Last Updated on October 18, 2019 by Admin
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019
-
Refer to the exhibit. Approximately what percentage of the physical memory is still available on this Windows system?
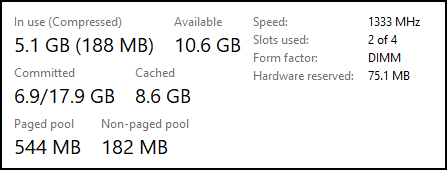
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 02
- 32%
- 53%
- 68%
- 90%
Explanation: The graphic shows that there is 5.1 GB (187 MB) of memory in use with 10.6 GB still available. Together this adds up to 16 GB of total physical memory. 5 GB is approximately 32% of 16 GB leaving 68% still available.
-
Which Windows tool can be used by a cybersecurity administrator to secure stand-alone computers that are not part of an active directory domain?
- Local Security Policy
- Windows Defender
- Windows Firewall
- PowerShell
Explanation: Windows systems that are not part of an Active Directory Domain can use the Windows Local Security Policy to enforce security settings on each stand-alone system.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which technology would contain information similar to the data shown for infrastructure devices within a company?
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 06
- Apache server
- firewall
- HIDS
- syslog server
Explanation: A syslog server consolidates and maintains messages from infrastructure devices that have been configured to send logging information. Data from the syslog server can be analyzed to detect anomalies..
-
What are three benefits of using symbolic links over hard links in Linux? (Choose three.)
- Symbolic links can be exported.
- They can be encrypted.
- They can be compressed.
- They can link to a directory.
- They can show the location of the original file.
- They can link to a file in a different file system.
Explanation: In Linux, a hard link is another file that points to the same location as the original file. A soft link (also called a symbolic link or a symlink) is a link to another file system name. Hard links are limited to the file system in which they are created and they cannot link to a directory; soft links are not limited to the same file system and they can link to a directory. To see the location of the original file for a symbolic link use the ls –l command.
-
Which two protocols are associated with the transport layer? (Choose two.)
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- PPP
- ICMP
Explanation: TCP and UDP reside at the transport layer in both the OSI and TCP/IP models.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A user reports that resources can no longer be reached on the local 192.168.1.0/24 network nor on the internet. A cybersecurity analyst investigates the issue by reviewing the routing table of the PC in question. What is the reason for the problem reported by the user?
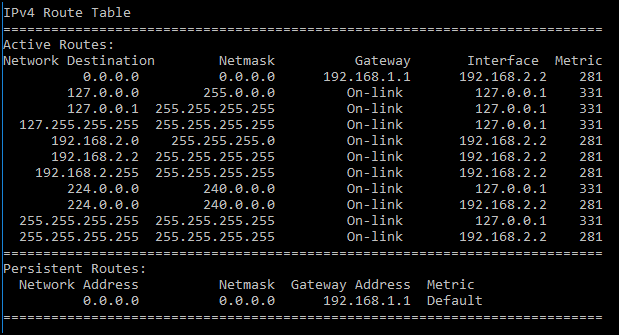
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 04
- incorrect host IP address
- incorrect subnet mask
- incorrect default gateway
- incorrect route metric
Explanation: In the routing table of the PC, the default gateway is 192.168.1.1 and the host IP address is 192.168.2.2. These addresses are on different networks. The host should have an IP address on the 192.168.1.0/24 network. To correct this problem the host IP must be changed to an address on the 192.168.1.0/24 local network.
-
What is the function of ARP?
- resolves domain names to IP addresses
- provides automatic IP address assignments to hosts
- sends error and operational information messages to hosts
- maps IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
Explanation: ARP, or Address Resolution Protocol, is used by hosts to resolve a destination MAC address from a given destination IP address.
-
A cybersecurity analyst believes an attacker is spoofing the MAC address of the default gateway to perform a man-in-the-middle attack. Which command should the analyst use to view the MAC address a host is using to reach the default gateway?
