain some important elements including these:
- Listening ports – the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
- User accounts – the parameters defining user access and behavior
- Service accounts – the definitions of the type of service that an application is allowed to run on a server
- Software environment – the tasks, processes, and applications that are permitted to run on the server
-
What are the three impact metrics contained in the CVSS 3.0 Base Metric Group? (Choose three.)
- attack vector
- availability
- confidentiality
- exploit
- integrity
- remediation level
Explanation: The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a vendor-neutral, industry standard, open framework for weighing the risks of a vulnerability using a variety of metrics. CVSS uses three groups of metrics to assess vulnerability, the Base Metric Group, Temporal Metric Group, and Environmental Metric Group. The Base Metric Group has two classes of metrics (exploitability and impact). The impact metrics are rooted in the following areas: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
-
Which metric in the CVSS Base Metric Group is used with an attack vector?
- the proximity of the threat actor to the vulnerability
- the determination whether the initial authority changes to a second authority during the exploit
- the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful
- the number of components, software, hardware, or networks, that are beyond the control of the attacker and that must
- be present in order for a vulnerability to be successfully exploited
Explanation: The attack vector is one of several metrics defined in the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics. The attack vector is how close the threat actor is to the vulnerable component. The farther away the threat actor is to the component, the higher the severity because threat actors close to the network are easier to detect and mitigate.
-
A cybersecurity analyst is performing a CVSS assessment on an attack where a web link was sent to several employees. Once clicked, an internal attack was launched. Which CVSS Base Metric Group Exploitability metric is used to document that the user had to click on the link in order for the attack to occur?
- availability requirement
- integrity requirement
- scope
- user interaction
Explanation: The CVSS Base Metric Group has the following metrics: attack vector, attack complexity, privileges required, user interaction, and scope. The user interaction metric expresses the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful.
-
Which statement describes the card verification value (CVV) for a credit card?
- It is the bank account number.
- It is a PIN number for the card.
- It is a security feature of the card.
- It is the credit card account number.
Explanation: The card verification value (CVV), or card verification code (CVC), or card security code (CSC) is a security feature of a credit card, usually 3 or 4 digits printed on the back of the card.
-
After a security monitoring tool identifies a malware attachment entering the network, what is the benefit of performing a retrospective analysis?
- A retrospective analysis can help in tracking the behavior of the malware from the identification point forward.
- It can identify how the malware originally entered the network.
- It can determine which network host was first affected.
- It can calculate the probability of a future incident.
Explanation: General security monitoring can identify when a malware attachment enters a network and which host is first infected. Retrospective analysis takes the next step and is the tracking of the behavior of the malware from that point forward.
-
What are two of the 5-tuples? (Choose two.)
- ACL
- source port
- IPS
- protocol
- IDS
Explanation: The components of a 5-tuple include a source IP address and port number, destination IP address and port number, and the protocol in use.
-
What are security event logs commonly based on when sourced by traditional firewalls?
- 5-tuples
- static filtering
- signatures
- application analysis
Explanation: Traditional firewalls commonly provide security event logs based on the 5-tuples of source IP address and port number, destination IP address and port number, and the protocol in use.
-
When real-time reporting of security events from multiple sources is being received, which function in SIEM provides capturing and processing of data in a common format?
- log collection
- aggregation
- normalization
- compliance
Explanation: SIEM combines SEM and SIM tools to provide some useful functions, one of which is data normalization. Data normalization is the process of mapping log messages from different systems into a common data model in order to analyze related security events, even if they are initially logged in different source formats.
-
What is a goal of deploying an in-line security device that can analyze data as a normalized stream?
- detect and block intrusions
- reduce the amount of event data
- satisfy compliance requirements
- decrease network latency and jitter
Explanation: An IPS is an in-line security device that can analyze data as a normalized stream to reduce or eliminate the possibility of security evasions.
-
What are two sources of data in the operation of a security information and event management (SIEM) system? (Choose two.)
