Last Updated on October 21, 2019 by Admin
RSE CCNA 2 Chapter 3 Quiz Answers 2018 2019
-
A network administrator has examined the routing table of a router and noted that the entry for the destination network 172.16.4.0/24 begins with the letter D. What does this letter signify?
- The route to network 172.16.4.0/24 is directly connected.
- The route source was learned dynamically.
- That is the direct route for packets to that network.
- The route to this network is configured statically on the router.
Explanation: Routing table entries that begin with the letter D are learned dynamically using the EIGRP routing protocol. Static route entries on the routing table are identified with S. Directly connected route entries are denoted by the letter C.
-
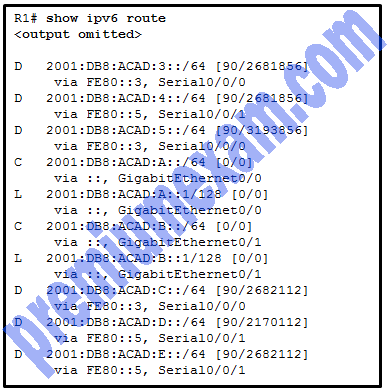
Refer to the exhibit. What is the metric to forward a data packet with the IPv6 destination address 2001:DB8:ACAD:E:240:BFF:FED4:9DD2?
- 90
- 128
- 2170112
- 2681856
- 2682112
- 3193856
Explanation: The IPv6 destination address 2001:DB8:ACAD:E:240:BFF:FED4:9DD2 belongs to the network of 2001:DB8:ACAD:E::/64. In the routing table, the route to forward the packet has Serial 0/0/1 as an exit interface and 2682112 as the cost.
-
Fill in the blank.
routing protocols are used to dynamically exchange routing information between routers.- Noted: In netacad system, you can use one of the following: “routing” or “dynamic routing“. But in our system, you can use only “routing“.
Explanation: Dynamic routing protocols are used on routers to exchange route information between routers to support network communication..
- Noted: In netacad system, you can use one of the following: “routing” or “dynamic routing“. But in our system, you can use only “routing“.
-
What are two functions of dynamic routing protocols? (Choose two.)
- to maintain routing tables
- to assure low router overhead
- to avoid exposing network information
- to discover the network
- to choose the path that is specified by the administrator
Explanation: Dynamic routing protocols exist to discover the network, maintain routing tables, and calculate the best path. Having low levels of routing overhead, using the path specified by the administrator, and avoiding the exposure of network information are functions of static routing.
-
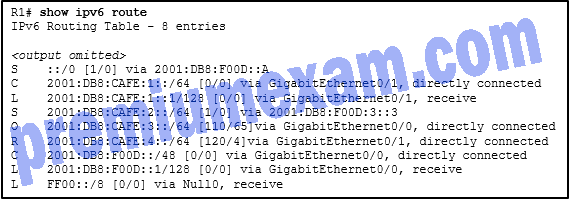
Refer to the exhibit. What is the administrative distance value of the route for router R1 to reach the destination IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::A?
- 1
- 4
- 110
- 120
Explanation: The RIP route with the source code R is used to forward data to the destination IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::A. This route has an AD value of 120.
-
A network administrator is examining a RIPv2 routing table and notices that several subnets are advertised in individual entries. What can an administrator do to enable a RIPv2 router to automatically group multiple directly attached subnetworks into a single network statement?
- Use the passive-interface command.
- Use the auto-summary command.
- Use the default-information originate command.
- Use the version 2 command.
Explanation: With the implementation of dynamic routing protocols, RIP summarizes networks at classful boundaries by default. To configure a router to automatically summarize networks, the auto-summary command would be used.
-
What type of route has a network address with a subnet mask that is less than the classful equivalent?
- a network route
- a default route
- a supernet route
- a child route
Explanation: A supernet route is a route that has a network address with a subnet mask that is less than the classful equivalent for the network. If the 192.168.1.0 network address was using a /16 (255.255.0.0) mask, this would be less than the classful equivalent for a 192.168.1.X network address. A summary address is an example of a supernet route.
-
What is the purpose of classifying Cisco IP routing table entries as ultimate route, level 1 route, level 1 parent route, and level 2 child routes?
- to enable the implementation of dynamic routing protocols
- to explain the operation of the routing table as a flat database
- to enable Cisco routers to implement both IPv4 and IPv6 routing
- to explain the operation of the hierarchical structure of the routing table
Explanation: The Cisco IP routing table is not a flat database. It has a hierarchical structure that is used to expedite the lookup process when locating routes and forwarding packets. The terms ultimate route, level 1 route, level 1 parent route, and level 2 child routes describe the operation and the hierarchical nature of the routing table contents.
-
Which route would be used to forward a packet with a source IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:F00D:1::1 and a destination IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::1?
- D 2001:DB8:CAFE::/48 [110/2] via FE80::201:64FF:FEAB:8501, GigabitEthernet0/1
- S 2001:DB8:CAFE::/48 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:F00D:3::3
- R 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64 [120/3] via FE80::201:84FF:FEAC:8501, GigabitEthernet0/0
- S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001:DB8:F00D::A
Explanation: Even though RIP has a higher administrative distance value (less trustworthy), the best match is the route in the routing table that has the most number of far left matching bits.
-
What occurs next in the router lookup process after a router identifies a destination IPv6 address and locates a matching level 1 network route?
- The level 2 child routes are examined.
- The level 1 supernet routes are examined.
- The router drops the packet.
- The router forwards the packet.
Explanation: In IPv6, all routes in the routing table are level 1 ultimate routes and contain a next-hop IPv6 address or exit interface or both.When a match is found, the traffic is forwarded.
-
Which two route source codes are automatically created within a routing table whenever a router interface is configured with an IP address and activated? (Choose two.)
- C
- O
- L
- R
- D
Explanation: Directly connected and local routes are automatically created whenever an interface is configured with an IP address and activated.
-
Match the steps that are taken by a router in the route look up process when it receives a packet, there is no match, and the packet is eventually dropped. (Not all options are used.)
- step 1 —> examining level 1 network routes for the best match
- step 2 —> examining child routes of the parent route for the best match
- step 3 —> searching level 1 supernet routes for the best match
- step 4 —> determining if a default route exists
- step 5 —> dropping the packet
-
Fill in the blank.
In the process of building and maintaining a larger network, you will find that dynamic routing is simpler to configure than static routing.- Noted: In netacad system, you can use one of the following: “dynamic“, “dynamic routing“, “dynamic protocol” or “dynamic protocols“. But in our system, you can use only “dynamic“.
Explanation: Dynamic routing is simpler to configure than static routing in larger networks. Static routing does not scale well as networks grow in .
- Noted: In netacad system, you can use one of the following: “dynamic“, “dynamic routing“, “dynamic protocol” or “dynamic protocols“. But in our system, you can use only “dynamic“.
-
Refer to the exhibit. All hosts and router interfaces are configured correctly. Pings to the server from both H1 and H2 and pings between H1 and H2 are not successful. What is causing this problem?
- RIPv2 does not support VLSM.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R1.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R2.
- RIPv2 is misconfigured on router R3.
- RIPv2 does not support discontiguous networks.
Explanation: RIP configuration on a router should contain network statements for connected networks only. Remote networks are learned from routing updates from other routers.
-
Match the routing table entry to the corresponding function. (Not all options are used.)
- administrative distance —> identifies the trustworthiness of a route source
- metric —> identifies the value assigned to reach a remote network
- route source —> identifies how the route was learned
- destination network —> identifies the address of a remote network