- ipconfig /all
- route print
- netstat -r
- arp -a
Explanation: ARP is a protocol used with IPv4 to map a MAC address to an associated specific IP address. The command arp -a will display the MAC address table on a Windows PC.
-
Which network service is used by clients to resolve the IP address of a domain name?
- DHCP
- DNS
- ARP
- ICMP
Explanation: The Domain Name System (DNS) is used by clients to resolve the IP address of a domain name. For example, a host may need to connect to www.cisco.com. The host would contact a DNS server to discover the IP address associated with the domain www.cisco.com.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity analyst is viewing captured packets forwarded on switch S1. Which device is the source of the captured packet?
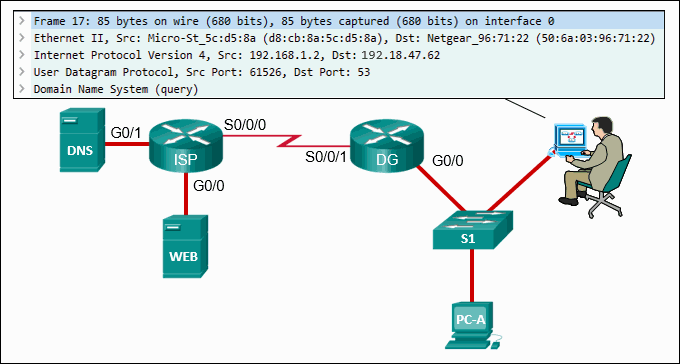
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 03
- DNS server
- PC-A
- DG router
- ISP router
- web server
Explanation: The Wireshark output is displaying a DNS query that was sent from PC-A to switch S1. DNS queries are sourced from DNS clients, which in this case would be PC-A.
-
What is a purpose of implementing VLANs on a network?
- They can separate user traffic.
- They prevent Layer 2 loops.
- They eliminate network collisions.
- They allow switches to forward Layer 3 packets without a router.
Explanation: VLANs are used on a network to separate user traffic based on factors such as function, project team, or application, without regard for the physical location of the user or device.
-
Which type of firewall is a combination of various firewall types?
- packet filtering
- stateful
- proxy
- hybrid
Explanation: A hybrid firewall is a combination of different firewall types such as combining a stateful firewall with an application gateway firewall.
-
What is a feature of an IPS?
- It can stop malicious packets.
- It has no impact on latency.
- It is deployed in offline mode.
- It is primarily focused on identifying possible incidents.
Explanation: An advantage of an intrusion prevention systems (IPS) is that it can identify and stop malicious packets. However, because an IPS is deployed inline, it can add latency to the network.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has written a standard access control list to prevent packets from the 192.168.2.0 LAN from reaching the restricted LAN 192.168.3.0 while permiting traffic from any other LAN. On what interface and in which direction should the access list be implemented on router R1?
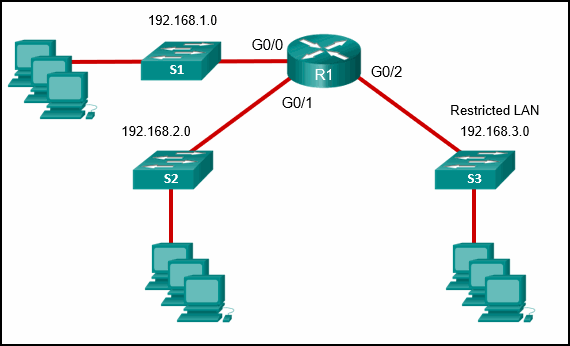
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 01
- interface G0/0 inbound
- interface G0/2 inbound
- interface G0/2 outbound
- interface G0/1 outbound
Explanation: The access list requires that the source network 192.168.2.0 is denied while other networks are permitted to reach the restricted LAN. The access list must be applied on interface G0/2 in the outbound direction.
-
What is an example of a local exploit?
- Port scanning is used to determine if the Telnet service is running on a remote server.
- A threat actor performs a brute force attack on an enterprise edge router to gain illegal access.
- A buffer overflow attack is launched against an online shopping website and causes the server crash.
