Last Updated on April 3, 2018 by Admin
CCNA 2 Chapter 9
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.
-
What two functions describe uses of an access control list? (Choose two.)
- ACLs assist the router in determining the best path to a destination.
- Standard ACLs can restrict access to specific applications and ports.
- ACLs provide a basic level of security for network access.
- ACLs can permit or deny traffic based upon the MAC address originating on the router.
- ACLs can control which areas a host can access on a network.
-
Which two characteristics are shared by both standard and extended ACLs? (Choose two.)
- Both kinds of ACLs can filter based on protocol type.
- Both can permit or deny specific services by port number.
- Both include an implicit deny as a final ACE.
- Both filter packets for a specific destination host IP address.
- Both can be created by using either a descriptive name or number.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of standard IPv4 ACLs?
- ey are configured in the interface configuration mode.
- They filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
- They can be created with a number but not with a name.
- They can be configured to filter traffic based on both source IP addresses and source ports.
-
A network administrator needs to configure a standard ACL so that only the workstation of the administrator with the IP address 192.168.15.23 can access the virtual terminal of the main router. Which two configuration commands can achieve the task? (Choose two.)
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit host 192.168.15.23
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.255
-
Which IPv4 address range covers all IP addresses that match the ACL filter specified by 172.16.2.0 with wildcard mask 0.0.1.255?
- 172.16.2.0 to 172.16.2.255
- 172.16.2.1 to 172.16.3.254
- 172.16.2.0 to 172.16.3.255
- 172.16.2.1 to 172.16.255.255
-
If a router has two interfaces and is routing both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, how many ACLs could be created and applied to it?
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
- 16
-
Which three statements are generally considered to be best practices in the placement of ACLs? (Choose three.)
- Place standard ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Place extended ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
- Filter unwanted traffic before it travels onto a low-bandwidth link.
- Place extended ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
- Place standard ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
- For every inbound ACL placed on an interface, there should be a matching outbound ACL.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A router has an existing ACL that permits all traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network. The administrator attempts to add a new ACE to the ACL that denies packets from host 172.16.0.1 and receives the error message that is shown in the exhibit. What action can the administrator take to block packets from host 172.16.0.1 while still permitting all other traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network?
- Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 5.
- Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 15.
- Create a second access list denying the host and apply it to the same interface.
- Add a deny any any ACE to access-list 1.
-
An administrator has configured an access list on R1 to allow SSH administrative access from host 172.16.1.100. Which command correctly applies the ACL?
- R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 in
- R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
- R1(config-line)# access-class 1 in
- R1(config-line)# access-class 1 out
-
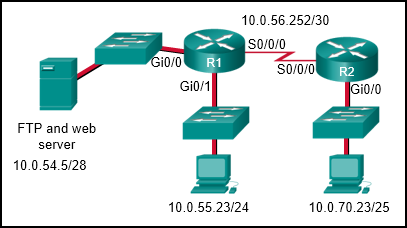
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator that has the IP address of 10.0.70.23/25 needs to have access to the corporate FTP server (10.0.54.5/28). The FTP server is also a web server that is accessible to all internal employees on networks within the 10.x.x.x address. No other traffic should be allowed to this server. Which extended ACL would be used to filter this traffic, and how would this ACL be applied? (Choose two.)
-
access-list 105 permit ip host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 permit ip any any
- access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.54.5 any eq www
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21 - access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
access-list 105 permit tcp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
access-list 105 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 host 10.0.54.5 eq www
access-list 105 deny ip any host 10.0.54.5
access-list 105 permit ip any any - R2(config)# interface gi0/0
R2(config-if)# ip access-group 105 in - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out
-
-
Consider the following access list that allows IP phone configuration file transfers from a particular host to a TFTP server:
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000
R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any
R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out
Which method would allow the network administrator to modify the ACL and include FTP transfers from any source IP address?
- R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21 - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# no ip access-group 105 out
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# no ip access-group 105 out
R1(config)# no access-list 105
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any
R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any
- R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
-
Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
- In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
- Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
- Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.
- On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
-
Which feature is unique to IPv6 ACLs when compared to those of IPv4 ACLs?
- the use of wildcard masks
- an implicit deny any any ACE
- the use of named ACL entries
- an implicit permit of neighbor discovery packets
-
Which three statements describe ACL processing of packets? (Choose three.)
- An implicit deny any rejects any packet that does not match any ACE.
- A packet can either be rejected or forwarded as directed by the ACE that is matched.
- A packet that has been denied by one ACE can be permitted by a subsequent ACE.
- A packet that does not match the conditions of any ACE will be forwarded by default.
- Each statement is checked only until a match is detected or until the end of the ACE list.
- Each packet is compared to the conditions of every ACE in the ACL before a forwarding decision is made.
-
Which three implicit access control entries are automatically added to the end of an IPv6 ACL? (Choose three.)
- deny ip any any
- deny ipv6 any any
- permit ipv6 any any
- deny icmp any any
- permit icmp any any nd-ns
- permit icmp any any nd-na
-
What is the only type of ACL available for IPv6?
- named standard
- named extended
- numbered standard
- numbered extended
-
Which IPv6 ACL command entry will permit traffic from any host to an SMTP server on network 2001:DB8:10:10::/64?
- permit tcp any host 2001:DB8:10:10::100 eq 25
- permit tcp host 2001:DB8:10:10::100 any eq 25
- permit tcp any host 2001:DB8:10:10::100 eq 23
- permit tcp host 2001:DB8:10:10::100 any eq 23
-
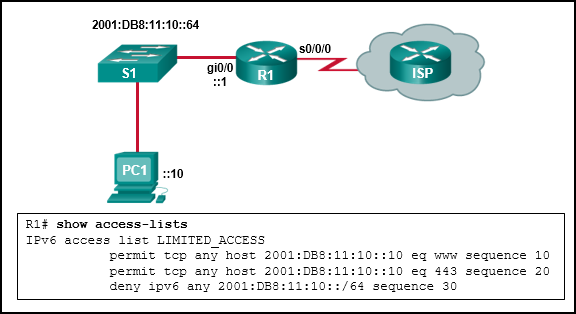
Refer to the exhibit. The IPv6 access list LIMITED_ACCESS is applied on the S0/0/0 interface of R1 in the inbound direction. Which IPv6 packets from the ISP will be dropped by the ACL on R1?
- HTTPS packets to PC1
- ICMPv6 packets that are destined to PC1
- packets that are destined to PC1 on port 80
- neighbor advertisements that are received from the ISP router
-
Match each statement with the example subnet and wildcard that it describes. (Not all options are used.)
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Why is the ACL not working?
- The interface has not been enabled.
- The ACL is applied in the wrong direction.
- The ACL is missing a deny ip any any ACE.
- The ACL is applied to the wrong interface.
- The access-list 105 command or commands are incorrect.
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to "Online Test" link below.