Last Updated on October 18, 2019 by Admin
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – CyberOps Chapter 13 Exam Answers 2019
-
Which top-level element of the VERIS schema would allow a company to log who the actors were, what actions affected the asset, which assets were affected, and how the asset was affected?
- discovery and response
- incident description
- incident tracking
- victim demographics
Explanation: The incident description top-level element uses the 4A model (actors, actions, assets, and attributes). Each section has subsections to further document the incident.
-
A threat actor has identified the potential vulnerability of the web server of an organization and is building an attack. What will the threat actor possibly do to build an attack weapon?
- Create a point of persistence by adding services.
- Install a webshell on the web server for persistent access.
- Collect credentials of the web server developers and administrators.
- Obtain an automated tool in order to deliver the malware payload through the vulnerability.
Explanation: One tactic of weaponization used by a threat actor after the vulnerability is identified is to obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload through the vulnerability.
-
Which schema or model was created to anonymously share quality information about security events to the security community?
- CSIRT
- Cyber Kill Chain
- Diamond
- VERIS
Explanation: Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing (VERIS) is a set of metrics designed to create a way to describe security incidents in a structured or repeatable way. A Computer Security Incident response Team (CSIRT) is an internal organizational group that provides services and functions to secure assets. Cyber Kill Chain contains seven steps which help analysts understand the techniques, tools, and procedures of threat actors. The Diamond Model of intrusion has four parts that represent a security incident.
-
What is the role of vendor teams as they relate to CSIRT?
- Coordinate incident handling across multiple CSIRTs.
- Handle customer reports concerning security vulnerabilities.
- Provide incident handling to other organizations as a fee-based service.
- Use data from many sources to determine incident activity trends.
Explanation: There are many different types of CSIRTs and related information security organizations. Vendor CSIRT teams provide remediation for vulnerabilities in the software or hardware of an organization and often handle customer reports concerning security vulnerabilities.
-
What is the role of a Computer Emergency Response Team?
- Receive, review, and respond to security incidents in an organization.
- Provide national standards as a fee-based service.
- Provide security awareness, best practices, and security vulnerability information to a specific population.
- Coordinate security incident handling across multiple CSIRTs.
Explanation: A Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) provides security awareness, best practices, and security vulnerability information to populations. A CERT does not respond directly to security incidents.
-
What is the purpose of the policy element in a computer security incident response capability of an organization, as recommended by NIST?
- It details how incidents should be handled based on the organizational mission and functions.
- It defines how the incident response teams will communicate with the rest of the organization and with other organizations.
- It provides metrics for measuring the incident response capability and effectiveness.
- It provides a roadmap for maturing the incident response capability.
Explanation: NIST recommends creating policies, plans, and procedures for establishing and maintaining a CSIRC. A purpose of the policy element is to detail how incidents should be handled based on the mission and functions of an organization.
-
Which action should be included in a plan element that is part of a computer security incident response capability (CSIRC)?
- Detail how incidents should be handled based on the mission and functions of an organization.
- Prioritize severity ratings of security incidents.
- Create an organizational structure and definition of roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority.
- Develop metrics for measuring the incident response capability and its effectiveness.
Explanation: NIST recommends creating policies, plans, and procedures for establishing and maintaining a CSIRC. A purpose of the plan element is to develop metrics for measuring the incident response capability and its effectiveness.
-
What is defined in the SOP of a computer security incident response capability (CSIRC)?
- the procedures that are followed during an incident response
- the metrics for measuring incident response capabilities
- the details on how an incident is handled
- the roadmap for increasing incident response capabilities
Explanation: A CSIRC will include standard operating procedures (SOPs) that are followed during an incident response. Procedures include following technical processes, filling out forms, and following checklists.
-
According to information outlined by the Cyber Kill Chain, which two approaches can help identify reconnaissance threats? (Choose two.)
- Conduct full malware analysis.
- Build playbooks for detecting browser behavior.
- Analyze web log alerts and historical search data.