- A threat actor tries to gain the user password of a remote host by using a keyboard capture software installed on it by a Trojan.
Explanation: Vulnerability exploits may be remote or local. In a local exploit, the threat actor has some type of user access to the end system, either physically or through remote access. The exploitation activity is within the local network.
-
After complaints from users, a technician identifies that the college web server is running very slowly. A check of the server reveals that there are an unusually large number of TCP requests coming from multiple locations on the Internet. What is the source of the problem?
- A DDoS attack is in progress.
- The server is infected with a virus.
- There is insufficient bandwidth to connect to the server.
- There is a replay attack in progress.
Explanation: The source of the problem cannot be a virus because in this situation the server is passive and at the receiving end of the attack. A replay attack uses intercepted and recorded data in an attempt to gain access to an unauthorized server. This type of attack does not involve multiple computers. The issue is not the bandwidth available, but the number of TCP connections taking place. Receiving a large number of connections from multiple locations is the main symptom of a distributed denial of service attack which use botnets or zombie computers.
-
A user receives an email requesting verification of the password that is used to access bank files. What type of security threat is this?
- virus
- social engineering
- phishing
- malware
Explanation: Phishing is a form of attack that starts with the attacker pretending to be a legitimate entity and then tries to gather information that can be used to conduct the exploit.
-
To which category of security attacks does man-in-the-middle belong?
- DoS
- access
- reconnaissance
- social engineering
Explanation: With a man-in-the-middle attack, a threat actor is positioned in between two legitimate entities in order to read, modify, or redirect the data that passes between the two parties.
-
What is the main goal of using different evasion techniques by threat actors?
- to launch DDoS attacks on targets
- to identify vulnerabilities of target systems
- to gain the trust of a corporate employee in an effort to obtain credentials
- to prevent detection by network and host defenses
Explanation: Many threat actors use stealthy evasion techniques to disguise an attack payload because the malware and attack methods are most effective if they are undetected. The goal is to prevent detection by network and host defenses.
-
What are two examples of DoS attacks? (Choose two.)
- phishing
- ping of death
- SQL injection
- port scanning
- buffer overflow
Explanation: The buffer overflow and ping of death DoS attacks exploit system memory-related flaws on a server by sending an unexpected amount of data or malformed data to the server.
-
Which attack is integrated with the lowest levels of the operating system of a host and attempts to completely hide the activities of the threat actor on the local system?
- rootkit
- traffic insertion
- traffic substitution
- encryption and tunneling
Explanation: A rootkit is a complex attack tool and it integrates with the lowest levels of the operating system. The goal of the rootkit is to completely hide the activities of the threat actor on the local system.
-
Which evasion method describes the situation that after gaining access to the administrator password on a compromised host, a threat actor is attempting to login to another host using the same credentials?
- pivoting
- traffic substitution
- resource exhaustion
- protocol-level misinterpretation
Explanation: Pivoting is an evasion method that assumes the threat actor has compromised an inside host and the actor wants to expand the access further into the compromised network.
-
Which two attacks target web servers through exploiting possible vulnerabilities of input functions used by an application? (Choose two.)
- SQL injection
- port scanning
- port redirection
- trust exploitation
- cross-site scripting
Explanation: When a web application uses input fields to collect data from clients, threat actors may exploit possible vulnerabilities for entering malicious commands. The malicious commands that are executed through the web application might affect the OS on the web server. SQL injection and cross-site scripting are two different types of command injection attacks.
-
What is the first line of defense when an organization is using a defense-in-depth approach to network security?
- IPS
- edge router
- firewall
- proxy server
Explanation: A defense-in-depth approach uses layers of security measures starting at the network edge, working through the network, and finally ending at the network endpoints. Routers at the network edge are the first line of defense and forward traffic intended for the internal network to the firewall.
-
What is the benefit of a defense-in-depth approach?
- The effectiveness of other security measures is not impacted when a security mechanism fails.
- The need for firewalls is eliminated.
