Last Updated on October 18, 2019 by Admin
CCNA Cybersecurity Operations (Version 1.1) – CyberOps Chapter 10 Exam Answers 2019
-
Which device in a LAN infrastructure is susceptible to MAC address-table overflow and spoofing attacks?
- server
- switch
- workstation
- firewall
Explanation: Switches are LAN infrastructure devices interconnecting endpoints. They are susceptible to LAN-related attacks including MAC address-table overflow attacks, spoofing attacks, LAN storm attacks, STP manipulation attacks, and VLAN attacks.
-
Which type of antimalware software detects and mitigates malware by analyzing suspicious activities?
- packet-based
- behavior-based
- signature-based
- heuristics-based
Explanation: Antimalware programs may detect viruses using three different approaches:
signature-based – by recognizing various characteristics of known malware files
heuristics-based – by recognizing general features shared by various types of malware
behavior-based – through analysis of suspicious activities
-
In most host-based security suites, which function provides robust logging of security-related events and sends logs to a central location?
- telemetry
- anti-phishing
- safe browsing
- intrusion detection and prevention
Explanation: The telemetry functionality in most host-based security suites provides robust logging functionality and submits logs to a central location for analysis.
-
Which statement describes agentless antivirus protection?
- The antivirus protection is provided by the ISP.
- Antivirus scans are performed on hosts from a centralized system.
- Host-based antivirus systems provide agentless antivirus protection.
- The antivirus protection is provided by the router that is connected to a cloud service.
Explanation: Host-based antivirus protection is also known as agent-based. Agent-based antivirus runs on every protected machine. Agentless antivirus protection performs scans on hosts from a centralized system.
-
Which statement describes the use of a Network Admission Control (NAC) solution?
- A Network Admission Control solution provides filtering of potentially malicious emails before they reach the endpoint.
- It provides filtering and blacklisting of websites being accessed by end users.
- It provides network access to only authorized and compliant systems.
- It provides endpoint protection from viruses and malware.
Explanation: Network Admission Control (NAC) allows only authorized and compliant systems to connect to a network.
-
What type of antimalware program is able to detect viruses by recognizing various characteristics of a known malware file?
- heuristic-based
- behavior-based
- agent-based
- signature-based
Explanation: Using a signature-based approach, host security software can detect viruses and malware by recognizing various characteristics of known malware files.
-
What is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)?
- It is an agentless system that scans files on a host for potential malware.
- It identifies potential attacks and sends alerts but does not stop the traffic.
- It detects and stops potential direct attacks but does not scan for malware.
- It combines the functionalities of antimalware applications with firewall protection.
Explanation: A current HIDS is a comprehensive security application that combines the functionalities of antimalware applications with firewall protection. An HIDS not only detects malware but also prevents it from executing. Because the HIDS runs directly on the host, it is considered an agent-based system.
-
Which statement describes the anomaly-based intrusion detection approach?
- It compares the operations of a host against a well-defined security policy.
- It compares the signatures of incoming traffic to a known intrusion database.
- It compares the antivirus definition file to a cloud based repository for latest updates.
- It compares the behavior of a host to an established baseline to identify potential intrusions.
Explanation: With an anomaly-based intrusion detection approach, a baseline of host behaviors is established first. The host behavior is checked against the baseline to detect significant deviations, which might indicate potential intrusions.
-
Which statement describes the term iptables?
- It is a DNS daemon in Linux.
- It is a DHCP application in Windows.
- It is a rule-based firewall application in Linux.
- It is a file used by a DHCP server to store current active IP addresses.
Explanation: Iptables is an application that allows Linux system administrators to configure network access rules.
-
On a Windows host, which tool can be used to create and maintain blacklists and whitelists?
- Task Manager
- Group Policy Editor
- Computer Management
- Local Users and Groups
Explanation: In Windows, blacklisting and whitelisting settings can be managed through the Group Policy Editor.
-
Which statement describes the term attack surface?
- It is the network interface where attacks originate.