- Audit endpoints to forensically determine origin of exploit.
- Understand targeted servers, people, and data available to attack.
Explanation: Threat actors may use port scanning toward a web server of an organization and identify vulnerabilities on the server. They may visit the web server to collect information about the organization. The web server logging should be enabled and the logging data should be analyzed to identify possible reconnaissance threats. Building playbooks by filtering and combining related web activities by visitors can sometimes reveal the intentions of threat actors.
-
When dealing with security threats and using the Cyber Kill Chain model, which two approaches can an organization use to help block potential exploitations of a system? (Choose two.)
- Conduct full malware analysis.
- Analyze the infrastructure path used for delivery.
- Collect email and web logs for forensic reconstruction.
- Conduct employee awareness training and email testing.
- Audit endpoints to forensically determine origin of exploit.
Explanation: The most common exploit targets, once a weapon is delivered, are applications, operating system vulnerabilities, and user accounts. Among other measures, conducting employee awareness training and email testing and auditing endpoints to forensically determine the origin of an exploit can help block future exploitations of systems.
-
What is the goal of an attack in the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain?
- Break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
- Establish command and control (CnC) with the target system.
- Create a back door in the target system to allow for future access.
- Use the information from the reconnaissance phase to develop a weapon against the target.
Explanation: In the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain, the threat actor establishes a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target.
-
What is the objective the threat actor in establishing a two-way communication channel between the target system and a CnC infrastructure?
- to launch a buffer overflow attack
- to send user data stored on the target to the threat actor
- to steal network bandwidth from the network where the target is located
- to allow the threat actor to issue commands to the software that is installed on the target
Explanation: In the command and control phase of the Cyber Kill Chain, the threat actor establishes command and control (CnC) with the target system. With the two-way communication channel, the threat actor is able to issue commands to the malware software installed on the target.
-
Which term is used in the Diamond Model of intrusion to describe a tool that a threat actor uses toward a target system?
- adversary
- capability
- infrastructure
- weaponization
Explanation: The Diamond Model of intrusion contains four parts:
Adversary – the parties responsible for the intrusion
Capability – a tool or technique that the adversary uses to attack the victim
Infrastructure – the network path or paths that the adversaries use to establish and maintain command and control over their capabilities
Victim – the target of the attack
-
What is a benefit of using the VERIS community database?
- The database can be easily compressed.
- It can be used to discover the name of known threat actors.
- It can be used to discover how other organizations dealt with a particular type of security incident.
- Companies who pay to contribute and access the database are protected from security threats.
Explanation: The VERIS community database is free. It can be used as a tool for risk management, to document security incidents, to discover over incidents, and to compare how other organizations dealt with a particular type of security incident.
-
Which action is taken in the postincident phase of the NIST incident response life cycle?
- Conduct CSIRT response training.
- Document the handling of the incident.
- identify and validate incidents.
- Implement procedures to contain threats.
Explanation: It is in the post-incident phase of the NIST incident response life cycle phase that the CSIRT documents how incidents are handled. Recommended changes for future response are also made to avoid reoccurrences.
-
What information is gathered by the CSIRT when determining the scope of a security incident?
- the networks, systems, and applications affected by an incident
- the strategies and procedures used for incident containment
- the processes used to preserve evidence
- the amount of time and resources needed to handle an incident
Explanation: The scoping activity performed by the CSIRT after an incident determines which networks, systems, or applications are affected; who or what originated the incident; and how the incident is occurring.
-
After containment, what is the first step of eradicating an attack?
- Patch all vulnerabilities.
- Change all passwords.
- Identify all hosts that need remediation.
- Hold meetings on lessons learned.
Explanation: Once an attack is contained, the next step is to identify all hosts that will need remediation so that the effects of the attack can be eliminated.
-
To ensure that the chain of custody is maintained, what three items should be logged about evidence that is collected and analyzed after a security incident has occurred? (Choose three.)