- All network vulnerabilities are mitigated.
- Only a single layer of security at the network core is required.
Explanation: The benefit of the defense-in-depth approach is that network defenses are implemented in layers so that failure of any single security mechanism does not impact other secuirty measures.
-
Which access control model allows users to control access to data as an owner of that data?
- mandatory access control
- nondiscretionary access control
- discretionary access control
- attribute-based access control
Explanation: In the discretionary access control (DAC) model, users can control access to data as owners of the data.
-
What is the principle behind the nondiscretionary access control model?
- It applies the strictest access control possible.
- It allows access decisions to be based on roles and responsibilities of a user within the organization.
- It allows users to control access to their data as owners of that data.
- It allows access based on attributes of the object be to accessed.
Explanation: The nondiscretionary access control model used the roles and responsibilities of the user as the basis for access decisions.
-
What is an example of privilege escalation attack?
- A threat actor sends an email to an IT manager to request the root access.
- A threat actor performs an access attack and gains the administrator password.
- A DDoS attack is launched against a government server and causes the server to crash.
- A port scanning attack finds that the FTP service is running on a server that allows anonymous access.
Explanation: With the privilege escalation exploit, vulnerabilities in servers or access control systems are exploited to grant an unauthorized user, or software process, higher levels of privilege than either should have. After the higher privilege is granted, the threat actor can access sensitive information or take control of a system.
-
Which access control model applies the strictest access control and is often used in military and mission critical applications?
- discretionary
- mandatory
- nondiscretionary
- attribute-based
Explanation: Military and mission critical applications typically use mandatory access control which applies the strictest access control to protect network resources.
-
Which data security component is provided by hashing algorithms?
- key exchange
- confidentiality
- integrity
- authentication
Explanation: Hashing algorithms are used to provide message integrity, which ensures that data in transit has not changed or been altered.
-
Which two algorithms use a hashing function to ensure message integrity? (Choose two.)
- SEAL
- AES
- 3DES
- MD5
- SHA
Explanation: Hashing algorithms are used to provide data integrity, which ensures that the data has not changed during transmission. MD5 and SHA are commonly used hashing algorithms.
-
What is a feature of asymmetrical encryption?
- Different keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data.
- Key lengths are short.
- It encrypts bulk data quickly.
- It requires fewer computations than symmetric encryption requires.
Explanation: Asymmetric encryption algorithms use different keys for encryption and decryption. These are known as private and public keys. The longer key lengths used by asymmetric algorithms make them slower than symmetrical encryption and inefficient for bulk data.
-
What technology supports asymmetric key encryption used in IPsec VPNs?
- 3DES
- IKE
- SEAL
- AES
Explanation: IKE, or Internet Key Exchange, is a protocol to support asymmetric encryption algorithms. It is used to securely exchange encryption keys in the setup of IPsec VPNs.
-
Which security function is provided by encryption algorithms?
- key management
- authorization
- integrity
- confidentiality
Explanation: Encryption algorithms are used to provide data confidentiality, which ensures that if data is intercepted in transit, it cannot be read.
-
A security professional is making recommendations to a company for enhancing endpoint security. Which security endpoint technology would be recommended as an agent-based system to protect hosts against malware?
- baselining
- blacklisting
- HIDS
- IPS
Explanation: A host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS) is a comprehensive security application that provides antimalware applications, a firewall, and monitoring and reporting.
-
Which firewall application runs on a Linux host and allows an administrator to configure network access rules as part of the Linux kernel?
- vShield
- nftables
- TCP Wrapper
- iptables
Explanation: The iptables is an application that allows Linux system administrators to configure network access rules that are part of the Linux kernel Netfilter modules.
-
Which security endpoint setting would be used by a security analyst to determine if a computer has been configured to prevent a particular application from running?
- baselining
- blacklisting
- services
- whitelisting
Explanation: Blacklisting can be used on a local system or updated on security devices such as a firewall. Blacklists can be manually entered or obtained from a centralized security system. Blacklists are applications that are prevented from executing because they pose a security risk to the individual system and potentially the company.