- incident management systems
- antimalware devices
- dashboards and reports
- automation and alerts
- firewalls
Explanation: Security information and event management (SIEM) systems receive data from IPS devices, firewalls, NetFlow devices, servers, endpoints, and syslog infrastructure devices.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which techology generated the event log?

CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 06
- web proxy
- NetFlow
- Wireshark
- syslog
Explanation: The output shown is from a web proxy.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is examining a NetFlow record. Why would the record indicate that both TRNS SOURCE PORT and TRNS DESTINATION PORT are 0?
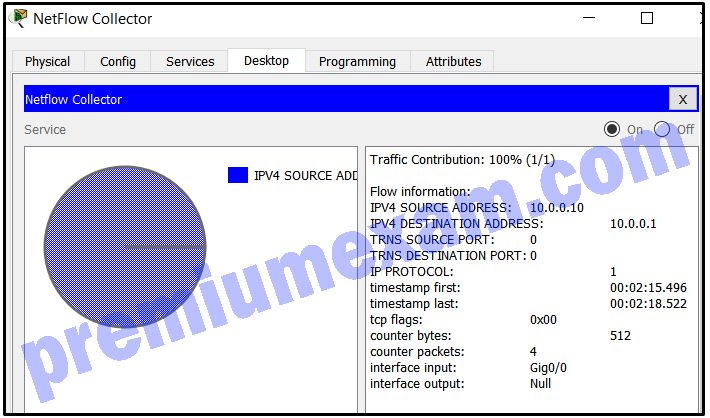
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 04
- The Gig0/0 interface has not transmitted any packets.
- The flow does not include transport layer protocols.
- The flow contains four packets and they use varying port numbers.
- The source host uses a different transport layer protocol from the one used by the destination host.
Explanation: The data flow recorded is ICMP traffic, indicated by the number 1 for IP PROTOCOL. Because ICMP is a Layer 3 protocol and has no need for a Layer 4 protocol such as TCP or UDP, the port numbers show a 0 within the NetFlow output.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is examining a NetFlow record. Which protocol is in use in the flow shown?
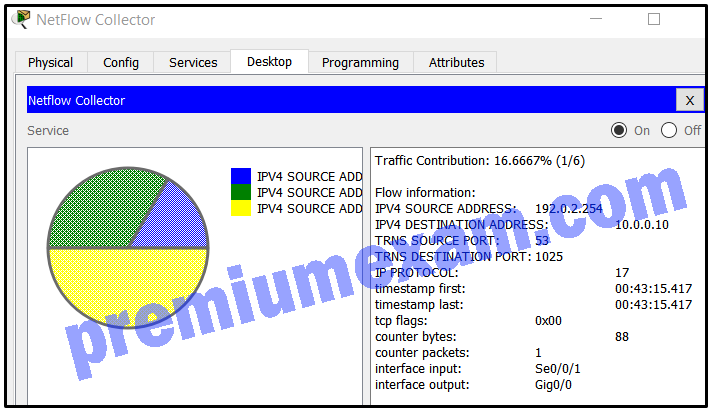
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 03
- TCP
- UDP
- ICMP
- HTTP
Explanation: The data flow shown is captured UDP traffic of a DNS response, indicated by the number 17 in the IP PROTOCOL output.
-
At the request of investors, a company is proceeding with cyber attribution with a particular attack that was conducted from an external source. Which security term is used to describe the person or device responsible for the attack?
- fragmenter
- skeleton
- threat actor
- tunneler
Explanation: Some people may use the common word of “hacker” to describe a threat actor. A threat actor is an entity that is involved with an incident that impacts or has the potential to impact an organization in such a way that it is considered a security risk or threat.
-
What classification is used for an alert that correctly identifies that an exploit has occurred?
- true positive
- false positive
- true negative
- false negative
Explanation: A true positive occurs when an IDS and IPS signature is correctly fired and an alarm is generated when offending traffic is detected.
