Last Updated on October 25, 2019 by Admin
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.
-
What are three primary benefits of using VLANs? (Choose three.)
- security
- a reduction in the number of trunk links
- cost reduction
- end user satisfaction
- improved IT staff efficiency
- no required configuration
Explanation: Security, cost reduction, and improved IT staff efficiency are all benefits of using VLANs, along with higher performance, broadcast storm mitigation, and simpler project and application management. End users are not usually aware of VLANs, and VLANs do require configuration. Because VLANs are assigned to access ports, they do not reduce the number of trunk links.
-
Which type of VLAN is used to designate which traffic is untagged when crossing a trunk port?
- data
- default
- native
- management
Explanation: A native VLAN is the VLAN that does not receive a VLAN tag in the IEEE 802.1Q frame header. Cisco best practices recommend the use of an unused VLAN (not a data VLAN, the default VLAN of VLAN 1, or the management VLAN) as the native VLAN whenever possible.
-
A network administrator is determining the best placement of VLAN trunk links. Which two types of point-to-point connections utilize VLAN trunking? (Choose two.)
- between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs
- between a switch and a client PC
- between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC
- between a switch and a network printer
- between two switches that share a common VLAN
Explanation: VLAN trunk links are used to allow all VLAN traffic to propagate between devices such as the link between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q-capable NIC. Switches can also utilize trunk links to routers, servers, and to other switches.
-
What must the network administrator do to remove Fast Ethernet port fa0/1 from VLAN 2 and assign it to VLAN 3?
- Enter the no vlan 2 and the vlan 3 commands in global configuration mode.
- Enter the switchport access vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode.
- Enter the switchport trunk native vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode.
- Enter the no shutdown command in interface configuration mode to return it to the default configuration and then configure the port for VLAN 3.
-
When a Cisco switch receives untagged frames on a 802.1Q trunk port, which VLAN ID is the traffic switched to by default?
- unused VLAN ID
- native VLAN ID
- data VLAN ID
- management VLAN ID
Explanation: A native VLAN is used to forward untagged frames that are received on a Cisco switch 802.1Q trunk port. Untagged frames that are received on a trunk port are not forwarded to any other VLAN except the native VLAN.
-
Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface, what will happen?
- Port Fa0/11 will be shutdown.
- An error message would be displayed.
- Port Fa0/11 will be returned to VLAN 1.
- VLAN 30 will be deleted.
Explanation: When the no switchport access vlan command is entered, the port is returned to the default VLAN 1. The port will remain active as a member of VLAN 1, and VLAN 30 will still be intact, even if no other ports are associated with it.
-
Which command is used to remove only VLAN 20 from a switch?
- delete vlan.dat
- delete flash:vlan.dat
- no vlan 20
- no switchport access vlan 20
Explanation: The command no vlan vlan-id is used to remove a particular VLAN from a switch. The delete vlan.dat and delete flash:vlan.dat commands will remove all VLANs after reloading the switch.
-
What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN 10 when the administrator deletes VLAN 10 from the switch?
- The port becomes inactive.
- The port goes back to the default VLAN.
- The port automatically associates itself with the native VLAN.
- The port creates the VLAN again.
Explanation: If the VLAN that is associated with a port is deleted, the port becomes inactive and cannot communicate with the network any more. To verify that a port is in an inactive state, use the show interfaces switchport command.
-
Which two characteristics match extended range VLANs? (Choose two.)
- CDP can be used to learn and store these VLANs.
- VLAN IDs exist between 1006 to 4094.
- They are saved in the running-config file by default.
- VLANs are initialized from flash memory.
- They are commonly used in small networks.
Explanation: Extended range VLANs are stored in the running-configuration file by default and must be saved after being configured. Extended VLANs use the VLAN IDs from 1006 to 4094.
-
A Cisco switch currently allows traffic tagged with VLANs 10 and 20 across trunk port Fa0/5. What is the effect of issuing a switchport trunk allowed vlan 30 command on Fa0/5?
- It allows VLANs 1 to 30 on Fa0/5.
- It allows VLANs 10, 20, and 30 on Fa0/5.
- It allows only VLAN 30 on Fa0/5.
- It allows a native VLAN of 30 to be implemented on Fa0/5.
Explanation: The switchport trunk allowed vlan 30 command allows traffic that is tagged with VLAN 30 across the trunk port. Any VLAN that is not specified in this command will not be allowed on this trunk port.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem?
