Last Updated on October 20, 2019 by Admin
Implementing Network Security ( Version 2.0) – CCNAS Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2019 Full 100%
-
An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
Explanation: There are four steps to configure SSH support on a Cisco router:
Step 1: Set the domain name.
Step 2: Generate one-way secret keys.
Step 3: Create a local username and password.
Step 4: Enable SSH inbound on a vty line.
-
Which set of commands are required to create a username of admin, hash the password using MD5, and force the router to access the internal username database when a user attempts to access the console?
- R1(config)# username admin password Admin01pa55
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# login local - R1(config)# username admin password Admin01pa55
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# login - R1(config)# username admin Admin01pa55 encr md5
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# login local - R1(config)# username admin secret Admin01pa55
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# login local - R1(config)# username admin secret Admin01pa55
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# loginExplanation: To configure a user account with an encrypted password, the username secret command is used. The line con 0 command defines the console line as configured for login and the login local command tells the router to look in the local database for the user credentials.
- R1(config)# username admin password Admin01pa55
-
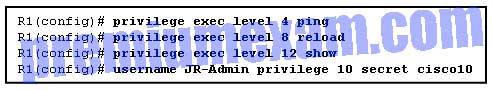
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the JR-Admin account is true?
- JR-Admin can issue show, ping, and reload commands.
- JR-Admin can issue ping and reload commands.
- JR-Admin can issue only ping commands.
- JR-Admin can issue debug and reload commands.
- JR-Admin cannot issue any command because the privilege level does not match one of those defined.
Explanation: When the username name privilege 10 command is issued, access to commands with a privilege level of 10 or less (0-10) is permitted to the user.
-
Which three areas of router security must be maintained to secure an edge router at the network perimeter? (Choose three.)
- physical security
- flash security
- operating system security
- remote access security
- router hardening
- zone isolation
Explanation: There are three areas of router security to maintain:
1) physical security
2) router hardening
3) operating system security
-
What is the default privilege level of user accounts created on Cisco routers?
- 0
- 1
- 15
- 16
Explanation: There are 16 privilege levels that can be configured as part of the username command, ranging from 0 to 15. By default, if no level is specified, the account will have privilege level 1,
-
Which recommended security practice prevents attackers from performing password recovery on a Cisco IOS router for the purpose of gaining access to the privileged EXEC mode?
- Keep a secure copy of the router Cisco IOS image and router configuration file as a backup.
- Disable all unused ports and interfaces to reduce the number of ways that the router can be accessed.
- Configure secure administrative control to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the router.
- Locate the router in a secure locked room that is accessible only to authorized personnel.
- Provision the router with the maximum amount of memory possible.
Explanation: Of the three areas of router security, physical security, router hardening, and operating system security, physical security involves locating the router in a secure room accessible only to authorized personnel who can perform password recovery.
-
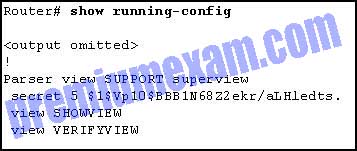
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output of the show running-config command, which type of view is SUPPORT?
- secret view, with a level 5 encrypted password
- root view, with a level 5 encrypted secret password
- superview, containing SHOWVIEW and VERIFYVIEW views
- CLI view, containing SHOWVIEW and VERIFYVIEW commands
Explanation: The superview role-based CLI view named SUPPORT has been configured on the router. The SUPPORT suerview consists of two CLI views called SHOWVIEW and VERIFYVIEW.
-
Which two characteristics apply to role-based CLI access superviews? (Choose two.)
- CLI views have passwords, but superviews do not have passwords.
- Users logged in to a superview can access all commands specified within the associated CLI views.
- A single superview can be shared among multiple CLI views.
- A specific superview cannot have commands added to it directly.
- Deleting a superview deletes all associated CLI views.
Explanation: By using a superview an administrator can assign users or groups of users to CLI views which contain a specific set of commands those users can access. Commands cannot be added directly to a superview but rather must be added to a CLI view and the CLI view added to the superview.
-
Which three types of views are available when configuring the role-based CLI access feature? (Choose three.)
- superuser view
- root view
- superview
- CLI view
- admin view
- config view
Explanation: There are three types of Role-based CLI views:
1) root view
2) CLI view
3) superview
-
If AAA is already enabled, which three CLI steps are required to configure a router with a specific view? (Choose three.)
- Assign a secret password to the view.
- Assign commands to the view.
- Assign users who can use the view.