-
Which type of analysis relies on predefined conditions and can analyze applications that only use well-known fixed ports?
- probabilistic
- deterministic
- statistical
- log
Explanation: Deterministic analysis uses predefined conditions to analyze applications that conform to specification standards, such as performing a port-based analysis.
-
Which type of analysis relies on different methods to establish the likelihood that a security event has happened or will happen?
- deterministic
- log
- statistical
- probabilistic
Explanation: Probabilistic methods use powerful tools to create a probabilistic answer as a result of analyzing applications.
-
What is the benefit of converting log file data into a common schema?
- creates a data model based on fields of data from a source
- allows easy processing and analysis of datasets
- creates a set of regex-based field extractions
- allows the implementation of partial normalization and inspection
Explanation: When data is converted into a universal format, it can be effectively structured for performing fast queries and event analysis.
-
What will match the regular expression ^83?
- any string that begins with 83
- any string that ends with 83
- any string that includes 83
- any string with values greater than 83
Explanation: The expression ^83 indicates any string that begins with 83 will be matched.
-
Using Tcpdump and Wireshark, a security analyst extracts a downloaded file from a pcap file. The analyst suspects that the file is a virus and wants to know the file type for further examination. Which Linux command can be used to determine the file type?
- tail
- file
- ls -l
- nano
Explanation: The Linux file command can be used to determine a file type, such as whether it is executable, ASCII text, or zip.
-
Which type of evidence cannot prove an IT security fact on its own?
- best
- corroborative
- hearsay
- indirect
Explanation: Indirect evidence cannot prove a fact on its own, but direct evidence can. Corroborative evidence is supporting information. Best evidence is most reliable because it is something concrete such as a signed contract.
-
A cybersecurity analyst has been called to a crime scene that contains several technology items including a computer. Which technique will be used so that the information found on the computer can be used in court?
- log collection
- rootkit
- Tor
- unaltered disk image
Explanation: A normal file copy does not recover all data on a storage device so an unaltered disk image is commonly made. An unaltered disk image preserves the original evidence, thus preventing inadvertent alteration during the discovery phase. It also allows recreation of the original evidence.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst issues the cat command to review the content of the file confidential2. Which encoding method was used to encode the file?

CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECOPS (210-255) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 01
- Hex
- ASCII
- Base64
- 8-bit binary
Explanation: Hex encodes binary data in hexidecimal string format. Base64 encodes binary data in an ASCII string format. In this case, the characters are 0-9 and a-f, typical hexidecimal numbers.
-
According to the Cyber Kill Chain model, after a weapon is delivered to a targeted system, what is the next step that a threat actor would take?
- installation
- exploitation
- weaponization
- action on objectives
Explanation: The Cyber Kill Chain specifies seven steps (or phases) and sequences that a threat actor must complete to accomplish an attack:
- Reconnaissance – The threat actor performs research, gathers intelligence, and selects targets.
- Weaponization – The threat actor uses the information from the reconnaissance phase to develop a weapon against specific targeted systems.
- Delivery – The weapon is transmitted to the target using a delivery vector.
- Exploitation – The threat actor uses the weapon delivered to break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
- Installation – The threat actor establishes a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target.
- Command and Control (CnC) – The threat actor establishes command and control (CnC) with the target system.
- Action on Objectives – The threat actor is able to take action on the target system, thus achieving the original objective.
-
What will a threat actor do to create a back door on a compromised target according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
- Add services and autorun keys.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Open a two-way communications channel to the CnC infrastructure.
Explanation: Once a target system is compromised, the threat actor will establish a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target. Adding services and autorun keys is a way to create a point of persistent access.
-
Which three things will a threat actor do to prepare a DDoS attack against a target system on the Internet? (Choose three.)
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
- Install attack software on zombies.
- Install a black door on the target system.
- Compromise many hosts on the Internet.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Establish two-way communications channels to the CnC infrastructure with zombies.