- It is the group of hosts that experiences the same attack.
- It is the total number of attacks toward an organization within a day.
- It is the total sum of vulnerabilities in a system that is accessible to an attacker.
Explanation: An attack surface is the total sum of the vulnerabilities in a system that is accessible to an attacker. The attack surface can consist of open ports on servers or hosts, software that runs on Internet-facing servers, wireless network protocols, and even users.
-
Which statement describes the Cisco Threat Grid Glovebox?
- It is a firewall appliance.
- It is a network-based IDS/IPS.
- It is a sandbox product for analyzing malware behaviors.
- It is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS) solution to fight against malware.
Explanation: Cisco ThreatGrid Glovebox is a sandbox product for analyzing malware behaviors.
-
Which security procedure would be used on a Windows workstation to prevent access to a specific set of websites?
- whitelisting
- baselining
- HIDS
- blacklisting
Explanation: Blacklists can be used to identify and prevent specific applications, websites, or services from being downloaded or executed within an enterprise network.
-
When a network baseline is being established for an organization, which network profile element indicates the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination?
- ports used
- total throughput
- session duration
- critical asset address space
Explanation: Important elements of a network profile include:
Total throughput – the amount of data passing from a given source to a given destination in a given period of time
Session duration – the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
Ports used – a list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
Critical asset address space – the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
-
In network security assessments, which type of test employs software to scan internal networks and Internet facing servers for various types of vulnerabilities?
- risk analysis
- penetration testing
- vulnerability assessment
- strength of network security testing
Explanation: In vulnerability assessment, security analysts use software to scan internal networks and Internet facing servers for various types of vulnerabilities. Tools for vulnerability assessment include the open source OpenVAS platform, Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer, Nessus, Qualys, and Fireeye Mandiant services.
-
Which two classes of metrics are included in the CVSS Base Metric Group? (Choose two.)
- Impact metrics
- Exploitability
- Modified Base
- Exploit Code Maturity
- Confidentiality Requirement
Explanation: The Base Metric Group of CVSS represents the characteristics of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across contexts. It contains two classes of metrics, Exploitability and Impact.
-
Which criterion in the Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics reflects the proximity of the threat actor to the vulnerable component?
- attack vector
- user interaction
- attack complexity
- privileges required
Explanation: The Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics include the criteria:
Attack vector – a metric that reflects the proximity of the threat actor to the vulnerable component
Attack complexity – a metric that expresses the number of components, software, hardware, or networks, that are beyond control of the attacker and that must be present in order for a vulnerability to be successfully exploited
Privileges required – a metric that captures the level of access that is required for a successful exploit of the vulnerability
User interaction – second component of the attack complexity metric that expresses the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful
Scope – a metric that expresses whether multiple authorities must be involved in an exploit
-
Which two criteria in the Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics are associated with the complexity of attacks? (Choose two)
- scope
- attack vector
- user interaction
- attack complexity
- privileges required
Explanation: The Base Metric Group Exploitability metrics include these criteria:
Attack vector – a metric that reflects the proximity of the threat actor to the vulnerable component
Attack complexity – a metric that expresses the number of components, software, hardware, or networks, that are beyond control of the attacker and that must be present in order for a vulnerability to be successfully exploited
Privileges required – a metric that captures the level of access that is required for a successful exploit of the vulnerability
User interaction – second component of the attack complexity metric that expresses the presence or absence of the requirement for user interaction in order for an exploit to be successful
Scope – a metric that expresses whether multiple authorities must be involved in an exploit
-
Which regulatory compliance regulation sets requirements for all U.S. public company boards, management and public accounting firms regarding the way in which corporations control and disclose financial information?
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA)
Explanation: There are five major regulatory compliance regulations including:
Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA) – specifies security standards for U.S. government systems and contractors to the U.S. government.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) – sets new or expanded requirements for all U.S. public company boards, management and public accounting firms regarding the way in which corporations control and disclose financial information.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) – established that financial institutions must ensure the security and confidentiality of customer information; protect against any anticipated threats or hazards to the security or integrity of such information; and protect against unauthorized access to or use of customer information that could result in substantial harm or inconvenience to any customer.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – requires that all patient personally identifiable healthcare information be stored, maintained, and transmitted in ways that ensure patient privacy and confidentiality.