- Associate the view with the root view.
- Create a superview using the parser view view-name command.
- Create a view using the parser view view-name command.
Explanation: There are five steps involved to create a view on a Cisco router.
1) AAA must be enabled.
2) the view must be created.
3) a secret password must be assigned to the view.
4) commands must be assigned to the view.
5) view configuration mode must be exited.
-
What occurs after RSA keys are generated on a Cisco router to prepare for secure device management?
- All vty ports are automatically configured for SSH to provide secure management.
- The general-purpose key size must be specified for authentication with the crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus command.
- The keys must be zeroized to reset Secure Shell before configuring other parameters.
- The generated keys can be used by SSH.
Explanation: Once RSA keys are generated, SSH is automatically enabled.
-
Which three statements describe limitations in using privilege levels for assigning command authorization? (Choose three.)
- There is no access control to specific interfaces on a router.
- The root user must be assigned to each privilege level that is defined.
- Commands set on a higher privilege level are not available for lower privilege users.
- Views are required to define the CLI commands that each user can access.
- Creating a user account that needs access to most but not all commands can be a tedious process.
- It is required that all 16 privilege levels be defined, whether they are used or not.
Explanation: An administrator can create customized privilege levels and assign different commands to each level. However, this method of controlling he level of access to the router has limitations. Using privilege levels access to specific interfaces or ports cannot be controlled and availability of commands cannot be customized across levels.
-
What command must be issued to enable login enhancements on a Cisco router?
- login block-for
- banner motd
- login delay
- privilege exec level
Explanation: Cisco IOS login enhancements can increase the security for virtual login connections to a router. Although login delay is a login enhancement command, all login enhancements are disabled until the login block-for command is configured.
-
A network administrator notices that unsuccessful login attempts have caused a router to enter quiet mode. How can the administrator maintain remote access to the networks even during quiet mode?
- Quiet mode behavior will only prevent specific user accounts from attempting to authenticate.
- Quiet mode behavior can be disabled by an administrator by using SSH to connect.
- Quiet mode behavior can be overridden for specific networks by using an ACL.
- Quiet mode behavior can be enabled via an ip access-group command on a physical interface.
Explanation: Quiet mode prevents any further login attempts for a period of time. Quiet mode is enabled via the login quiet-mode access-class command. Quiet mode behavior can be overridden for specific networks by building and implementing an access control list (ACL).
-
What is a characteristic of the Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration feature?
- It maintains a secure working copy of the bootstrap startup program.
- The secure boot-image command works properly when the system is configured to run an image from a TFTP server.
- Once issued, the secure boot-config command automatically upgrades the configuration archive to a newer version after new configuration commands have been entered.
- A snapshot of the router running configuration can be taken and securely archived in persistent storage.
Explanation: The Cisco IOS Resilient Configuration feature maintains a secure working copy of the router IOS image file and a copy of the running configuration file. The secure boot-image command functions properly only when the system is configured to run an image from a flash drive with an ATA interface. The secure boot-config command has to be used repeatedly to upgrade the configuration archive to a newer version after new configuration commands have been issued. A snapshot of the router running configuration can be taken and securely archived in persistent storage using the secure boot-config command.
-
What is a requirement to use the Secure Copy Protocol feature?
- The Telnet protocol has to be configured on the SCP server side.
- A transfer can only originate from SCP clients that are routers.
- At least one user with privilege level 1 has to be configured for local authentication.
- A command must be issued to enable the SCP server side functionality.
Explanation: The Secure Copy Protocol feature relies on SSH and requires that AAA authentication and authorization be configured so that the router can determine whether the user has the correct privilege level. For local authentication, at least one user with privilege level 15 has to be configured. Transfers can originate from any SCP client whether that client is another router, switch, or workstation. The ip scp server enable command has to be issued to enable the SCP server side functionality.
-
What is a characteristic of the MIB?
- Information is organized in a flat manner so that SNMP can access it quickly.
- The OIDs are organized in a hierarchical structure.
- A separate MIB tree exists for any given device in the network.
- Information in the MIB cannot be changed.
Explanation: SNMP set, get, and trap messages are used to access and manipulate the information contained in the MIB. This information is organized hierarchically so that SNMP can access it quickly. Each piece of information within the MIB is given an object ID (OID), that is organized based on RFC standards into a hierarchy of OIDs. The MIB tree for any given device includes branches with variables common to many networking devices and branches with variables specific to that device or vendor.
-
Which three items are prompted for a user response during interactive AutoSecure setup? (Choose three.)