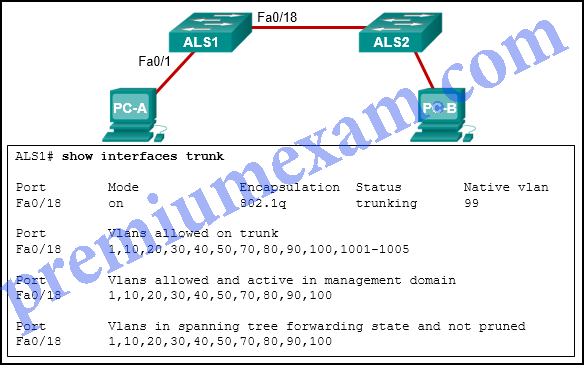
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 06
- The native VLAN should be VLAN 60.
- The native VLAN is being pruned from the link.
- The trunk has been configured with the switchport nonegotiate command.
- The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the trunk.
Explanation: Because PC-A and PC-B are connected to different switches, traffic between them must flow over the trunk link. Trunks can be configured so that they only allow traffic for particular VLANs to cross the link. In this scenario, VLAN 60, the VLAN that is associated with PC-A and PC-B, has not been allowed across the link, as shown by the output of show interfaces trunk.
-
Refer to the exhibit. DLS1 is connected to another switch, DLS2, via a trunk link. A host that is connected to DLS1 is not able to communicate to a host that is connected to DLS2, even though they are both in VLAN 99. Which command should be added to Fa0/1 on DLS1 to correct the problem?
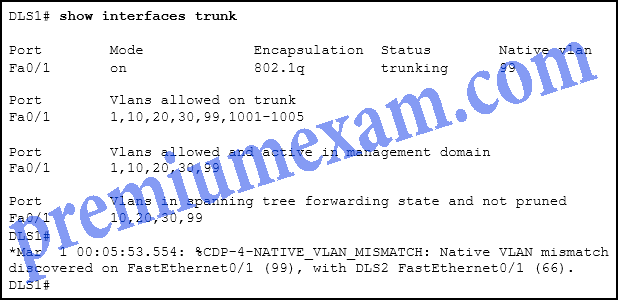
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 05
- switchport nonegotiate
- switchport mode dynamic auto
- switchport trunk native vlan 66
- switchport trunk allowed vlan add 99
Explanation: When configuring 802.1Q trunk links, the native VLAN must match on both sides of the link, or else CDP error messages will be generated, and traffic that is coming from or going to the native VLAN will not be handled correctly.
-
What is a characteristic of legacy inter-VLAN routing?
- Only one VLAN can be used in the topology.
- The router requires one Ethernet link for each VLAN.
- The user VLAN must be the same ID number as the management VLAN.
- Inter-VLAN routing must be performed on a switch instead of a router.
Explanation: Multiple VLANs are supported with legacy inter-VLAN routing, but each VLAN requires its own Ethernet router link. Ethernet ports are limited on a router. That is why the router-on-a-stick model evolved. The user VLAN should never be the same number as the management VLAN and using a Layer 3 switch as a router is a modern technique, not a legacy one.
-
What is a disadvantage of using router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing?
- does not support VLAN-tagged packets
- requires the use of more physical interfaces than legacy inter-VLAN routing
- does not scale well beyond 50 VLANs
- requires the use of multiple router interfaces configured to operate as access links
Explanation: Router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing does not scale beyond 50 VLANs. The router can receive VLAN-tagged packets and send VLAN-tagged packets to a destination. Router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing can utilize a single router interface as a trunk link to receive and forward VLAN traffic and does not require multiple interfaces.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Router RA receives a packet with a source address of 192.168.1.35 and a destination address of 192.168.1.85. What will the router do with this packet?
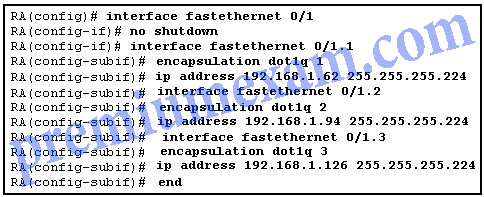
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 03
- The router will drop the packet.
- The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1.
- The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2.
- The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
- The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 and interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
Explanation: The IP address 192.168.1.85 belongs to network 192.168.1.64/27. The valid host addresses in this network include 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.94. The IP address configured for the subinterface of Fa0/1.2 is in the same network, which serves as the default gateway for the VLAN 2.