-
Which statement describes the threat-vulnerability (T-V) pairing?
- It is the advisory notice from a vulnerability research center.
- It is the comparison between known malware and system risks.
- It is the detection of malware against a central vulnerability research center.
- It is the identification of threats and vulnerabilities and the matching of threats with vulnerabilities.
Explanation: A mandatory activity in risk assessment is the identification of threats and vulnerabilities and the matching of threats with vulnerabilities, also called threat-vulnerability (T-V) pairing.
-
In addressing an identified risk, which strategy aims to stop performing the activities that create risk?
- risk sharing
- risk retention
- risk reduction
- risk avoidance
Explanation: There are four potential strategies for responding to risks that have been identified:
Risk avoidance – Stop performing the activities that create risk.
Risk reduction – Decrease the risk by taking measures to reduce vulnerability.
Risk sharing – Shift some of the risk to other parties.
Risk retention – Accept the risk and its consequences.
-
In addressing a risk that has low potential impact and relatively high cost of mitigation or reduction, which strategy will accept the risk and its consequences?
- risk sharing
- risk retention
- risk reduction
- risk avoidance
Explanation: There are four potential strategies for responding to risks that have been identified:
Risk avoidance – Stop performing the activities that create risk.
Risk reduction – Decrease the risk by taking measures to reduce vulnerability.
Risk sharing – Shift some of the risk to other parties.
Risk retention – Accept the risk and its consequences.
-
The IT security personnel of an organization notice that the web server deployed in the DMZ is frequently targeted by threat actors. The decision is made to implement a patch management system to manage the server. Which risk management strategy method is being used to respond to the identified risk?
- risk sharing
- risk retention
- risk reduction
- risk avoidance
Explanation: There are four potential strategies for responding to risks that have been identified:
Risk avoidance – Stop performing the activities that create risk.
Risk reduction – Decrease the risk by taking measures to reduce vulnerability.
Risk sharing – Shift some of the risk to other parties.
Risk retention – Accept the risk and its consequences.
-
Which step in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle determines a baseline risk profile to eliminate risks based on asset criticality, vulnerability threat, and asset classification?
- verify
- assess
- discover
- prioritize assets
Explanation: The steps in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle include these:Discover – inventory all assets across the network and identify host details, including operating systems and open services, to identify vulnerabilities
Prioritize assets – categorize assets into groups or business units, and assign a business value to asset groups based on their criticality to business operations
Assess – determine a baseline risk profile to eliminate risks based on asset criticality, vulnerability threats, and asset classification
Report – measure the level of business risk associated with assets according to security policies. Document a security plan, monitor suspicious activity, and describe known vulnerabilities.
Remediate – prioritize according to business risk and fix vulnerabilities in order of risk
Verify – verify that threats have been eliminated through follow-up audits
-
For network systems, which management system addresses the inventory and control of hardware and software configurations?
- risk management
- asset management
- vulnerability management
- configuration management
Explanation: Configuration management addresses the inventory and control of hardware and software configurations of network systems.
-
What is the first step taken in risk assessment?
- Identify threats and vulnerabilities and the matching of threats with vulnerabilities.
- Compare to any ongoing risk assessment as a means of evaluating risk management effectiveness.
- Establish a baseline to indicate risk before security controls are implemented.
- Perform audits to verify threats are eliminated.
Explanation: The three steps of risk assessment in order are as follows:
- Identify threats and vulnerabilities and the matching of threats with vulnerabilities.
- Establish a baseline to indicate risk before security controls are implemented.
- Compare to an ongoing risk assessment as a means of evaluating risk management effectiveness.