- measures used to prevent an incident
- location of all evidence
- time and date the evidence was collected
- serial numbers and hostnames of devices used as evidence
- extent of the damage to resources and assets
- vulnerabilities that were exploited in an attack
Explanation: A chain of custody refers to the proper accounting of evidence collected about an incident that is used as part of an investigation. The chain of custody should include the location of all evidence, the identifying information of all evidence such as serial numbers and hostnames, identifying information about all persons handing the evidence, and the time and date that the evidence was collected.
-
Which meta-feature element in the Diamond Model describes information gained by the adversary?
- results
- direction
- resources
- methodology
Explanation: The meta-feature element results are used to delineate what the adversary gained from the intrusion event.
-
What is the main purpose of exploitations by a threat actor through the weapon delivered to a target during the Cyber Kill Chain exploitation phase?
- Launch a DoS attack.
- Establish a back door into the system.
- Break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
- Send a message back to a CnC controlled by the threat actor.
Explanation: After the weapon has been delivered, the threat actor uses it to break the vulnerability and gain control of the target. The threat actor will use an exploit that gains the effect desired, does it quietly, and avoids detections. Establishing a back door in the target system is the phase of installation.
-
A threat actor collects information from web servers of an organization and searches for employee contact information. The information collected is further used to search personal information on the Internet. To which attack phase do these activities belong according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
- exploitation
- weaponization
- reconnaissance
- action on objectives
Explanation: According to the Cyber Kill Chain model, in the reconnaissance phase the threat actor performs research, gathers intelligence, and selects targets.
-
When a security attack has occurred, which two approaches should security professionals take to mitigate a compromised system during the Actions on Objectives step as defined by the Cyber Kill Chain model? (Choose two.)
- Train web developers for securing code.
- Build detections for the behavior of known malware.
- Perform forensic analysis of endpoints for rapid triage.
- Collect malware files and metadata for future analysis.
- Detect data exfiltration, lateral movement, and unauthorized credential usage.
Explanation: When security professionals are alerted about the system compromises, forensic analysis of endpoints should be performed immediately for rapid triage. In addition, detection efforts for further attacking activities such as data exfiltration, lateral movement, and unauthorized credential usage should be enhanced to reduce damage to the minimum.
-
Match the security incident stakeholder with the role.
-
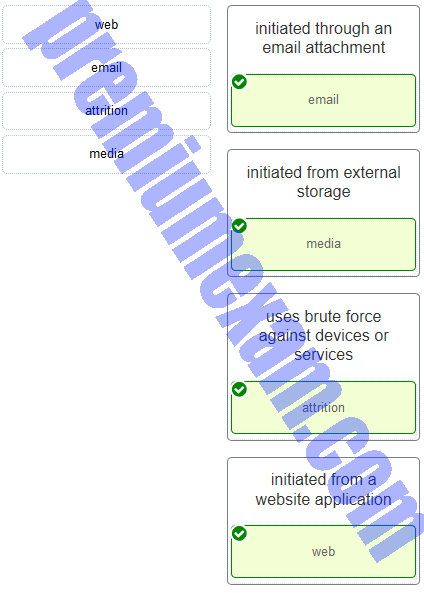
Match the attack vector with the description.
-
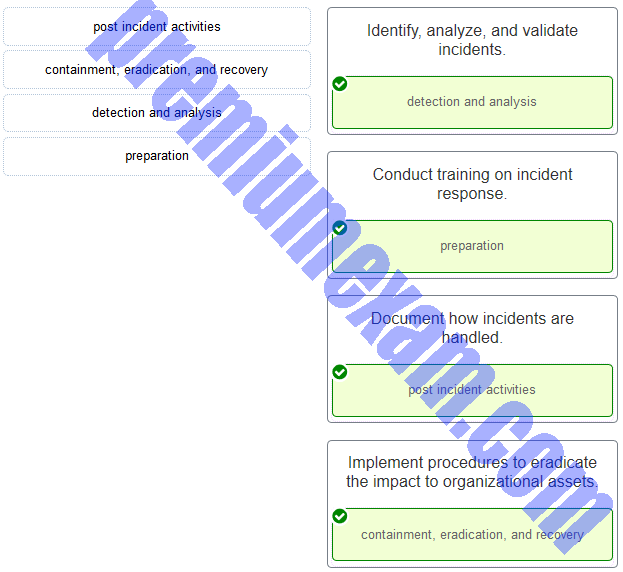
Match the NIST incident response life cycle phase with the description.