-
Refer to the exhibit. In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?
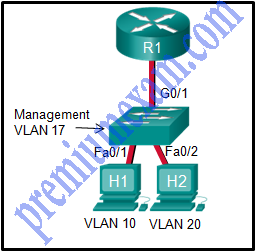
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 01
- access
- trunk
- native
- auto
Explanation: The router is used to route between the two VLANs, thus switch port G0/1 needs to be configured in trunk mode.
-
A small college uses VLAN 10 for the classroom network and VLAN 20 for the office network. What is needed to enable communication between these two VLANs while using legacy inter-VLAN routing?
- A router with at least two LAN interfaces should be used.
- Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
- A router with one VLAN interface is needed to connect to the SVI on a switch.
- A switch with a port that is configured as trunk is needed to connect to a router.
Explanation: With legacy inter-VLAN routing, different physical router interfaces are connected to different physical switch ports. The switch ports that connect to the router are in access mode, each belonging to a different VLAN. Switches can have ports that are assigned to different VLANs, but communication between VLANs requires routing function from the router.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure router-on-a-stick for the networks that are shown. How many subinterfaces will have to be created on the router if each VLAN that is shown is to be routed and each VLAN has its own subinterface?
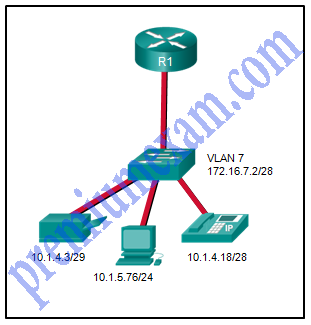
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 04
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Explanation: Based on the IP addresses and masks given, the PC, printer, IP phone, and switch management VLAN are all on different VLANs. This situation will require four subinterfaces on the router.
-
When configuring a router as part of a router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing topology, where should the IP address be assigned?
- to the interface
- to the subinterface
- to the SVI
- to the VLAN
Explanation: The IP address and the encapsulation type should be assigned to each router subinterface in a router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN topology.
-
A high school uses VLAN15 for the laboratory network and VLAN30 for the faculty network. What is required to enable communication between these two VLANs while using the router-on-a-stick approach?
- A multilayer switch is needed.
- A router with at least two LAN interfaces is needed.
- Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
- A switch with a port that is configured as a trunk is needed when connecting to the router.
Explanation: With router-on-a-stick, inter-VLAN routing is performed by a router with a single router interface that is connected to a switch port configured with trunk mode. Multiple subinterfaces, each configured for a VLAN, can be configured under the single physical router interface. Switches can have ports that are assigned to different VLANs, but communication between those VLANs requires routing function from the router. A multilayer switch is not used in a router-on-a-stick approach to inter-VLAN routing.
-
Which four steps are needed to configure a voice VLAN on a switch port? (Choose four).
- Configure the interface as an IEEE 802.1Q trunk.
- Assign the voice VLAN to the switch port.
- Activate spanning-tree PortFast on the interface.
- Ensure that voice traffic is trusted and tagged with a CoS priority value.
- Add a voice VLAN.
- Configure the switch port interface with subinterfaces.
- Assign a data VLAN to the switch port.
- Configure the switch port in access mode.
Explanation: To add an IP phone, the following commands should be added to the switch port:
SW3(config-vlan)# vlan 150
SW3(config-vlan)# name voice
SW3(config-vlan)# int fa0/20
SW3(config-if)# switchport mode access
SW3(config-if)# mls qos trust cos
SW3(config-if)# switchport access vlan 150
-
A network administrator issues the show vlan brief command while troubleshooting a user support ticket.
- What output will be displayed? the VLAN assignment and membership for device MAC addresses
- the VLAN assignment and membership for all switch ports
- the VLAN assignment and trunking encapsulation
- the VLAN assignment and native VLAN
Explanation: The show vlan brief command will provide information displaying the VLAN assignment and membership for all switch ports on a switch.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A router-on-a-stick configuration was implemented for VLANs 15, 30, and 45, according to the show running-config command output. PCs on VLAN 45 that are using the 172.16.45.0 /24 network are having trouble connecting to PCs on VLAN 30 in the 172.16.30.0 /24 network. Which error is most likely causing this problem?