-
Which technique could be used by security personnel to analyze a suspicious file in a safe environment?
- baselining
- blacklisting
- sandboxing
- whitelisting
Explanation: Sandboxing allows suspicious files to be executed and analyzed in a safe environment. There are free public sandboxes that allow for malware samples to be uploaded or submitted and analyzed.
-
Which attack surface, defined by the SANS Institute, is delivered through the exploitation of vulnerabilities in web, cloud, or host-based applications?
- host
- human
- network
- software
Explanation: The SANS Institute describes three components of the attack surface:
- Network Attack Surface – exploits vulnerabilities in networks
- Software Attack Surface – delivered through the exploitation of vulnerabilities in web, cloud, or host-based software applications
- Human Attack Surface – exploits weaknesses in user behavior
-
What is an action that should be taken in the discovery step of the vulnerability management life cycle?
- assigning business value to assets
- determining a risk profile
- developing a network baseline
- documenting the security plan
Explanation: During the discovery step of the vulnerability management life cycle, an inventory of all network assets is made. A network baseline is developed, and security vulnerabilities are identified.
-
Which security management plan specifies a component that involves tracking the location and configuration of networked devices and software across an enterprise?
- asset management
- risk management
- vulnerability management
- patch management
Explanation: Asset management involves tracking the location and configuration of networked devices and software across an enterprise.
-
Which risk management plan involves discontinuing an activity that creates a risk?
- risk reduction
- risk retention
- risk avoidance
- risk sharing
Explanation: During a risk assessment it may be determined that an activity involves more risk than benefit. In such a situation an organization may decide to avoid the risk altogether by discontinuing the activity. This is known as risk avoidance.
-
A piece of malware has gained access to a workstation and issued a DNS lookup query to a CnC server. What is the purpose of this attack?
- to request a change of the IP address
- to send stolen sensitive data with encoding
- to check the domain name of the workstation
- to masquerade the IP address of the workstation
Explanation: A piece of malware, after accessing a host, may exploit the DNS service by communicating with command-and-control (CnC) servers and then exfiltrate data in traffic disguised as normal DNS lookup queries. Various types of encoding, such as base64, 8-bit binary, and hex can be used to camouflage the data and evade basic data loss prevention (DLP) measures.
-
Why does HTTPS technology add complexity to network security monitoring?
- HTTPS uses tunneling technology for confidentiality.
- HTTPS hides the true source IP address using NAT/PAT.
- HTTPS conceals data traffic through end-to-end encryption.
- HTTPS dynamically changes the port number on the web server.
Explanation: With HTTPS, a symmetric key is generated by the client after the client verifies the trustworthiness of the web server. The symmetric key is encrypted with the public key of the web server and then sent to the web server. The web server uses its public key to decrypt the key. The key is then used to encrypt the data requested by the client and the data is sent to the client. This end-to-end encryption complicates inline network security monitoring. The HTTPS port number, typically 443, is configured statically on the web server.
-
Which type of attack is carried out by threat actors against a network to determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs?
- phishing
- reconnaissance
- denial of service
- social engineering
Explanation: Packet filtering ACLs use rules to filter incoming and outgoing traffic. These rules are defined by specifying IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols to be matched. Threat actors can use a reconnaissance attack involving port scanning or penetration testing to determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs.
-
How can NAT/PAT complicate network security monitoring if NetFlow is being used?
- It changes the source and destination MAC addresses.
- It conceals the contents of a packet by encrypting the data payload.
- It disguises the application initiated by a user by manipulating port numbers.
- It hides internal IP addresses by allowing them to share one or a few outside IP addresses.
Explanation: NAT/PAT maps multiple internal IP addresses with only a single or a few outside IP addresses breaking end-to-end flows. The result makes it difficult to log the inside device that is requesting and receiving the traffic. This is especially a problem with a NetFlow application because NetFlow flows are unidirectional and are defined by the addresses and ports that they share.