- content of a security banner
- interfaces to enable
- enable secret password
- enable password
- IP addresses of interfaces
- services to disable
Explanation: During AutoSecure setup, the following steps occur:
– The auto secure command is entered.
– The wizard gathers information about the outside interfaces.
– AutoSecure secures the management place by disabling unnecessary services.
– AutoSecure prompts for a security banner.
– AutoSecure prompts for passwords and enables password and login features.
– Interfaces are secured.
– The forwarding plane is secured.
-
A network engineer is implementing security on all company routers. Which two commands must be issued to force authentication via the password 1A2b3C for all OSPF-enabled interfaces in the backbone area of the company network? (Choose two.)
- ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 1A2b3C
- area 1 authentication message-digest
- username OSPF password 1A2b3C
- enable password 1A2b3C
- area 0 authentication message-digest
Explanation: The two commands that are necessary to configure authentication via the password 1A2b3C for all OSPF-enabled interfaces in the backbone area (Area 0) of the company network would be ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 1A2b3C and area 0 authentication message-digest. The option area 1 authentication message-digest is incorrect because it refers to Area 1, not Area 0. The option enable password 1A2b3C is incorrect because it would set the privileged EXEC mode password instead of the OSPF authentication password. The option username OSPF password 1A2b3C is required to create a username database in a router, which is not required with OSPF authentication.
-
What is the purpose of using the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password command and the area area-id authentication message-digest command on a router?
- to encrypt OSPF routing updates
- to enable OSPF MD5 authentication on a per-interface basis
- to configure OSPF MD5 authentication globally on the router
- to facilitate the establishment of neighbor adjacencies
Explanation: To configure OSPF MD5 authentication globally, the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password interface configuration command and the area area-id authentication message-digest router configuration command are issued. To configure OSPF MD5 authentication per interface, the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password interface configuration command and the ip ospf authentication message-digest interface configuration command are issued. Authentication does not encrypt OSPF routing updates. The requirements to establish OSPF router neighbor adjacencies are separate from authentication.
-
What are two reasons to enable OSPF routing protocol authentication on a network? (Choose two.)
- to ensure more efficient routing
- to ensure faster network convergence
- to provide data security through encryption
- to prevent data traffic from being redirected and then discarded
- to prevent redirection of data traffic to an insecure link
Explanation: The reason to configure OSPF authentication is to mitigate against routing protocol attacks like redirection of data traffic to an insecure link, and redirection of data traffic to discard it. OSPF authentication does not provide faster network convergence, more efficient routing, or encryption of data traffic.
-
What is the Control Plane Policing (CoPP) feature designed to accomplish?
- manage services provided by the control plane
- prevent unnecessary traffic from overwhelming the route processor
- disable control plane services to reduce overall traffic
- direct all excess traffic away from the route processor
Explanation: Control Plane Policing (CoPP) does not manage or disable any services. It does not direct traffic away from the route processor, but rather it prevents unnecessary traffic from getting to the route processor.
-
Which two options can be configured by Cisco AutoSecure? (Choose two.)
- enable secret password
- SNMP
- syslog
- security banner
- interface IP address
Explanation: AutoSecure executes a script that first makes recommendations for fixing security vulnerabilities and then modifies the security configuration of the router. AutoSecure can lock down the management plane functions and the forwarding plane services and functions of a router, and this includes setting an enable password, and a security banner.
-
Which three functions are provided by the syslog logging service? (Choose three.)
- authenticating and encrypting data sent over the network
- gathering logging information
- specifying where captured information is stored
- setting the size of the logging buffer
- distinguishing between information to be captured and information to be ignored
- retaining captured messages on the router when a router is rebooted
Explanation: Syslog operations include gathering information, selecting which type of information to capture, and directing the captured information to a storage location. The logging service stores messages in a logging buffer that is time-limited, and cannot retain the information when a router is rebooted. Syslog does not authenticate or encrypt messages.
-
Which three actions are produced by adding Cisco IOS login enhancements to the router login process? (Choose three.)
- permit only secure console access
- slow down an active attack
- create syslog messages
- create password authentication
- automatically provide AAA authentication
- disable logins from specified hosts
Explanation: Cisco IOS login enhancements provide increased security in three ways:Implement delays between successive login attempts
Enable login shutdown if DoS attacks are suspected
Generate system-logging messages for login detection
Banners and password authentication are disabled by default and must be enabled by command. Virtual login enhancements do not apply to console connections.