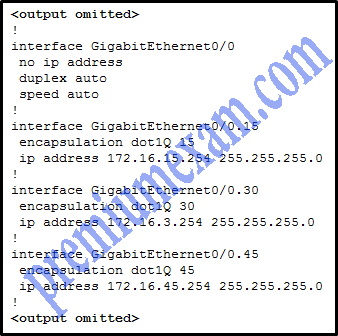
CCNA 2 RSE 6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2018 2019 02
- The wrong VLAN has been configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.45.
- The command no shutdown is missing on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.
- The GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface is missing an IP address.
- There is an incorrect IP address configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.
Explanation: he subinterface GigabitEthernet 0/0.30 has an IP address that does not correspond to the VLAN addressing scheme. The physical interface GigabitEthernet 0/0 does not need an IP address for the subinterfaces to function. Subinterfaces do not require the no shutdown command.
-
Match the IEEE 802.1Q standard VLAN tag field with the description. (Not all options are used.)
- Question
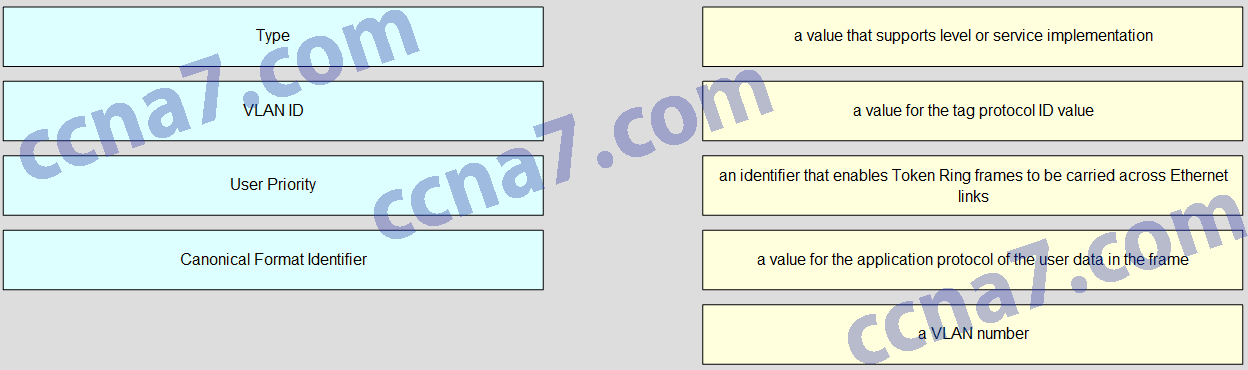
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 6 Exam Q001
- Answer
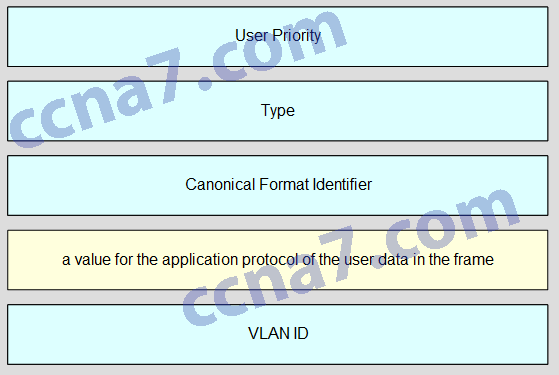
CCNA2 v6.0 Chapter 6 Exam A001
Explanation: The IEEE 802.1Q standard header includes a 4-byte VLAN tag:
Type – A 2-byte value called the tag protocol ID (TPID) value.
User priority – A 3-bit value that supports level or service implementation.
Canonical Format Identifier (CFI) – A 1-bit identifier that enables Token Ring frames to be carried across Ethernet links.
VLAN ID (VID) – A 12-bit VLAN identification number that supports up to 4096 VLAN IDs.
- Question
-
Fill in the blank. Use the full command syntax.
The show vlan command displays the VLAN assignment for all ports as well as the existing VLANs on the switch.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which PCs will receive the broadcast sent by PC-C?
- PC-A, PC-B
- PC-D, PC-E
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-E
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-E
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-E, PC-F
Explanation: Only hosts in the same VLAN as PC-C (VLAN 20) will receive the broadcast. The trunk links will carry the broadcast to ALS2 where it will be send to PC-D and PC-E, which are also in VLAN 20. PC-A, PC-B, and PC-F are not in the same VLAN as PC-C. This information can be verified by issuing the show vlan and show interfaces trunk commands.
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.