-
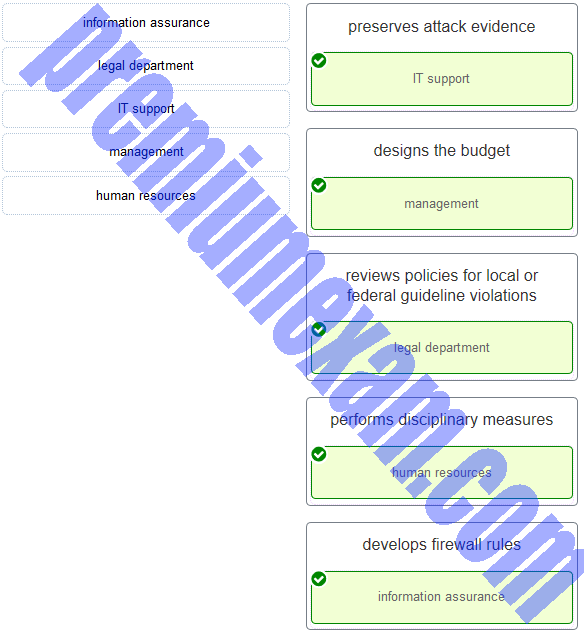
Match the NIST incident response stakeholder with the role.
-
A school has a web server mainly used for parents to view school events, access student performance indicators, and communicate with teachers. The network administrator suspects a security-related event has occurred and is reviewing what steps should be taken.
-
The threat actor has already placed malware on the server causing its performance to slow. The network administrator has found and removed the malware as well as patched the security hole where the threat actor gained access. The network administrator can find no other security issue. What stage of the Cyber Kill Chain did the threat actor achieve?
- actions on objectives
- command and control
- delivery
- exploitation
- installation
Explanation: During the installation step, the threat actor installed a server backdoor in order to install the malware (installation step), and an outside server command channel was created to manipulate the target (CnC step). The final step is used to access the server to achieve the objective of the attack.
The Cyber Kill Chain has seven steps:- reconnaissance
- weaponization
- delivery
- exploitation
- installation
- command and control (CnC)
- actions on objectives
-
If the web server runs Microsoft IIS, which Windows tool would the network administrator use to view the access logs?
- Event Viewer
- net command
- PowerShell
- Task Manager
Explanation: Information provided in the IIS access log includes the date, time, client IP address, username, port number, requested action, bytes sent, bytes received, and content of the cookie sent or received.
-
Reports of network slowness lead the network administrator to review server alerts. The administrator confirms that an alert was an actual security incident. Which type of security alert classification would this be?
- false negative
- false positive
- true negative
- true positive
Explanation: A positive alert of any type means that the system generated a system alert. A true positive indicates the incident occurred. A false positive is that no incident occurred (the system alerted, but there was no problem). A negative alert of any type means there was no alert generated. A true negative indicates that there wasn’t any incident (thus no alert). A false negative indicates that there was an incident, but an alert was not generated.
-
The network administrator believes that the threat actor used a commonly available tool to slow the server down. The administrator concludes that based on the source IP address identified in the alert, the threat actor was probably one of the students. What type of hacker would the student be classified as?
- black hat
- gray hat
- red hat
- white hat
Explanation: Three classifications of hackers are black hat, gray hat, and white hat. White hat hackers use their security skills for good, ethical, legal purposes. Gray hat hackers do not compromise the network for personal gain or to cause damage such as when users leave their computers logged into the corporate network and walk away. Black hat hackers penetrate computers or servers for malicious reasons, such as to slow down system performance.
-