Explanation: To prepare for launching a DDoS attack, a threat actor will compromise many hosts on the Internet, called zombies. The threat actor will then install attack software on zombies and establish a two-way communications channel to CnC infrastructure with zombies. The threat actor will issue the command to zombies through the CnC to launch a DDoS attack against a target system.
-
In which top-level element of the VERIS schema does VERIS use the A4 threat model to describe an incident?
- incident tracking
- incident description
- impact assessment
- discovery and response
Explanation: In the top-level element incident description of the VERIS schema, VERIS uses the A4 threat model that was developed by the RISK team at Verizon to describe an incident completely.
-
What are three of the four interactive landscapes that VERIS schema use to define risk?
- threat
- attack
- impact
- control
- evidence
- response
Explanation: In the VERIS schema, risk is defined as the intersection of four landscapes of threat, asset, impact, and control. Information from each landscape helps to understand the level of risk to the organization.
-
Which specification provides a common language for describing security incidents in a structured and repeatable way?
- VERIS schema
- Diamond model
- Cyber Kill Chain
- NIST Incident Response Life Cycle
Explanation: Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing (VERIS) was created to provide a common language for describing security incidents. VERIS addresses the problems of dealing with different security tools and the tendency of humans to refer to incidents and events inconsistently.
-
What is the VERIS Community Database (VCDB)?
- an open and free collection of publicly-reported security incidents posted in a variety of data formats
- a central location for the security community to learn from experience and help with decision making before, during, and after a security incident
- a collection of incident data collected and categorized by a selected group of cybersecurity professionals
- a collection of research of trend and potential security intrusions
Explanation: The VERIS Community Database (VCDB) is an open and free collection of publicly-reported security incidents in VERIS format. The VCDB is in a universal format that allows for manipulation and transformation.
-
Which type of computer security incident response team is responsible for determining trends to help predict and provide warning of future security incidents?
- vendor teams
- analysis centers
- coordination centers
- national CSIRT
Explanation: There are many different types of computer security incident response teams (CSIRTs) and related information security organizations. Analysis centers use data from many sources to determine security incident trends that can help predict future incidents and provide early warning.
-
What is the role of vendor teams as they relate to a computer security incident response team?
- They handle customer reports concerning security vulnerabilities.
- They coordinate incident handling across multiple teams.
- They provide incident handling to other organizations as a fee-based service.
- They use data from many sources to determine incident activity trends.
Explanation: There are many different types of computer security incident response teams (CSIRTs) and related information security organizations. Vendor CSIRT teams provide remediation for vulnerabilities in the software or hardware of an organization and often handle customer reports concerning security vulnerabilities.
-
Which two actions should be taken during the preparation phase of the incident response life cycle defined by NIST? (Choose two.)
- Fully analyze the incident.
- Create and train the CSIRT.
- Detect all the incidents that occurred.
- Acquire and deploy the tools that are needed to investigate incidents.
- Meet with all involved parties to discuss the incident that took place.
Explanation: According to the guideline defined in the NIST Incident Response Life Cycle, several actions should be taken during the preparation phase including (1) creating and training the CSIRT and (2) acquiring and deploying the tools needed by the team to investigate incidents.
-
During the detection and analysis phase of the NIST incident response process life cycle, which sign category is used to describe that an incident might occur in the future?
- attrition
- indicator
- precursor
- impersonation
Explanation: There are two categories for the signs of an incident:
- Precursor – a sign that an incident might occur in the future
- Indicator – a sign that an incident might already have occurred or is currently occurring
-
A company is applying the NIST.SP800-61 r2 incident handling process to security events. What are two examples of incidents that are in the category of precursor? (Choose two.)
- an IDS alert message being sent
- multiple failed logins from an unknown source
- log entries that show a response to a port scan
- a host that has been verified as infected with malware
- a newly-discovered vulnerability in Apache web servers
Explanation: As an incident category, the precursor is a sign that an incident might occur in the future. Examples of precursors are log entries that show a response to a port scan or a newly-discovered vulnerability in web servers using Apache.