-
Which statement describes the function provided by the Tor network?
- It distributes user packets through load balancing.
- It allows users to browse the Internet anonymously.
- It conceals packet contents by establishing end-to-end tunnels.
- It manipulates packets by mapping IP addresses between two networks.
Explanation: Tor is a software platform and network of P2P hosts that function as Internet routers on the Tor network. The Tor network allows users to browse the Internet anonymously.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing an alert message generated by Snort. What does the number 2100498 in the message indicate?

CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 05
- the message length in bits
- the Snort rule that is triggered
- the session number of the message
- the id of the user that triggers the alert
Explanation: The sid field in a Snort alert message indicates the Snort security rule that is triggered.
-
Which type of data is used by Cisco Cognitive Threat Analytics to find malicious activity that has bypassed security controls, or entered through unmonitored channels, and is operating inside an enterprise network?
- alert
- session
- statistical
- transaction
Explanation: Cisco Cognitive Threat Analytics utilizes statistical data for statistical analysis in order to find malicious activity that has bypassed security controls, or entered through unmonitored channels (including removable media), and is operating inside the network of an organization.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing the logs of an Apache web server. Which action should the analyst take based on the output shown?
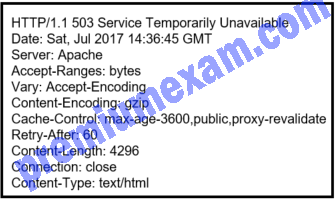
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – SECFND (210-250) Cert Practice Exam Answers 2019 Full 100% 07
- Ignore the message.
- Notify the server administrator.
- Restart the server.
- Notify the appropriate security administration for the country.
Explanation: An Apache web server is an open source server that delivers web pages. Security access logs for an Apache web server include a 3-digit HTTP code that represents the status of the web request. A code that begins with 2 indicates access success. A code that begins with 3 represents redirection. A code that begins with 4 represents a client error and a code that begins with 5 represents a server error. The server administrator should be alerted if a server error such as the 503 code occurs.
-
Which Windows application is commonly used by a cybersecurity analyst to view Microsoft IIS access logs?
- Event Viewer
- Notepad
- SIEM
- Word
Explanation: Event Viewer is an application on a Windows-based device used to view event logs including IIS access logs.
-
Which tool captures full data packets with a command-line interface only?
- nfdump
- NBAR2
- tcpdump
- Wireshark
Explanation: The command-line tool tcpdump is a packet analyzer. Wireshark is a packet analyzer with a GUI interface.
-
What is a key difference between the data captured by NetFlow and data captured by Wireshark?
- NetFlow provides transaction data whereas Wireshark provides session data.
- NetFlow data is analyzed by tcpdump whereas Wireshark data is analyzed by nfdump.
- NetFlow collects metadata from a network flow whereas Wireshark captures full data packets.
- NetFlow data shows network flow contents whereas Wireshark data shows network flow statistics.
Explanation: Wireshark captures the entire contents of a packet. NetFlow does not. Instead, NetFlow collects metadata, or data about the flow.
-
Which Cisco appliance can be used to filter network traffic contents to report and deny traffic based on the web server reputation?
- ASA
- AVC
- ESA
- WSA
Explanation: The Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) acts as a web proxy for an enterprise network. WSA can provide many types of logs related to web traffic security including ACL decision logs, malware scan logs, and web reputation filtering logs. The Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) is a tool to monitor most aspects of email delivery, system functioning, antivirus, antispam operations, and blacklist and whitelist decisions. The Cisco ASA is a firewall appliance. The Cisco Application Visibility and Control (AVC) system combines multiple technologies to recognize, analyze, and control over 1000 applications.
-
Which type of event is logged in Cisco Next-Generation IPS devices (NGIPS) using FirePOWER Services when changes have been detected in the monitored network?
- intrusion
- connection
- host or endpoint
- network discovery
Explanation: Network discovery events in Cisco NGIPS represent changes that have been detected in the monitored network.