-
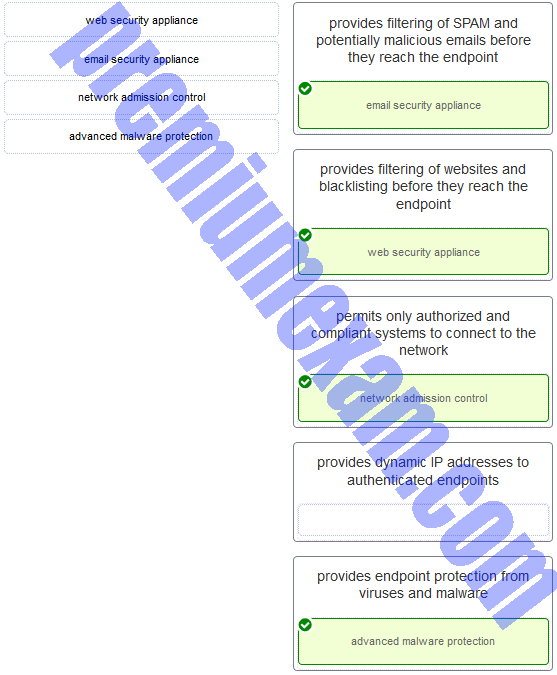
Match the network-based antimalware solution to the function. (Not all options are used.)
-
Match the description to the antimalware approach. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: Antimalware programs may detect viruses using three different approaches:
signature-based – by recognizing various characteristics of known malware files
heuristics-based – by recognizing general features shared by various types of malware
behavior-based – through analysis of suspicious activities
-
Use the following scenario to answer the questions. An entrepreneur is starting a small business and is considering the server services needed for the startup company. The company handling the IT service is presenting options to the company.
-
If the entrepreneur decides to go with Linux server, how are services handled differently from how Windows server services would be handled?
- The services are managed using configuration files.
- Services can only be managed from the Administrator account.
- Services use only TCP port numbers because they are more secure.
- The PowerShell environment can be used to make configuration changes.
Explanation: Linux server services are managed using configuration files that contain specific information about the service including port number, location of the hosted resources, and client authorization details.
-
The company will be using both Linux- and Windows-based hosts. Which two solutions would be used in a distributed firewall network design? (Choose two.)
- iptables
- SIEM
- Snort
- Windows Firewall
- Wireshark
Explanation: A network design that uses distributed firewalls centrally manages security rules and pushes those rules to the Linux and Windows host machines. Windows-based hosts use the Windows Firewall, whereas the Linux-based hosts use a firewall application such as iptables or nftables. Snort is an open source network intrusion prevention software. Wireshark is a packet capture tool and Security information and event management (SIEM) provides real-time analysis of alerts and log entries generated by network appliances such as IDSs and firewalls.
-
Which protocol should be recommended to the company to monitor and manage network performance?
- NTP
- PAT
- SNMP
- SSH
Explanation: The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol used to monitor and manage the network. Network devices have SNMP agents that communicate with the SNMP manager where the SNMP management software runs.
-
The IT company is recommending the use of PKI applications. In which two instances might the entrepreneur make use of PKIs? (Choose two.)
- 802.1x authentication
- FTP transfers
- HTTPS web service
- local NTP server
- file and directory access permission
Explanation: The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a third party-system referred to as a certificate authority or CA. The PKI is the framework used to securely exchange information between parties. Common PKI applications are as follows:SSL/TLS certificate-based peer authentication
IPsec VPNs
HTTPS web traffic
network access control using 802.1x authentication
secure email using S/MIME
secure instant messaging
approve and authorize applications with Code signing
protect data with EFS
use two-factor authentication
secure USB storage devices
-
The entrepreneur is concerned about company employees having uninterrupted access to important resources and data. Which of the CIA triad components would address the concern?
- authentication
- availability
- confidentiality
- integrity
Explanation: Communications security is usually discussed using the CIA triad: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality ensures that only authorized individuals, devices, entities, or processes can access sensitive information. Integrity protects data from unauthorized alteration. Availability provides uninterrupted access for authorized users to important resources and data.
-