-
Which two actions can help identify an attacking host during a security incident? (Choose two.)
- Determine the location of the recovery and storage of all evidence.
- Validate the IP address of the threat actor to determine if it is viable.
- Use an Internet search engine to gain additional information about the attack.
- Log the time and date that the evidence was collected and the incident remediated.
- Develop identifying criteria for all evidence such as serial number, hostname, and IP address.
Explanation: The following actions can help identify an attacking host during a security incident:Use incident databases to research related activity.
Validate the IP address of the threat actor to determine if it is a viable one.
Use an Internet search engine to gain additional information about the attack.
Monitor the communication channels that some threat actors use, such as IRC.
-
What is defined in the policy element of the NIST incident response plan?
- how to handle incidents based on the mission and functions of an organization
- how the incident response team of an organization will communicate with organization stakeholders
- the metrics used for measuring incident response capability in an organization
- a roadmap for updating the incident response capability
Explanation: The policy element of the NIST incident response plan details how incidents should be handled based on the mission and function of the organization.
-
What is specified in the plan element of the NIST incident response plan?
- metrics for measuring the incident response capability and effectiveness
- organizational structure and the definition of roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority
- priority and severity ratings of incidents
- incident handling based on the mission of the organization
Explanation: NIST recommends creating policies, plans, and procedures for establishing and maintaining a CSIRC. One component of the plan element is to develop metrics for measuring the incident response capability and its effectiveness.
-
Which NIST-defined incident response stakeholder is responsible for coordinating incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident?
- IT support
- the legal department
- management
- human resources
Explanation: The management team creates the policies, designs the budget, and is in charge of staffing all departments. Management is also responsible for coordinating the incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident.
-
What is the responsibility of the IT support group when handing an incident as defined by NIST?
- reviews the incident policies, plans, and procedures for local or federal guideline violations
- performs actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence
- coordinates the incident response with other stakeholders and minimizes the damage of an incident
- performs disciplinary measures if an incident is caused by an employee
Explanation: IT support best understands the technology used in the organization and can perform the correct actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence.
-
What is the responsibility of the human resources department when handing a security incident as defined by NIST?
- Coordinate the incident response with other stakeholders and minimize the damage of an incident.
- Review the incident policies, plans, and procedures for local or federal guideline violations.
- Perform actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence.
- Perform disciplinary actions if an incident is caused by an employee.
Explanation: The human resources department may be called upon to perform disciplinary measures if an incident is caused by an employee.
-
After containing an incident that infected user workstations with malware, what are three effective remediation procedures that an organization can take for eradication? (Choose three.)
- Use clean and recent backups to recover hosts.
- Change assigned names and passwords for all devices.
- Rebuild DHCP servers using clean installation media.
- Rebuild hosts with installation media if no backups are available.
- Update and patch the operating system and installed software of all hosts.
- Disconnect or disable all wired and wireless network adapters until the remediation is complete.
Explanation: To recover infected user workstations, use clean and recent backups or rebuild the PCs with installation media if no backups are available or they have been compromised. Also, fully update and patch the operating system and installed software of all hosts. All users are encouraged to change their passwords for the workstation or workstations they use. Rebuilding DHCP servers is needed only if they are affected by the incident.Also not all devices need to change the name and password configuration setting unless they are affected by the incident.
-
In which step of the NIST incident response process does the CSIRT perform an analysis to determine which networks, systems, or applications are affected; who or what originated the incident; and how the incident is occurring?
- scoping
- detection
- incident notification
- attacker identification
Explanation: In the detection and analysis phase of the NIST incident response process life cycle, the CSIRT should immediately perform an initial analysis to determine the scope of the incident, such as which networks, systems, or applications are affected; who or what originated the incident; and how the incident is occurring.